The independent variable in an experiment is the
A. group you are comparing to.
B. data you are collecting as the outcome.
C. thing being changed between groups.
D. thing that is the same between groups.
C. thing being changed between groups.
Is this organism be made up of A. eukaryotic or B. prokaryotic cells?
A. Eukaryotic
Enzymes are typically which type of molecule?
A. Nucleic acid
B. Carbohydrate
C. Lipid
D. Protein
Protein
One major function of which type of molecule is to store genetic information:
A. Protein
B. Carbohydrate
C. Lipid
D. Nucleic acid
D. Nucleic acid
Diffusion and osmosis are examples of
A. Passive transport, because they do not require energy.
B. Active transport, because they do not require energy.
C. Passive transport, because they require energy.
D. Active transport, because they require energy.
E. Isotonic solutions, because they are the same.
A. Passive transport, because they do not require energy.
If you are testing the effect of pH on the germination rate of seeds, what is the dependent variable?
A. pH
B. Germination rate
C. Type of plant
D. A plant that doesn't have pH added
germination rate
What part of a cell can be called the "recycling center" because it is where materials are broken down?
(type it in!)
Lysosome
Lactase is the enzyme that breaks lactose sugar apart into smaller sugars during digestion. What is the substrate in this reaction?
A. Lactase
B. Lactose
C. Smaller sugars
D. Digestion
Lactose sugar
The monomers that make up proteins are called
A. Nucleotides
B. Enzymes
C. Amino acids
D. Chromosomes
C. Amino acids
The concentration of solute inside a jellyfish is isotonic to sea-water. If the jellyfish was moved to a freshwater aquarium, what would happen to the jellyfish due to osmosis?
A. The jellyfish would lose water and shrivel up.
B. The jellyfish would lose salt and shrivel up.
C. The jellyfish would gain water and swell up.
D. The jellyfish would gain salt and swell up.
E. The jellyfish would remain isotonic to the solution.
C. The jellyfish would gain water and swell up.
A control group is a sample where you
A. have changed the independent variable
B. do not treat the sample with the independent variable
C. test the highest amount of your independent variable possible
D. test the sample at pH=7
B. do not treat the sample with the independent variable
Which part of the cell has a variety of functions in different cells including manufacturing lipids and storing calcium?
(type it in!)
Smooth ER
What is the optimum pH of pepsin (green)?
A. 2 B. 4 C. 7 D. 9
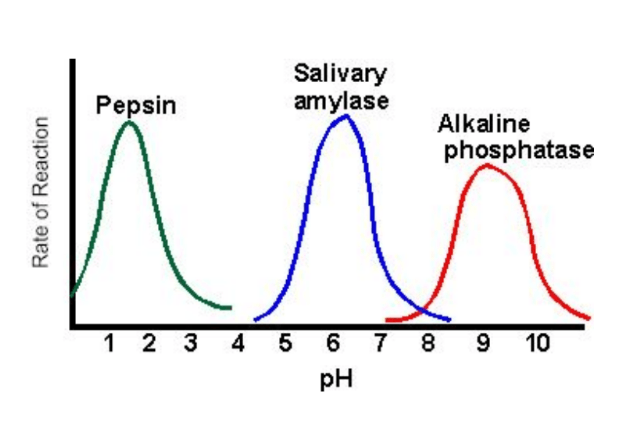
A. 2
The types of bonds listed in order from weakest to strongest:
A. Hydrogen, ionic, covalent
B. Ionic, covalent, hydrogen
C. Covalent, ionic, hydrogen
D. They’re all the same strength
A. Hydrogen, ionic, covalent
You dissolve the shell from an egg using vinegar. You then put the shell-less egg into RockStar energy drink. After 24 hours you observe that the egg has shrunk. Which of the following statements is true?
A. The energy drink made the molecules move more quickly with respect to the egg.
B. Rockstar is hypertonic to an egg.
C. Eggs are hypertonic to Rockstar.
D. Eggs and Rockstar are isotonic.
E. Vinegar reacts with eggs and Rockstar to produce a hypertonic reaction.
B. Rockstar is hypertonic to an egg.
A confounding variable is
A. the variable you are changing.
B. a variable that you compare your results to.
C. a variable that is constant between all your samples.
D. a variable that is not constant between all your samples.
D. a variable that is not constant between all your samples.
Which part of the cell assembles amino acids together into a chain?
(type it in!)
Ribosome
What are two environmental conditions that can denature an enzyme?
(type them in!)
Temperature and pH
Which of these has the most complex 3-D structure
A. Protein
B. Carbohydrate
C. Lipid
D. Nucleic acid
A. Protein
Sodium ions are at a higher concentration outside the cell than inside. If the cell wanted to move sodium ions into the cell, it would need to use
A. Osmosis
B. Diffusion
C. Facilitated diffusion
D. Active transport
E. Endocytosis
D. Active transport
You are testing whether various scents will repel mice. You put a blob of peanut butter (which attracts mice) into different boxes, and you put one of the scents you are testing around the door of the box. You count the number of mice that go into each box. What would you want to use as a control group in this experiment?
A. Number of mice
B. Using the same type of peanut butter
C. Peanut butter in a box with ALL the scents around the door
D. Peanut butter in a box with NO scent around the door.
D. Peanut butter in a box with NO scent around the door.
Some bacteria can perform photosynthesis and all can perform a form of cellular respiration. Do bacteria contain chloroplasts and mitochondria?
A. Yes
B. No
B. NO, they don't contain any membrane-bound organelles
DNA polymerase is the enzyme in DNA replication that joins individual DNA nucleotides together into a chain. What is the substrate in this reaction?
A. DNA polymerase
B. Individual DNA nucleotides
C. Chain of DNA nucleotides
D. Nucleus
Individual DNA nucleotides
Lipids are able to store energy because they
A. are entirely hydrophobic
B. can be used for anaerobic respiration
C. contain many carbon-carbon bonds
D. can easily pass through the cell membrane
C. contain many carbon-carbon bonds
Potassium must be actively transported into cells. This means that the concentration of potassium is higher
A. inside the cell
B. outside the cell
C. it is isotonic
D. it uses exocytosis
A. inside the cell