The seven dimensions of ABA.
What are Generality, Effective, Technological, Applied, Conceptually Systematic, Behavioral (GET A CAB)
A group of responses which serve the same function (i.e. change the environment in the same way)
What is a response class?
Examples include:
Count, Rate, Duration, Latency, Interresponse time (IRT), Celeration
What is Continuous Measurement?
Continuous measurement involves measuring every instance of the target behavior
The degree to which the changes in the dependent variable truly result from the manipulation of the independent variable and not from other causes
What is internal validity?
The four core principles laid out by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board that behavior analysts should strive to embody.
What are
- Benefit others
- Treat others with compassion, dignity, and respect
- Behave with integrity
- Ensure their competence
The goal of behavior analysis as a science that includes facts regarding observable events that can be analyzed and compared with other facts.
What is Description?
This influences the effectiveness of a reinforcer or punisher while also influencing the frequency of the specific behavior.
What is a MO?
The analysis of the anticipated benefits of an intervention compared to the anticipated costs
What is a Cost-Benefit Analysis?
This is the degree to which the results yielded by the study can be generalized to other target behaviors, populations, etc.
What is external validity?
A behavior analyst can establish these by seeking out mutually beneficial relationships with more experienced individuals.
What is a mentor?
The goal of behavior analysis as a science that includes the highest level of scientific understanding.
What is control?
Functional relations can be derived from control
This a type of motivating operation that increases the effectiveness of a reinforcer
What is an EO?
This involves measuring how many responses it took in order to achieve a specific performance goal.
What is Trials to Criterion?
This is important because if students aren't making any progress towards goals or mastering goals, then we might be intervening in an inappropriate way for them.
Examples of this include:
- History
- Maturation
- Participants dropping out of a study
What is a confounding variable?
This is a factor which is not controlled by experimenters that is either suspected or known to have influence on the dependent variable of a study
This in service delivery is the acknowledgement of and openness to learning about the different cultures of clients and stakeholders as well as self-reflection and action regarding power dynamics or imbalances.
What is cultural humility?
The goal of behavior analysis as a science that includes anticipating the outcome of a future event.
What is prediction?
Trends in data points are a great way to use prediction. Another example would be correlations.
This means that, in verbal behavior, multiple variables are often influencing a single response and a single variable is often influencing multiple responses
What is multiple control?
Simply put: Our behavior is based on context
The extent to which a measurement is consistent/repeatable.
What is Reliability?
Each participant serves as their own control.
What is a single-case design?
This means that the effects of each condition are compared to the participant's own data
This involves a behavior analyst acting as more than one role in another person's life when they are professionally involved with that person
What is a multiple relationship?
What are the six attitudes of science?
Determinism, empiricism, parsimony, experimentation, replication, and philosophic doubt
This is the continued ability of the learner to perform a behavior even after part or all of an intervention has been removed.
What is response maintenance?
Response maintenance is an important component of generality. If a behavior persists across time, it is maintained
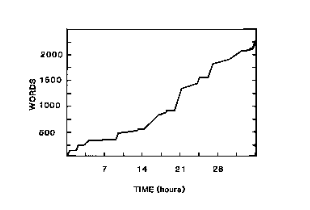
What is a cumulative record?
Think of a cumulative record as a graph of a person's accumulation of a skill or behavior. Cumulative records will never trend downward.
This involves demonstrating that baseline data of the dependent variable would have remained consistent if the independent variable had not been manipulated
What is verification?
Example: In an ABA design, the second baseline phase helps verify whether or not a treatment was effective.
This a belief whether conscious or unconscious that some people or traits are better than others which can lead to unfair or inequitable treatment.
What is a personal biases?