The process after ingestion.
What is digestion?
The storage sac for bile.
What is the gallbladder?
Waste moves here after the ureters.
What is the bladder?
#1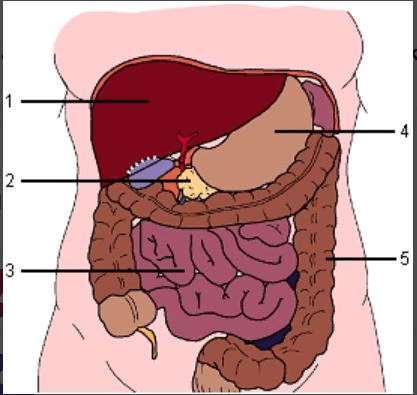
What is the liver?
The type(s) of digestion in the stomach.
What is mechanical and chemical?
Produced by the stomach for chemical digestion.
What is hydrochloric acid?
What is the mouth?
The main function of the kidneys.
What is filtering blood?
Not part of the digestive tract.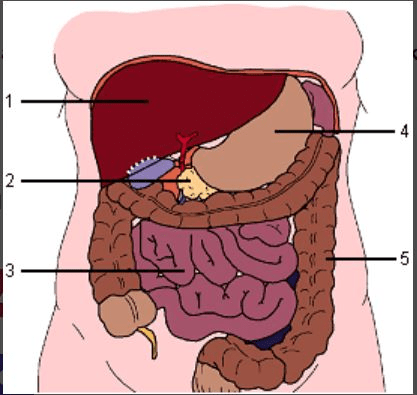
What is #2?
This organ does not participate in chemical digestion of food.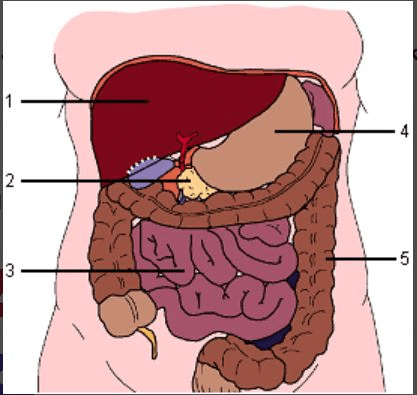
What is the large intestine?
The flap that prevents food from entering the trachea.
What is the epiglottis?
This organ sends neutralizing juices to the small intestine.
What is the pancreas?
This is the urethra.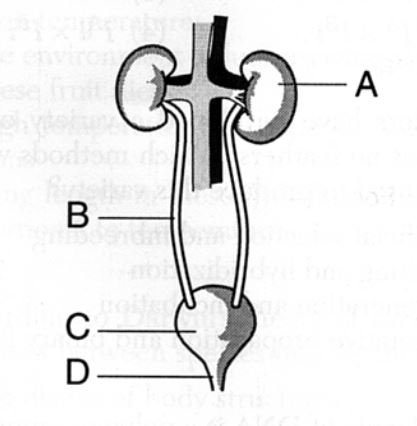
What is letter D?
Function is for water absorption.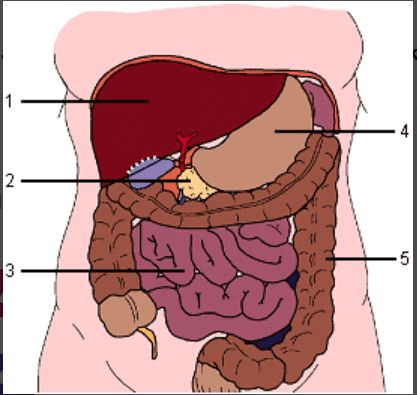
What is #5?
Digestion that includes stomach acid breaking bonds.
What is chemical digestion?
The purpose of the digestive system.
What is nutrient absorption?
The #3 cancer in both men and women.
What is colon?
Site of blood filtration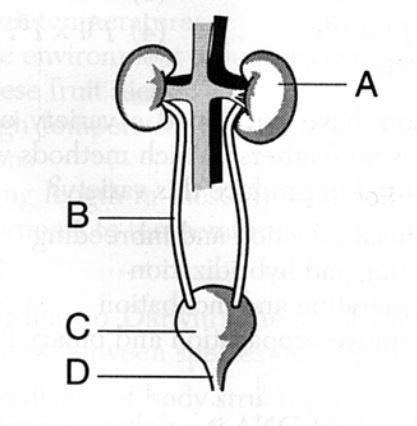
What is A?
#5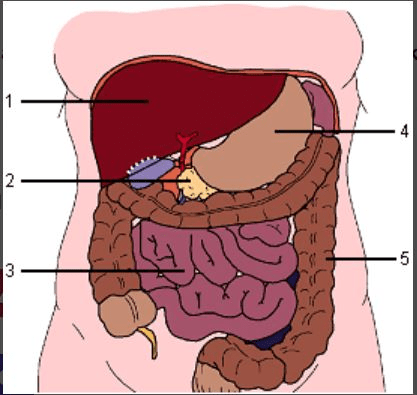
What is the large intestine?
Body's ability to maintain an internal balance.
What is homeostasis?
The phase of digestion the stomach is involved in.
What is digestion?
The liver, gallbladder and pancreas are these.
What are accessory organs?
Caused when waste moves slowly through the tract and the colon absorbs too much water.
What is the constipation?
#4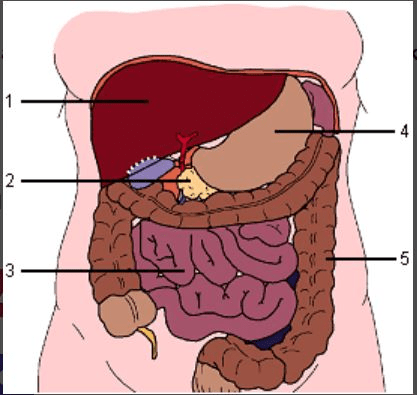
What is the stomach?
The wave-like muscle contractions that push food through the digestive tract.
What is peristalsis?