Located in the upper right corner of the atrium, responsible for normal conduction.
What is the SA Node?
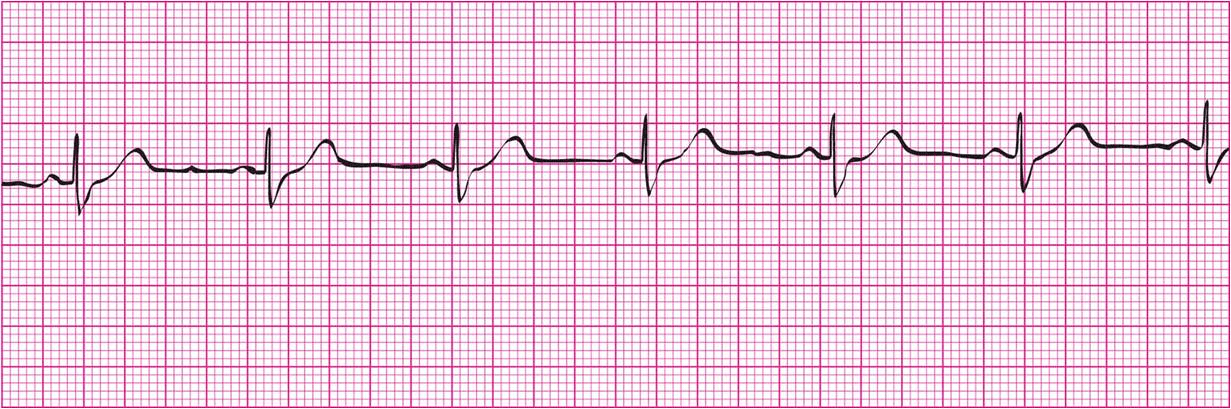
What is a Normal Sinus Rhythm?
Continuous information about heart's electrical activity to monitor cardiac status.
 What is telemetry?
What is telemetry?
The period when neither the ventricles nor atria are contracting.
What is diastole?
What is Sinus Bradycardia?
Extends from the Bundle Branches into the endocardium and into the myocardial tissue, responsible for the mechanical ventricular response.
 What are Purkinje Fibers?
What are Purkinje Fibers?

What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Electrical impulse representative of mechanical ventricular contraction.
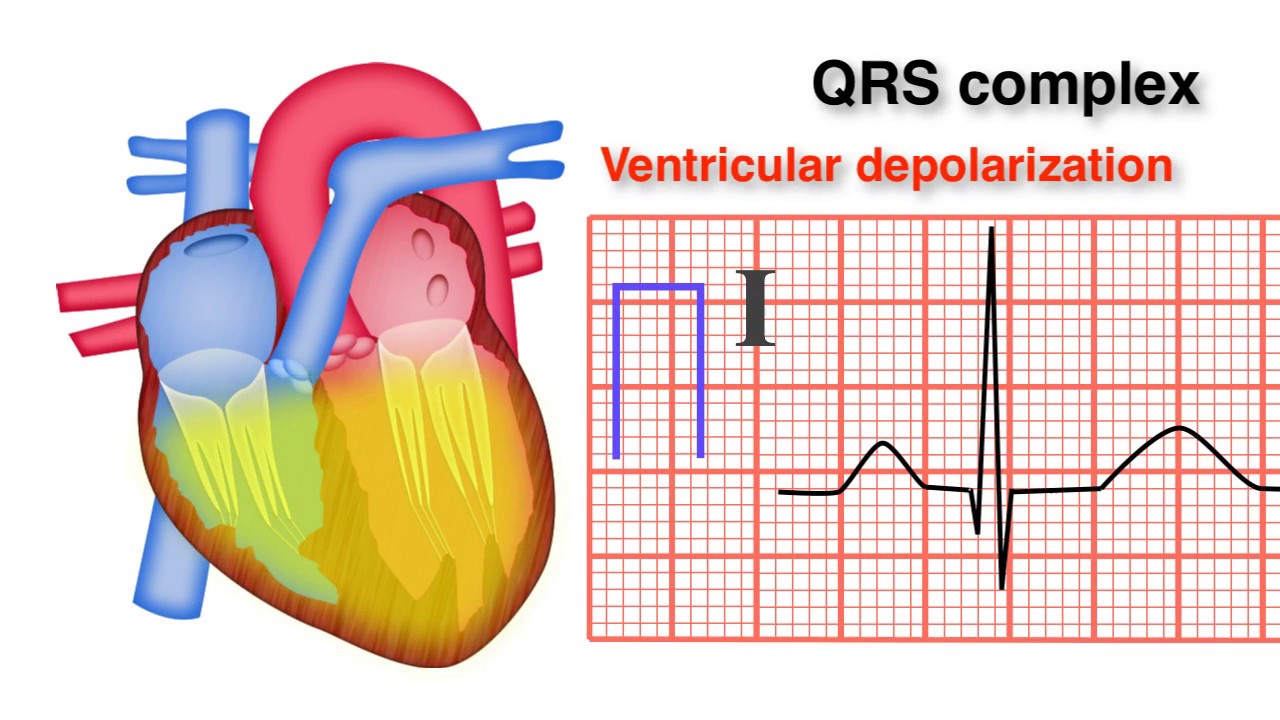 What is the QRS complex?
What is the QRS complex?
The amount of blood pumped out of a ventricle after one contraction
 What is stroke volume?
What is stroke volume?
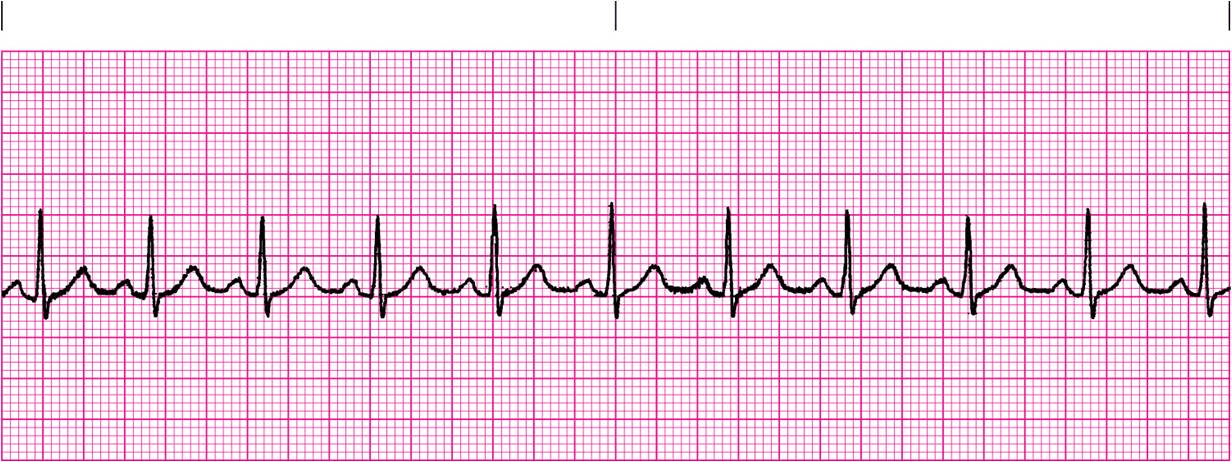
What is Sinus Tachycardia?
The main function is to delay impulses by 0.04 seconds to keep the ventricles from contracting too quickly.
The intrinsic rate is 40 -60 bpm.

What is the AV node?

What is Atrial Paced?
The first small wave is seen on the cardiac strip.
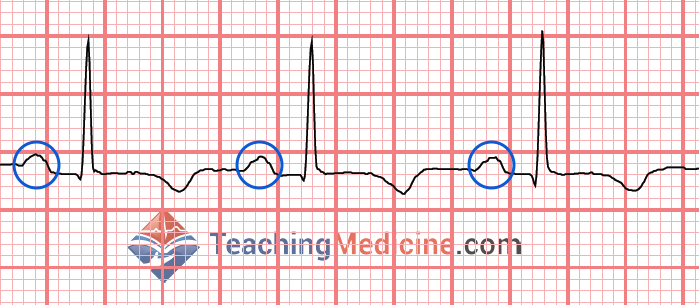 What is a p-wave?
What is a p-wave?
The period of the cardiac cycle when both the atria and ventricles are contracting.
What is Systole?

What is Atrial Flutter?
Located between left & right bundle branches and AV node.
 What is the Bundle of His?
What is the Bundle of His?

What is Atrial and Ventricular paced?
Cardiac muscle has undergone reversible damage due to lack of perfusion.
What is ischemia?
The amount of pressure the LV must work against to pump blood into the circulation.
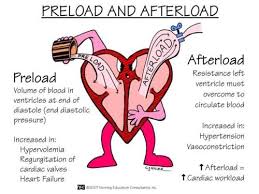 What is afterload?
What is afterload?
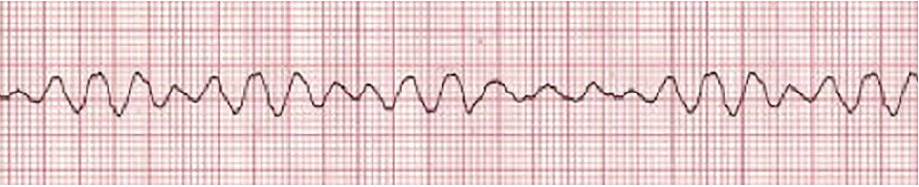
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
Please state the correct path of electrical impulses through the heart.
What is SA -->AV -->Bundle of His -->R/L Bundle Branches -->Purkinje Fibers?
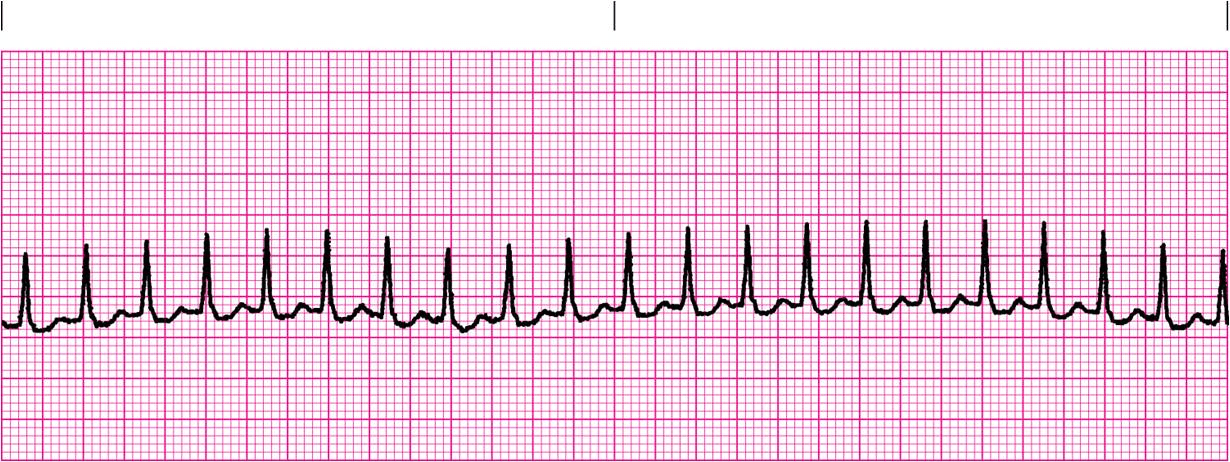
What is Supraventricuar Tachycardia?
Cardiac muscle which has undergone irreversible damage due to lack of perfusion.
 What is infarction?
What is infarction?
The amount of blood the heart pumps in one minute.
/Cardiac-Output-and-Cardiac-Index-%E2%80%93-What-s-the-Diff/Cardiac-Output.png.aspx) What is cardiac output?
What is cardiac output?

What is Ventricular Tachycardia?