What is the name of the angle shown in the attached diagram?
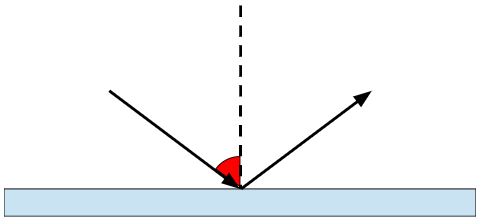
Angle of Incidence
What does the blue arrow represent?
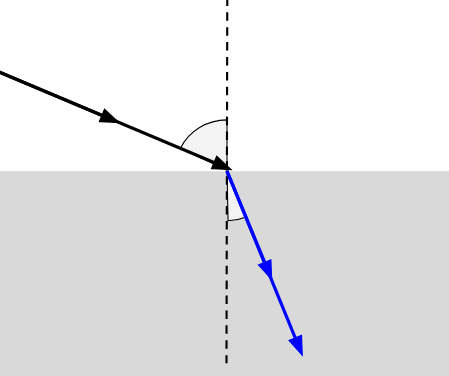
The refracted ray.
What seven colours make up the visible light spectrum?
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
Name one model scientists use to explain light.
- The Ray Model
- The Particle Model
- The Wave Model
What word describes materials that let light pass through easily?
Transparent
What is the straight path that light travels in called?
A ray
What is the distance between one crest and the next called?
Wavelength
If a light ray hits a mirror at a 30° angle from the normal, what is the angle of reflection?
30°
What is refraction?
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
What makes an object appear black?
All the visible light is being absorbed.
What does the ray model of light help us explain?
How light moves in straight lines, which helps explain reflection and refraction.
What kind of material lets some light through but scatters it?
Translucent
What is the line drawn at a right angle to a mirror’s surface called?
The normal
What do we call the height of a wave from its rest position to its crest?
Amplitude
What law states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection?
The Law of Reflection
When light slows down as it enters a denser medium, does it bend toward or away from the normal?
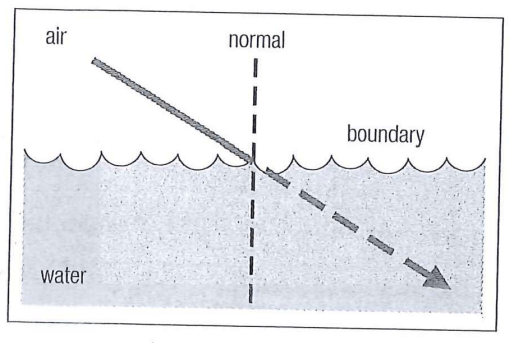
Toward the normal
Why does an object appear red when seen with white light?
Because the object reflects red light and absorbs the rest of the visible light spectrum.
What are the particles of light called in the Particle Model of Light?
Photons
What kind of material blocks all light from passing through?
Opaque
What do we call the incoming light ray that hits a surface?
The incident ray
Is light a compression or a transverse wave?
Transverse
What type of surface produces clear reflections (e.g. you can see yourself in them)?
Smooth, shiny surfaces, like mirrors
Compare the speed of light in air, water, and glass (fastest to slowest).
Fastest in air → slower in water → slowest in glass
Why does a green object appear green in white light?
The green light is being reflected, while the rest of the visible light spectrum is being absorbed.
What property of light would be explained using the Wave Model of Light?
Frequency or wavelength or amplitude
Give one example each of a transparent, translucent, and opaque object.
Transparent: glass; Translucent: frosted window; Opaque: wood
What term describes the bending of light as it enters a new medium?
Refraction
What is the process of light being taken in by a material instead of reflected or transmitted?
Absorption
Why does a rough surface scatter light in many directions instead of forming a clear reflection?
Because the surface’s irregularities make light reflect at many different angles
When a ray of light passes from air into water at an angle of incidence of 90°, which way does the ray of light bend?
The light does not bend - it is already perpendicualr (normal) to the surface of the water.
Why does a blue shirt look black in red light?
Because it absorbs red light and has no blue light to reflect
Explain why scientists use different models to describe light instead of just one.
No single model explains all behaviours of light; each model is useful for different phenomena (e.g., reflection vs. frequency)
Explain why frosted glass allows light but not clear images to pass through.
Because it scatters light in many directions, so the image becomes blurred
Define “medium” in the context of light waves.
A substance or material through which light travels (e.g., air, water, glass)
Define “scattering” in terms of light.
The process by which light is sent in many directions when it hits uneven surfaces or particles.