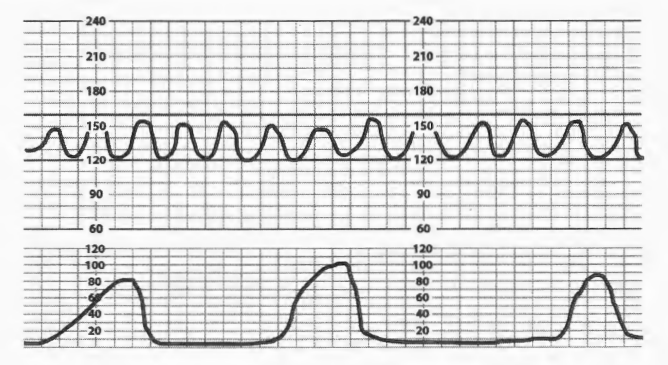
True/False: Category 1 FHR tracing and a reactive NST are the same thing.
What is False;
Categories are for describe tracing. NST is a test to assess current fetal well being , and require accelerations for reactivity.
What is the external device used to record tension changes in the abdomen resulting from uterine contractions.
What is a TOCO
Identify the periodic changes seen on this monitor strip. 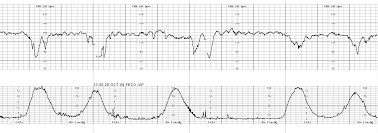
What are recurrent Variable decelerations.
Your monitor tracing shows fetal tachycardia. What should be your initial nursing intervention/assessment.
What is check maternal temperature.
What is the physiological cause of late decelerations
What is uteroplacental insufficiency. ( Think VEAL-CHOP)
Abrupt increase in FHR that goes 15 bpm above baseline and lasts at least 15 secs in a baby that is greater than 32 weeks gestation.
What is an acceleration
Greater than 5 contractions in 10 minutes, averaged over a 30 minute window.
What is tachysystole
The presence of these 2 FHR characteristics suggest an intact CNS, well oxygenated baby and absence of metabolic academia.
What are: Moderate variability and FHR accelerations.
You place your ante-partum patient on EFM. This is your tracing. What do you do?
Reposition patient on side, Start 02- 10L via mask, IV bolus of NS or LR, Call MD immediately, prepare for transfer to L&D
Recurrent Late Decelerations- Category II
What can cause decreased variability?
What is Narcotics, Cocaine, steroids- Betamethasone , Magnesium sulfate, fetal sleep pattern, Infections, Maternal fever, placental insufficiency
What is the baseline FHR 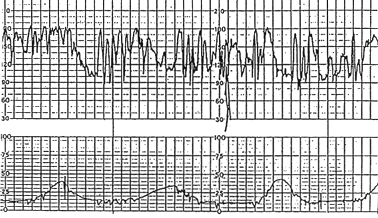
what is: Unable to determine due to marked variability
Decelerations that occur with more than 50% of uterine contractions in a 20 minute window.
What are recurrent decelerations.
What is the systematic approach of assessing a fetal heart rate tracing?
1. Baseline Rate
2. Variability
3.Periodic vs Episodic Changes ( Acceleration/ Deceleration)
4.Uterine Activity
Is oxygen indicated for this tracing. 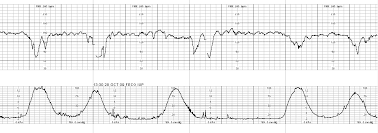
What is No. there is variability. Try other interventions first.
True or False: The NST can be extended 20 minutes when the initial 20 minutes is non-reactive
What is True
A decel that lasts > or = to 2 mins but less that 10 mins
what is a prolonged decel
What 4 things are assessed when doing a contraction assessment.
What are: Frequency, intensity, duration and resting tone/time
Identify the FHR change in this picture. 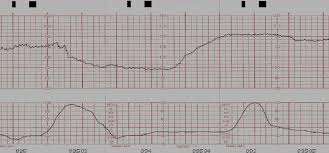
What is a prolonged deceleration
These interventions would be indicated for a Category III tracing.
What is reposition, O2, IVfluids, notify provider, prepare for imminent delivery.
What is the definition of an acceleration? Is gestational age important? Why or Why no?
•Visually apparent, abrupt (onset to peak less than 30 seconds) increases in the FHR above the baseline.
•In a fetus greater than 32 weeks, accelerations should last greater than 15 seconds and increase by 15 beats above the baseline.
•In a fetus less than 32weeks. Accelerations are defined as having a peak >10 bpm and durations of > 10 seconds.
Name the components of a category III FHR tracing.
What is:FHR tracing with one of the following
Absent variability with Recurrent lates,
Absent variability with Recurrent Variabiles
Absent variability with Bradycardia or
Sinusoidal
What interventions would be appropriate for a fetal tracing that is showing signs of uteroplacental insufficiency
Position change
Hydration
Reduce maternal pain/ Anxiety
Medications
Possibly Oxygen
List some troubleshooting techniques for the times that the fetal monitor tracing and audible do not match.
What is: palpate maternal pulse, verify correct monitor placements, check cords, US or doptone (for arrhythmias), place FSE (although can trace maternal in fetal demise)
Here is your patients current tracing. How would you chart in the medical Record.
Baseline- 125
Variability- Moderate
Acceleration- present
Decelerations- Absent
Category 1
Contractions- 6mins apart, 70-80 seconds, Intensity and resting tone- Can only be on palpation
What is this fetal tracing? Category? what is the cause of it?

Sinusoidal, Category III, fetal anemia