single-celled or non-cellular microorganisms which lack chlorophyll and reproduce by fission
bacteria
plant pathogens which cause harm to plants
disease
agents which are not alive, such as weather conditions, air pollution and toxic chemicals
Non-Living Agents
Are nearly impossible to eliminate if not treated immediately, especially soil-borne disease.
Fungal Diseases

Potato Scab
diseases in plants caused by bacteria
bacterial diseases
any agent which destroys or prevents the growth of fungi
Fungicides
disease-producing agents which cause harm to other organisms
Pathogens
Are easier to prevent rather than cure
bacterial diseases

galls
cause discoloration, wilting and death in plants
blights
process of a seed sprouting and beginning to grow
germination
small openings on the surface of leaves which allow for gases and water to pass in and out
Stomata
Are microscopic, infectious agents consisting of a protein coat surrounding nucleic acid
Viruses
Crown Gall
practice of growing different crops on the same land over a period of several growing seasons; aids in insect control and preservation of soil quality; example: growing corn for two years, then switching to soybeans on the same land
crop rotation
organisms such as fungi, bacteria and viruses
living agents
type of root which grows straight down into the soil to reach water
Taproots
Are specific pesticides for fungal diseases in plants
Fungicides
bacterial spot
where the stem of the plant meets the roots
crown
single-celled organisms including viruses, fungi and bacteria
Microorganisms
tissue which conducts water and nutrients through the plant
Vascular Tissue
infects cucumbers, melons and squash
usually appears on fruit in the middle stage of development
causes small, saturated areas to develop on stems and fruit
Angular Leaf Spot
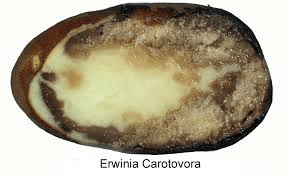
bacterial soft rot