What is the difference between a gene pool and allele frequency
Gene pool = all the alleles in a population; allele frequency = how much of an allele is present in a population
What is the difference between anatomy and physiology
Anatomy = study of body structure and its relationship with one another; Physiology = study of body function at various levels of organization
What is the heart
A muscular pump that aims to take in deoxygenated blood, oxygenate it via the lungs, and deliver oxygen to the rest of the body
Give two functions of bones
Protects organs, provides framework for muscles, stores calcium, forms blood, etc.
What are the general types of neurons involved in relaying messages in response to a stimulus?
Sensory/afferent neuron, interneuron, motor/efferent neuron
Name three things that cause evolution
What are mutation, gene flow, small population size, nonrandom mating, and natural selection
What is the function of connective tissue? Give an example of one
To connect different parts of the body together (example = cartilages, blood, bones, etc.)
When you see "this" in a microscope, you will immediately know that what you're looking at is cardiac muscle
Intercalated discs (gap junctions where electrical impulses travel so that the heart beats synchronously)
Why are "false ribs" called the way they are
They either indirectly attach to the sternum (8th to 10th pairs) or do not attach at all (11th and 12th pairs)
Name two parts of the brain and state their functions
Thalamus = “train station;” takes in signals in sensory nerve tracts and bring them to the basal nuclei (cluster of neuron cell bodies)
Hypothalamus = homeostatic balance (hunger for example); exposed to the bloodstream and can monitor the chemical makeup and temperature of the blood
Pituitary Gland = structure where many hormones are released (ADH, oxytocin, GH, etc.)
Pineal Body/Gland = melatonin
Corpus Callosum = bridge between the left and right hemisphere
Hippocampus = promotes short-term memory into long-term memory
Gene flow = addition/removal of alleles in a population via immigration and emigration respectively; genetic drift = random change in allele frequencies over time
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
Picks up leaked fluid and brings it back to the bloodstream, cleans blood of pathogens, and protect the body from foreign substances
What is the difference between the pulmonary and systemic circuits?
Pulmonary = to the lungs (blood oxygenation); systemic = to the entire body (oxygen distribution)
What are the two more well-known proteins involved in the sliding filament mechanism
Actin and myosin
One of the most well-known neurotransmitters we know of is dopamine. What are some of its effects/involvements?
Contributes to memory and learning
Fine motor coordination (posture for example)
Favoring traits that help an organism acquire a mate, typically done through various ways of courtship (songs, behaviors, physical features, etc.)
We have our own system in us to regulate our temperatures (sweating and shivering for example)
List four things that your cardiovascular system circulates around the body
Nitrogenous wastes, respiratory gases, electrolytes, water, antibodies, proteins, nutrients, etc.
What is the difference between isotonic and isometric contraction?
Isotonic = "same tension" (muscle shortens, lifting a dumbbell); Isometric = "same length" (muscle does not shorten, holding a dumbbell in place)
What are the three meninges that work together to protect the brain
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
A specific type of natural selection wherein two different phenotypes do well because of more than one useful resource
Disruptive selection (example = hard beaks for big nuts and soft beaks for small nuts)
Why does homeostasis allow protein function within specific ranges?
Hydrogen bonds, which make up a significant amount of most proteins, are sensitive to many external factors (salinity, pH, temperature, etc.)
1.) filters out toxins and waste products from the blood to prevent it from circulating throughout the body
2.) has immune cells to neutralize any pathogens in the blood stream coming from the digestive tract
What are the three types of joints? (extra +500 if you can give an example for each)
Fibrous = to your jawbone
Cartilaginous = ribs and sternum, adjacent vertebrae
Synovial = shoulders, pelvis, elbow, etc.
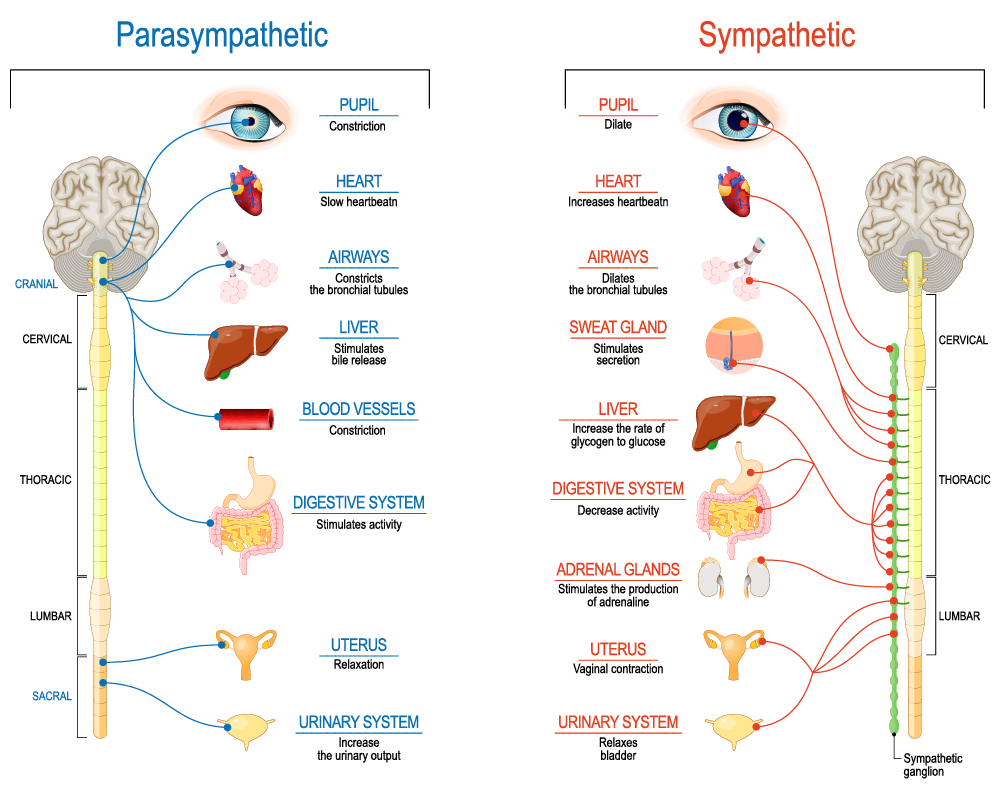
List three physiological effects seen respectively in the sympathetic versus parasympathetic system