The large air passages that lead from the windpipe to the lungs.
bronchi
Endocrine gland that surrounds the trachea in the neck.
thyroid gland

The main function of this organ is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth. "womb"
uterus
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/endometrium/lqOVbqxEDXXoSn96DtKYg_mtalyUnSVFF7UbU2KTYRg_Endometrium_01.png)
each of the series of small bones forming the backbone
vertebra
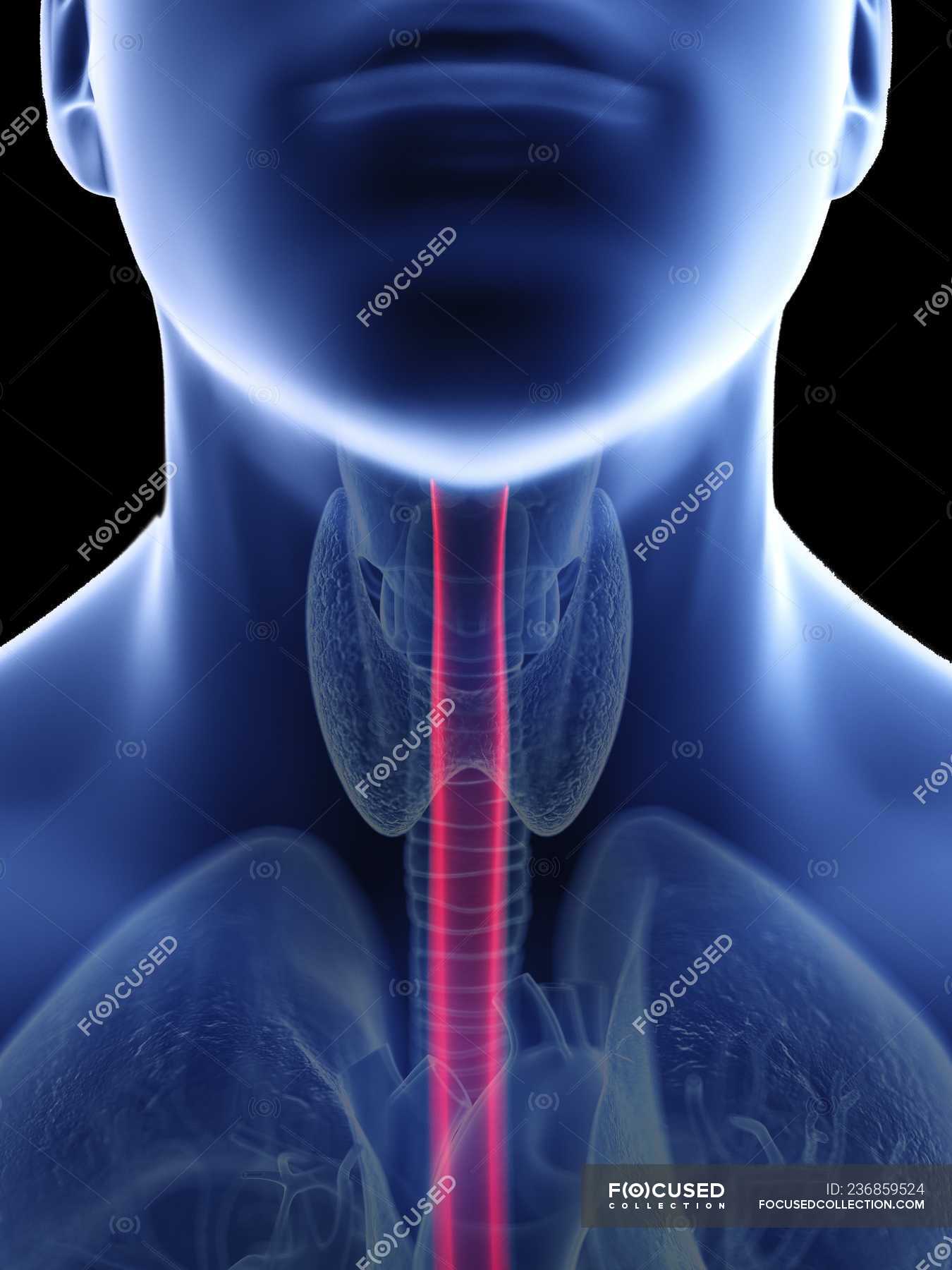
The passage for air that moistens and warms it while it passes into the lungs, and protects the respiratory surface from an accumulation of foreign particles. "windpipe"
trachea
glands that produce parathyroid hormone, which plays a key role in the regulation of calcium levels in the blood.
parathyroid glands

glands in which the eggs form and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone are made. These hormones play an important role in female traits, such as breast development, body shape, and body hair.
ovaries
the juncture where bones and muscles come together, facilitating movement and stability
joint

tiny air sacs in your lungs that take up the oxygen you breathe in and keep your body going.
alveoli/Alveoli-56a14da83df78cf772696d4f.jpg)
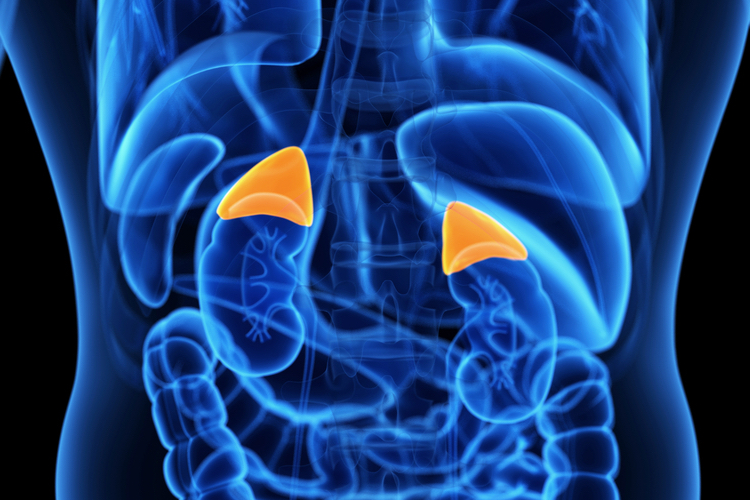
glands that produce hormones that help regulate metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
adrenal glands
glands responsible for making sperm and are also involved in producing a hormone called testosterone.
Testes (testicles)

fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
ligament

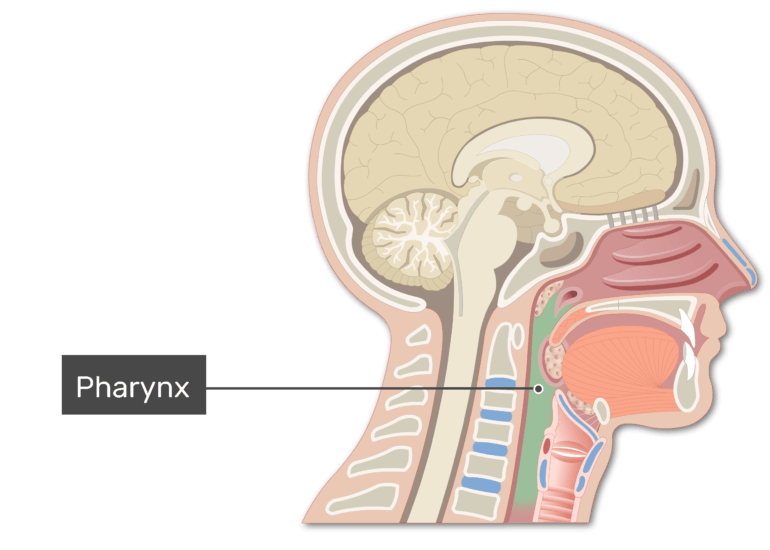
Common passageway for food (from the mouth going to the esophagus) and air (from the nose to the trachea).
pharynx
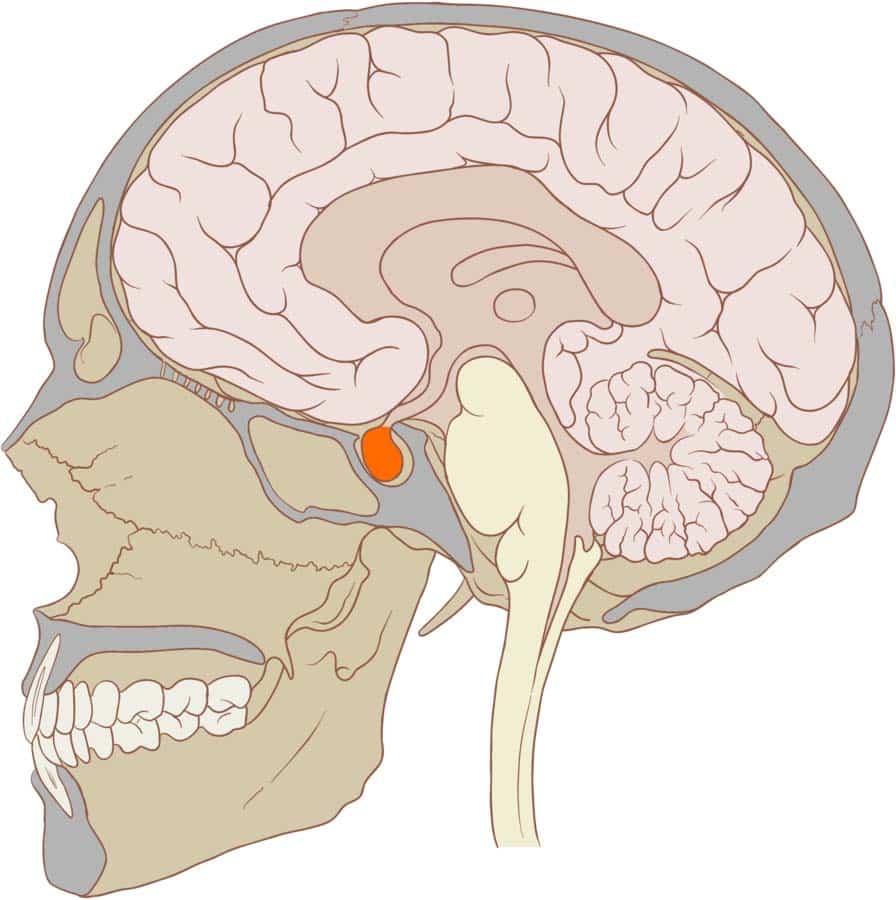
Endocrine gland at the base of the brain that regulates many bodily functions through the hormones that it produces, including: Growth and sexual/reproductive development and function, other glands and organs (kidneys, uterus, and breasts).
pituitary gland
Tube from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
urethra

fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
tendon
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1855/x6GOgCla1vVx43sGczA_q3uaAtbzmL_Lig._patellae_1.png)
“Voice box”; located at the upper part of the trachea.
larynx

gland that receives information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and conveys this information to produce and secrete the hormone melatonin.
pineal gland
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14167/A5HDQYRFdSF2pSwX6AzQ_Glandula_pinealis_1.png)
One of two tubes, each leading from a single kidney to the urinary bladder.
ureter
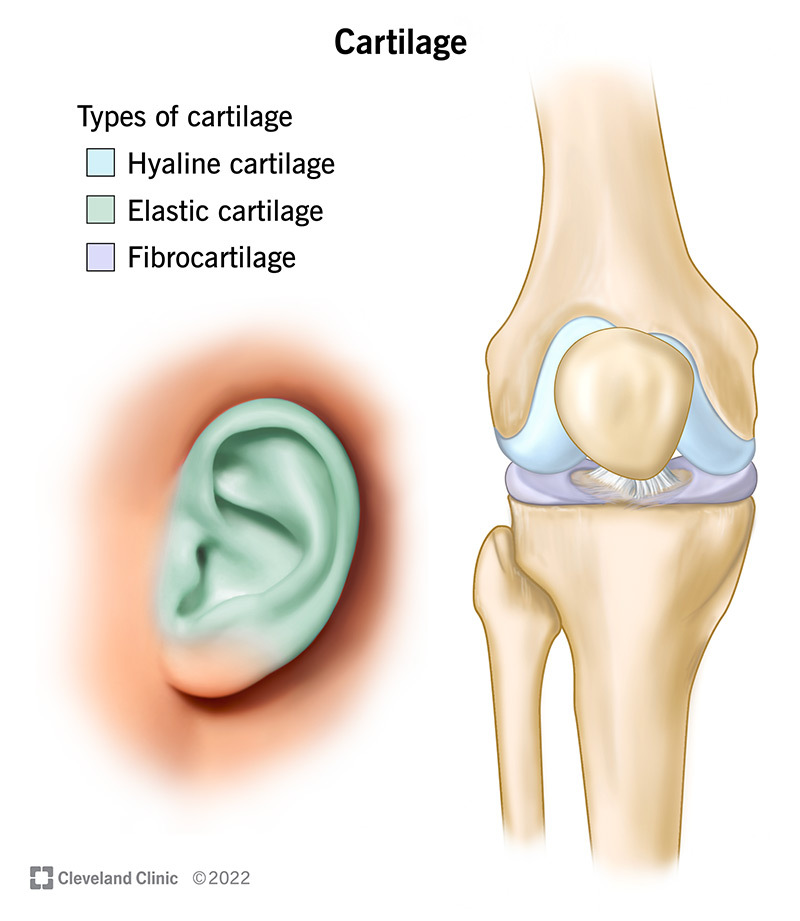
Flexible connective tissue attached to bones at joints. For example, it surrounds the trachea and forms part of the external ear and nose.
cartilage