Define Demand
Demand is the ability and willingness to buy a quantity good at a given price
Define Supply
Supply is the ability and willingness of producers to sell a quantity of good at a given price.
Allocative Efficiency exists when
quantity demand = quantity supply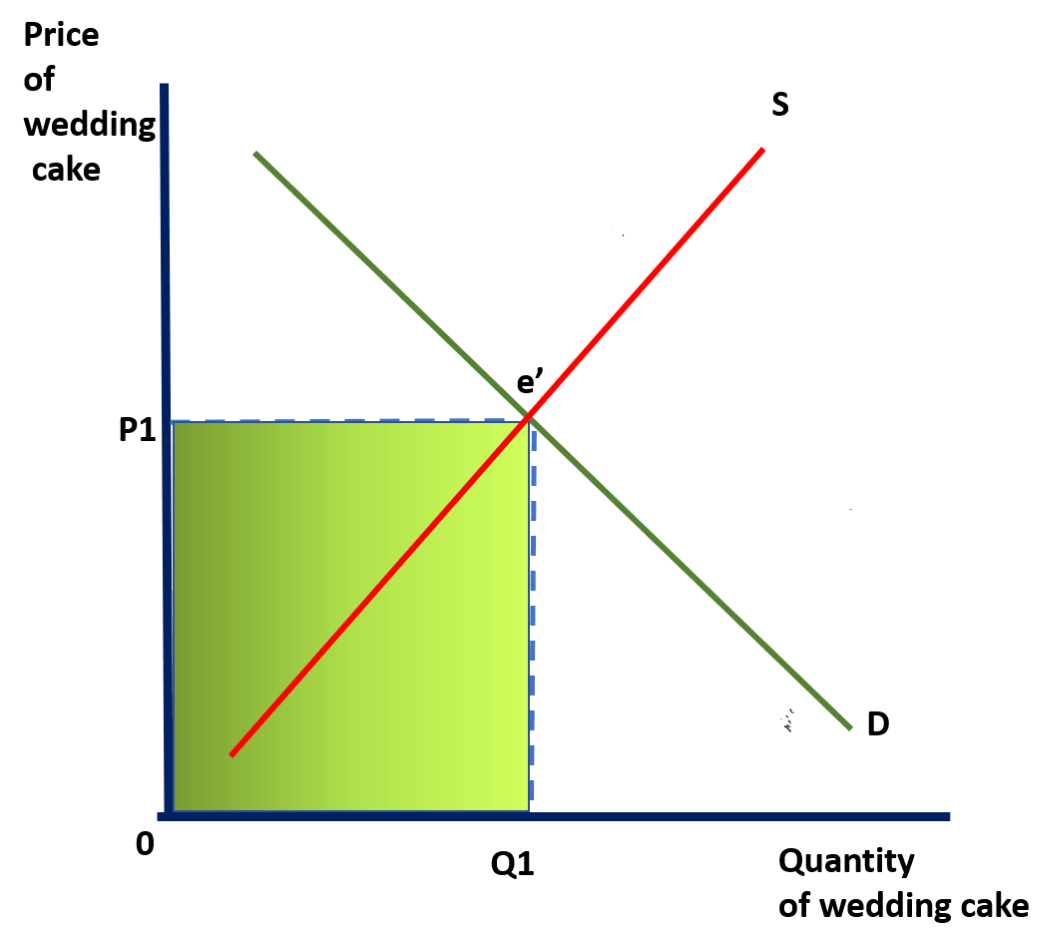
List the four main factors of production
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Labour
Define price elasticity of supply
PES measures the responsiveness of supply to changes in price.
Law of Demand states that
as price rises the quantity demand falls, ceteris paribus.
Law of supply states that
as price rises, the quantity of supply will increase, ceteris paribus.
the price, Pe, at the allocatively efficient point where quantity demand equals supply is known as the
Market Clearing Price ( Equilibrium price)
Give TWO ways in which changes in population can shift the PPF outwards. 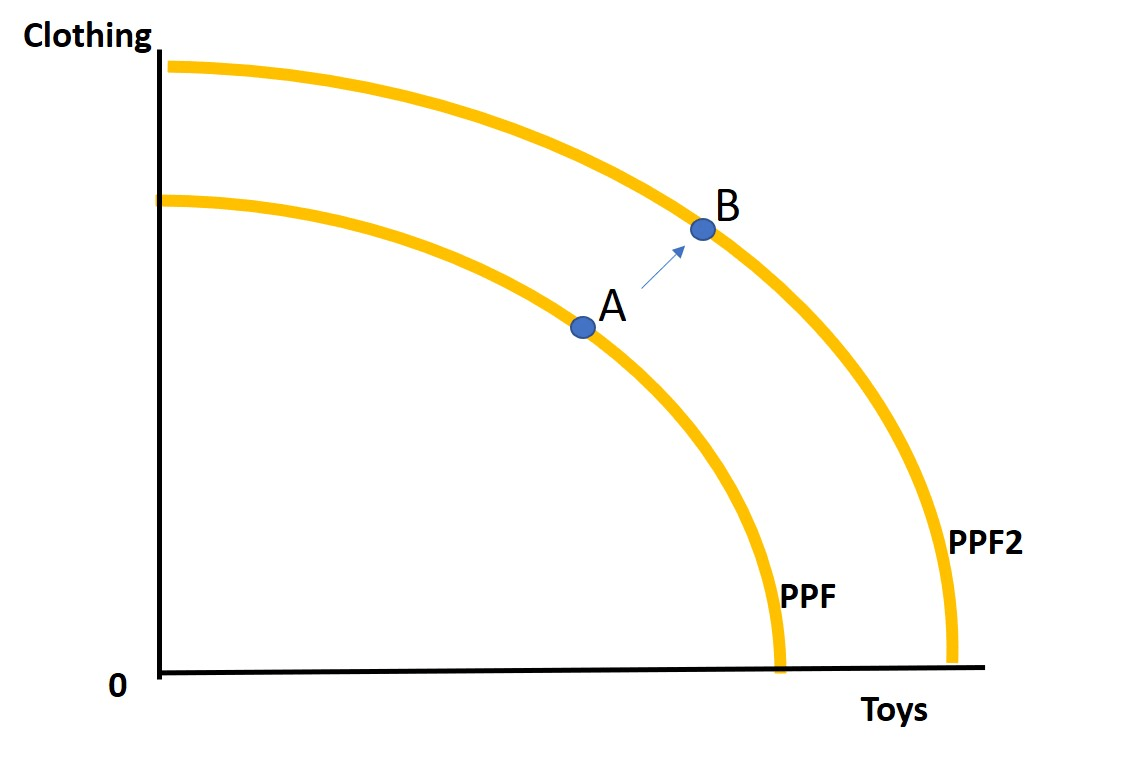
Natural increase ( birth rate > death rate)
High net migration ( Immigration > emigration)
Give the formula to PED and PES
PED= % change in Qd / % change in p
PES = % change in Qs / % change in p
This movement in the demand curve is called a ___________ in demand as quantity demand falls as price rises.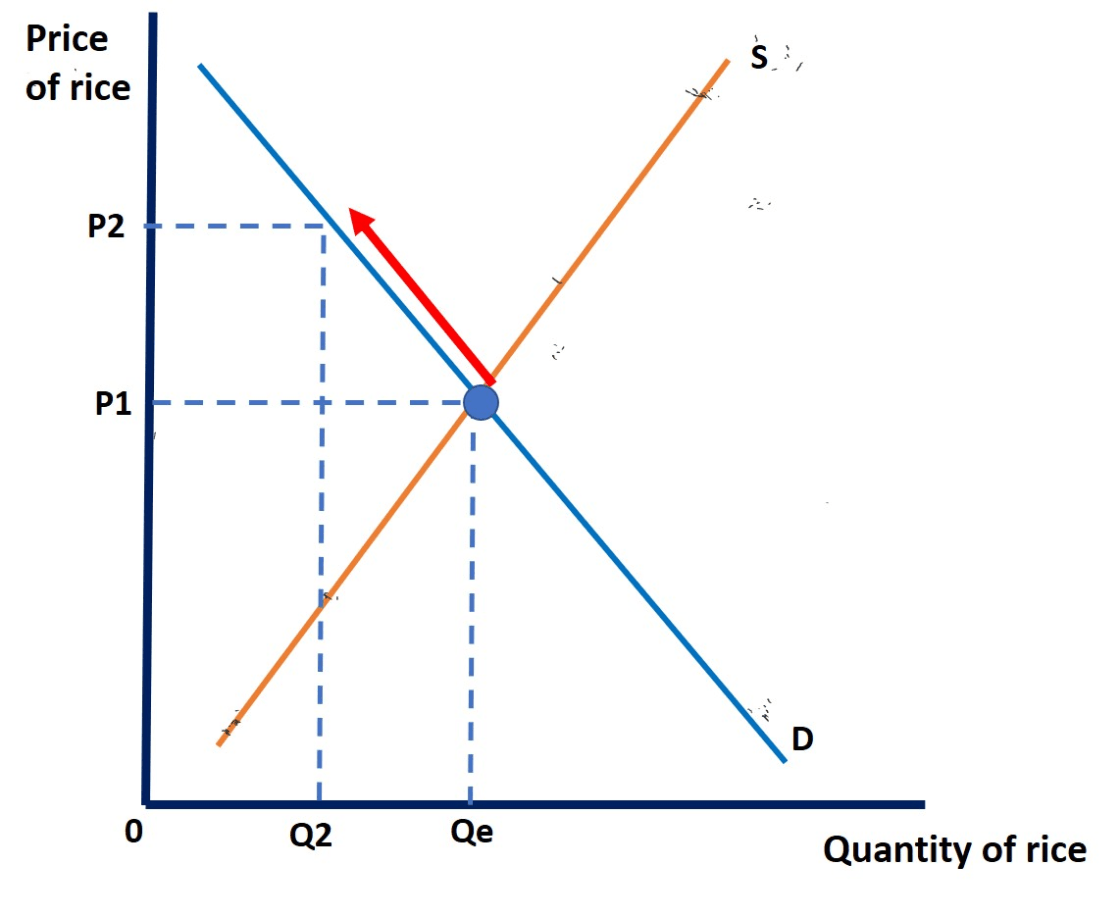
Contraction
The movement along the supply curve is known as an __________________ in supply
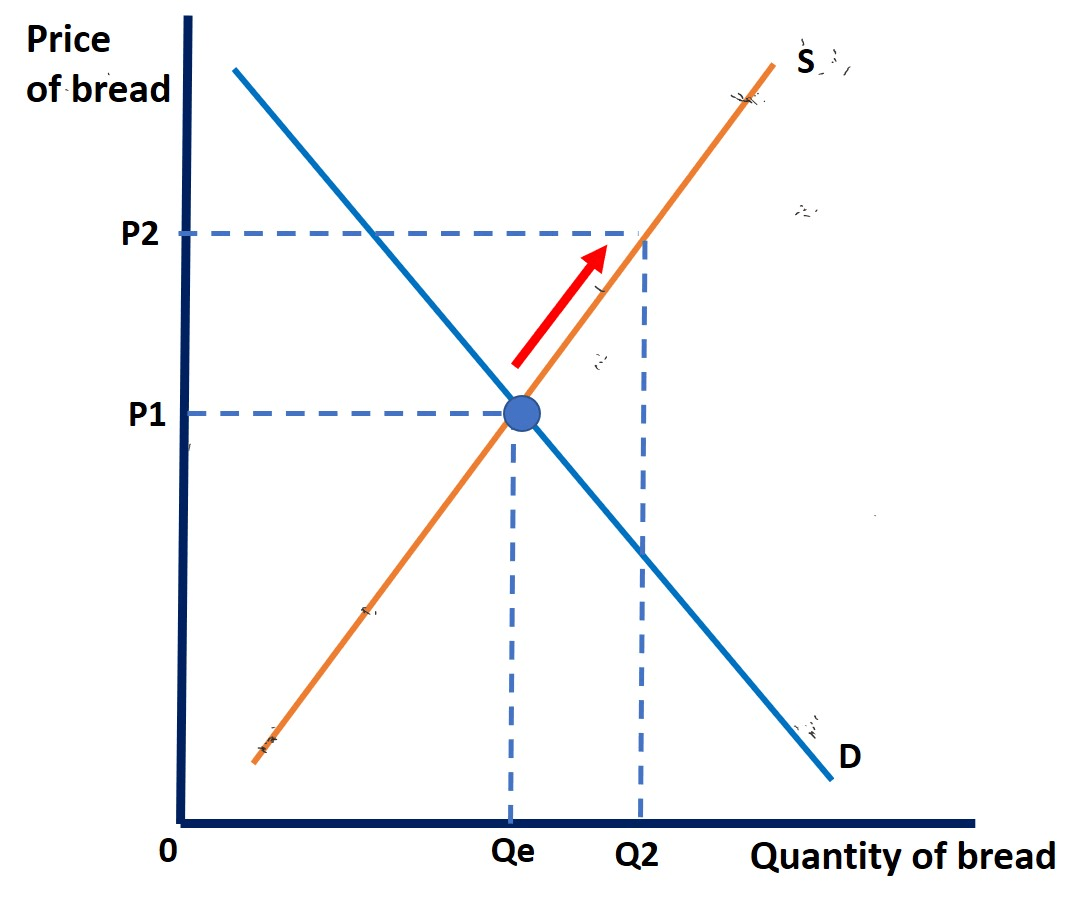
extension
Which points are allocatively efficient on the PPF?Which point(s) is/are not allocatively efficient?
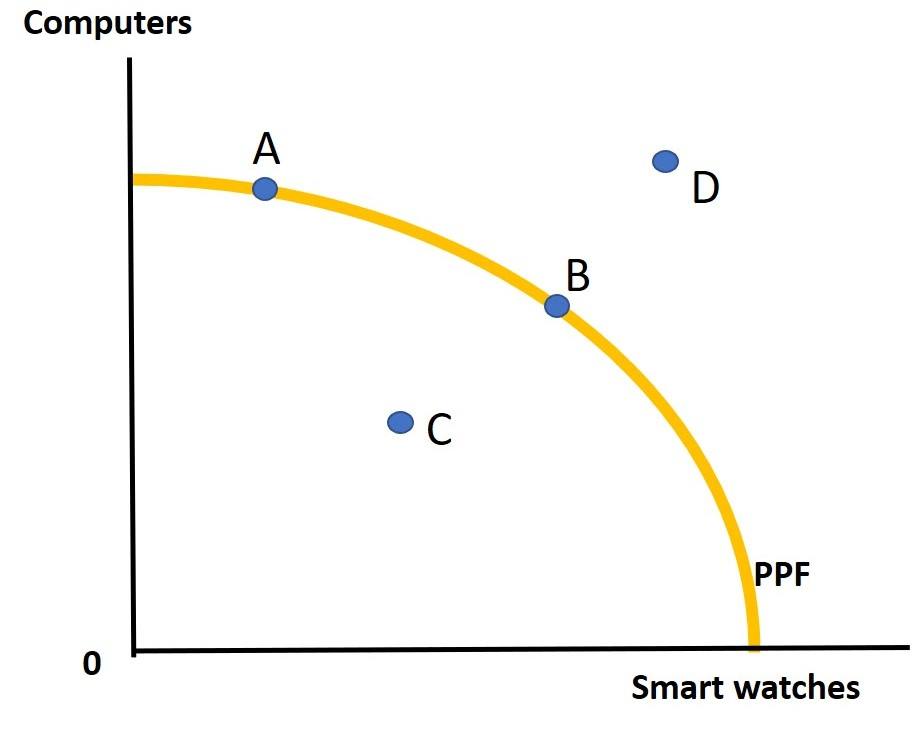
A and B are allocatively efficient: all resources / factors of production are used fully
C and D are not allocatively efficient:
C has underemployed resources
D cannot be produced as there is not enough
factors of production to make that combination
Name three different ways in three different industries that has substituted labour with automated machinery or robots.
Any three methods in any appropriate industry.
Robots in the production of microchips
Automated enquiry / customer service in banking
Barcode / self checkout in retail / supermarket
Online computer orders in Amazon books
What is the difference between a good with a value of -0.5 YED and a value +1.5 YED?
-0.5 YED
is an INFERIOR
+1.5 YED
Give 4 factors that may have caused the outward shift in the demand curve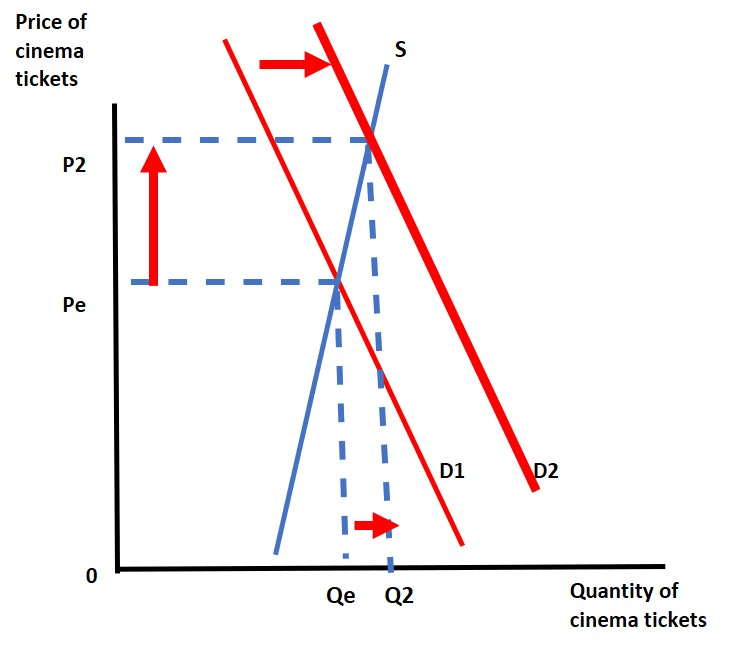
Any factors that shift demand curve outwards:
1. Advertising (increases willingness)
2. Lower income tax or VAT (increases ability)
3. New movie / sequel (increases willingness)
4. Holidays, weekends (increases willingness)
Name 4 goods or services that would exhibit a perfectly inelastic supply curve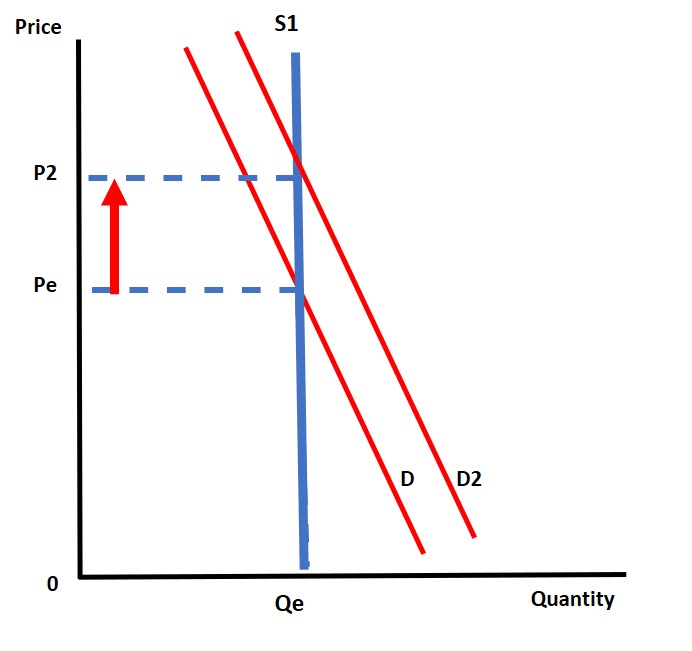
Any examples including:
1. Land
2. Commodities such as oil, gold, diamonds, iron ore, rice, wheat etc.
3. Seats in a stadium or theatre
4. Tickets to a concert
Name all parts of the diagram below:
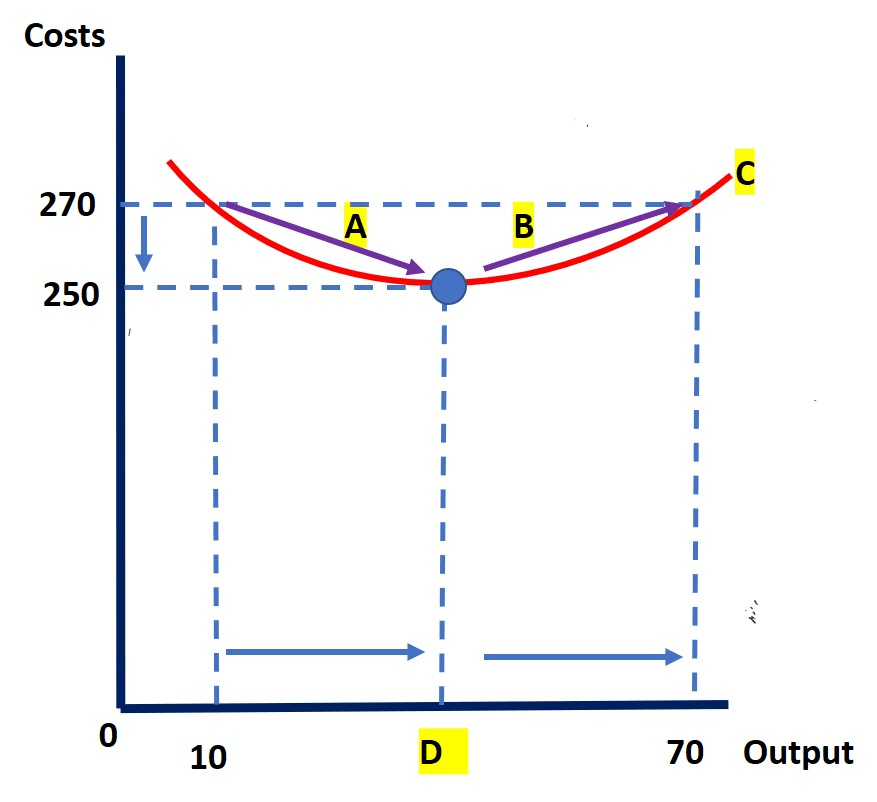
A= economies of scale
B=diseconomies of scale
C=Long run average cost
D= Production efficiency
For each of the factors of production, give one reason why that factor of production cannot be increased.
Capital: Lack of profit to invest in new machinery/ High rates of interest=expensive
Enterprise: Education standard is low in the country for LEDCs /
Land:Scarcity / Exhaustion
Labour: High costs/ Occupational immobility
Explain how companies use PED determine whether to increase the of their good
Companies revenue will RISE if price of INELASTIC goods rise
Revenue rise if price of ELASTIC goods fall.
Complete the sentence: The demand for labour is
The demand for labour is DERIVED from the demand for goods and services.
Give five ways in which governments can help increase the supply of a good
Any five supply policies:
1. Subsidies for solar power
2. Grants for training
3. Reduce or remove tariff (import tax)
4. Privatisation-reduces barriers of entry
5. Deregulation-reduces barriers of entry
Allow government provision of merit / public goods
Name 5 ways governments can improve production efficiency for companies.
Any five ways to reduce LRAC
1. Subsidies-helps to reduce costs
2. Grants -helps to reduce costs
3. Lower tariffs- lower price of raw materials -reduce costs
4. Lower VAT-lower price of raw materials -reduce costs
5. Deregulation / privatisation- increases competition, increases supply, lower prices
6. Provision of public goods-external e.o.s
Give 5 ways government can help to improve or increase the factors of production in the country
Any 5 government policies
1. Capital: Lower interest rates / provide grants / subsidies
2. Enterprise: Lower immigration control/ fund universities / enterprise grant to start own business
3. Land: Fund reclamation / deregulation of land use control/ privatisation of nationalized industries
4. Labour: Lower immigration control/ fund universities / grant for training
How should governments use PES to determine which goods to increase VAT on?
Increase VAT for PES Inelastic goods to maximise tax revenue
Reduce VAT for PES elastic goods to maximise tax revenue