Who gets pap smears and when?
21-29 yo: cytology q3y
30-65: cytology alone q3y OR cytology + HPV q5y
65+: up for disussion if expected to live 10+ years
- discontinued in patients age ≥ 65 with no history of CIN 2 or higher
List a daily, weekly, monthly, and *yearly* option for birth control
- pill
- patch
- ring
- IUD
post void urine volume that is pathological for urinary retention
150 cc
What is the A
Uterus
Primary vs secondary ammenorhea
Primary amenorrhea— does not get first period by age 15.
Secondary amenorrhea—no menses for 3 months or more in someone who already menstruates.
Breast cancer screening recommendations per USPSTF
40-49 - shared decision making!
50-74 - mammograms q 2 years
How do Locally acting progestins work?
(bonus: name examples)
1. Thickens cervical mucus → impairs sperm penetration
2. Endometrial thinning → impairs implantation
(mini-pill, levonorgestrel IUD (mini/local))
Post-op Milestones for GYN
1. pain controlled on PO meds
2. ambulating
3. voiding trial*4. BM or passing gas*
Structure that contains the ovarian vessels
Suspensory/infundibulopelvic ligament
Pathophysiology and sx of endometriosis
(bonus 300: treatment options)
3 "d"
- dysmenorrhea, dysparunia, dyschezia
Routine STI Screening per USPSTF
CG for all sexually active women age < 25 yo - screen in those at risk if >25 yo
Contraindications to OCPs (list 3)
- smokers (more than 15 cigarettes per day) over age 35 (risk for cardiovascular)
- hypertension (systolic BP ≥140 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg ),
- Breast cancer,
- Ischemic heart disease
- Migraines with auras
- Endometrial cancer
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatocellular adenoma
- Call for temperature of 101 or greater.
- No baths for 2 weeks, only showers.
- No intercourse for 6-8 weeks depending on type of hysterectomy.
- No lifting over 10 pounds.
- No driving for 1-2 weeks or until not taking narcotics.
- Keep incision clean and dry.
- Light vaginal spotting and bleeding is normal. Report heavy bright red bleeding
- Increase fluid intake after surgery to help prevent constipation
- May take stool softeners such as Colase 100 mg twice a day or Surfak 240mg twice a day
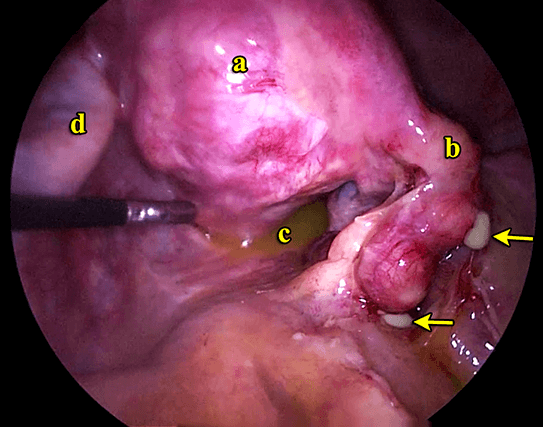
What is C?
Right Fallopian tube/fimbrae
Primary vs secondary dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrhea characteristically begins when adolescents attain ovulatory cycles, usually within 6–12 months of menarche.
Secondary dysmenorrhea = painful menses due to pelvic pathology or a recognized medical condition. most common cause = endometriosis.
When to screen for colon cancer?
Basically screen anyone 45-75
- Grade A rec: for 50-75
- Grade B rec: 45-49
What can be used as an emergency contraceptive?

What is an active vs passive voiding trial?
Active: bladder is back filled with saline (300cc) - patient has 30 min to urinate - bladder scan afterwards
Passive: bladder fills as urine is naturally produced
What lymph nodes are first involved in the spread of ovarian cancer?
Para Aortic
- P - Polyp
- A - Adenomyosis
- L - Leiomyoma
- M - Malignancy
- C - Coagulopathy
- O - Ovulatory dysfunction
- E - Endometrial
- I - Iatrogenic
Management of an ASC-US pap


What are the forms of estrogen and progesterone in OCPS?
- ethinyl estradiol: SYNTHETIC version of estrogen. It is much more bioavailable than plan estradiol. It acts more potently on liver, uterus and ovaries
- Progestin: a SYNTHETIC form of progesterone.
These both give your body hormone and suppress ovarian function
Post-operative pain management per ERAS protocol
(Bonus: what does ERAS stand for)
- oral acetaminophen 1 g QID + NSAID (ibuprofen, celecoxib)
- oxy for breakthrough pain
What artery runs beneath the round ligament?
Sampsons artery
What is the work-up for a palpable breast mass?
