What is the phenotypic frequency of the recessive trait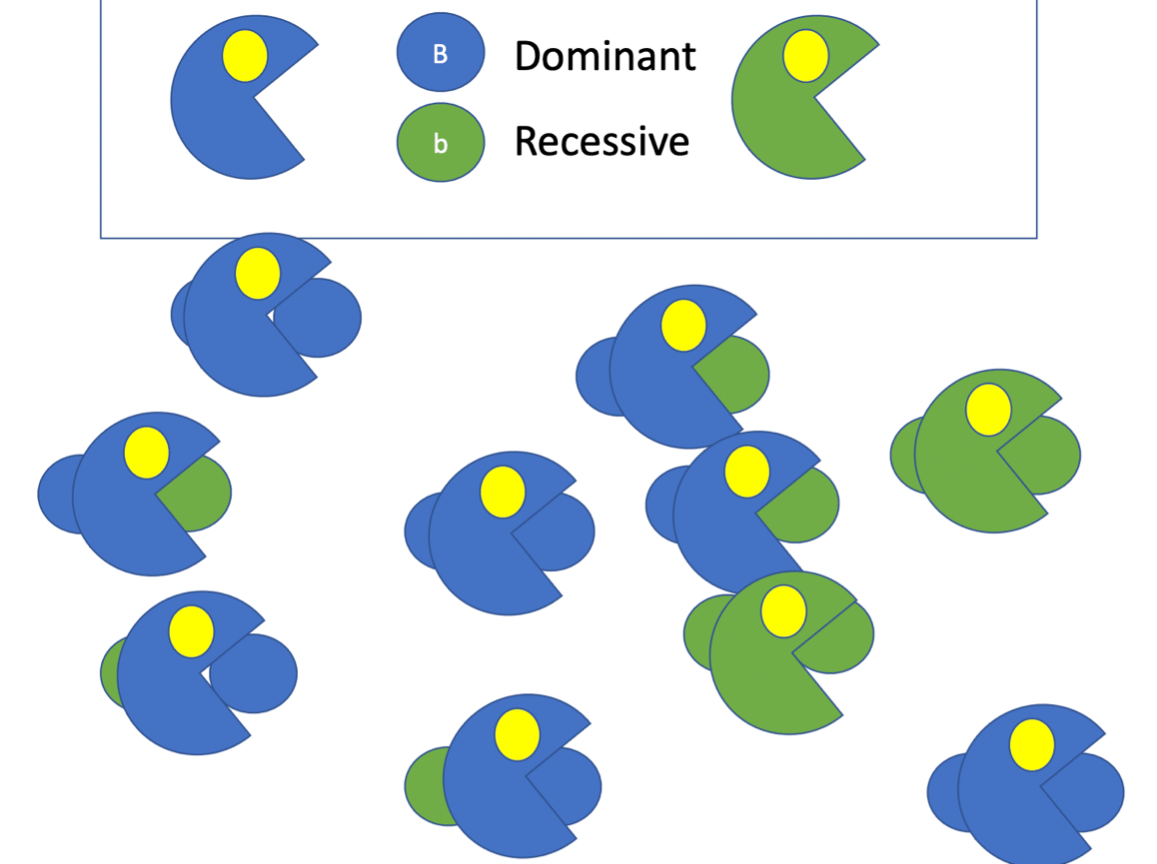
2/10 (or 0.2)
The birds prefer to eat the green beetles...what phenomenon is happening here?
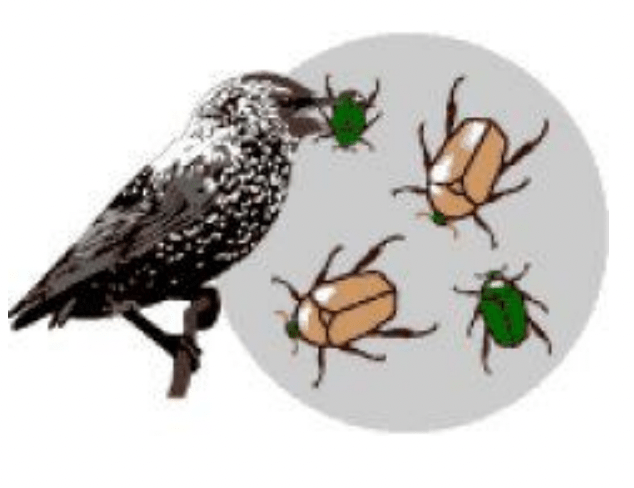
Natural selection
shared derived traits provide evidence of the common ancestry of a group are called..
synapomorphies
What is speciation?
divergence of biological lineages and emergence of reproductive isolation between lineages
Define evolution
the genetic change in a population over time.
What does p2 represent (dominant, heterozygote, or recessive)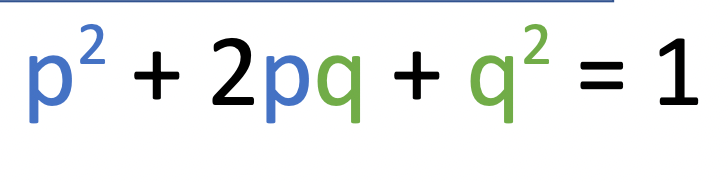
dominant
When a mouse is exposed to higher temperatures, the expression patterns of many of its genes change. Is this mouse evolving? Why or why not?
No the mouse is not evolving, individuals do NOT evolve
Which traits unite the mouse and lizard?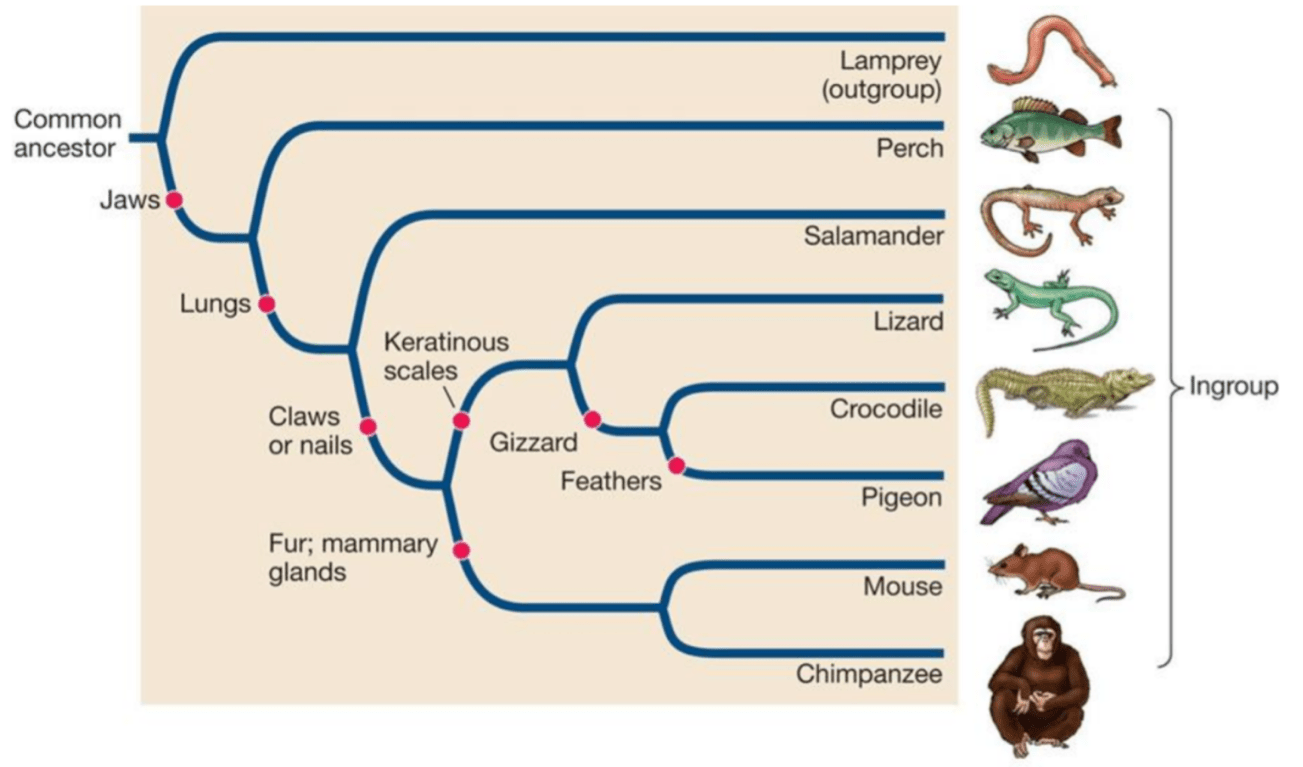
claws or nails, lungs, and jaw
Explain the "biological species concept"
“Species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.”
Describe "Descent with modification"
Divergent species share a common ancestor and have diverged from one another gradually over time
If q2=0.2, calculate for q
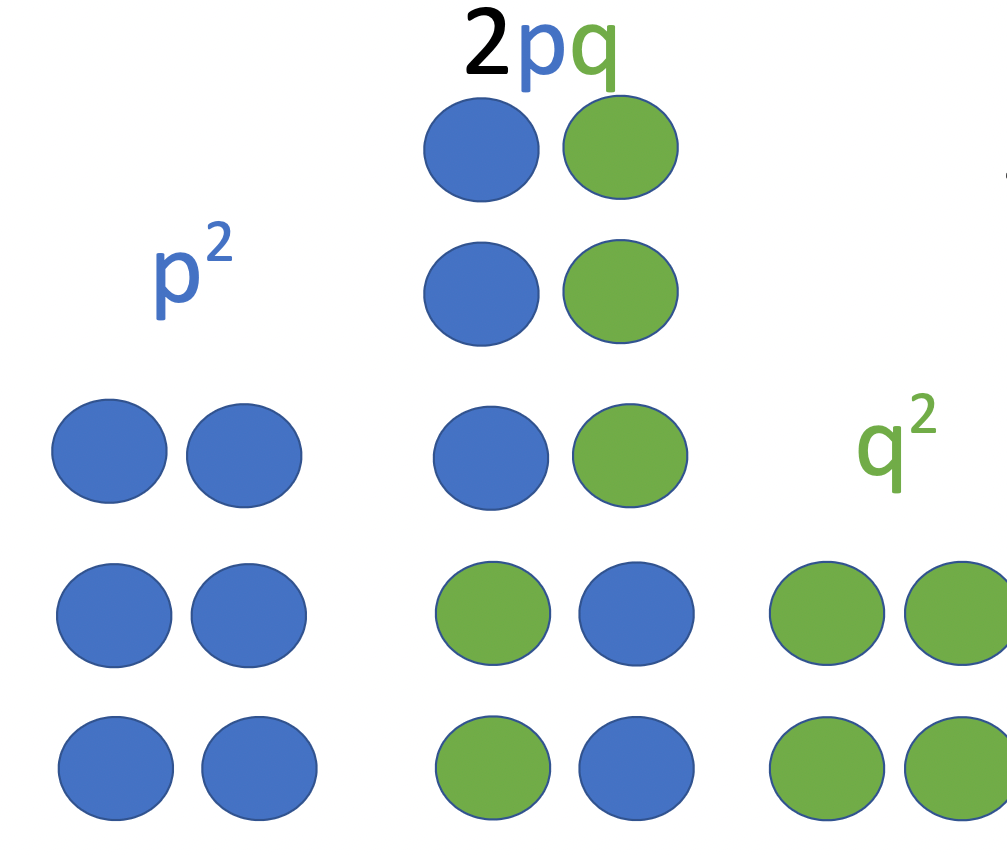
what is 0.44?
______ are different forms of a gene
allele
What are the sister species in this phylogenetic tree?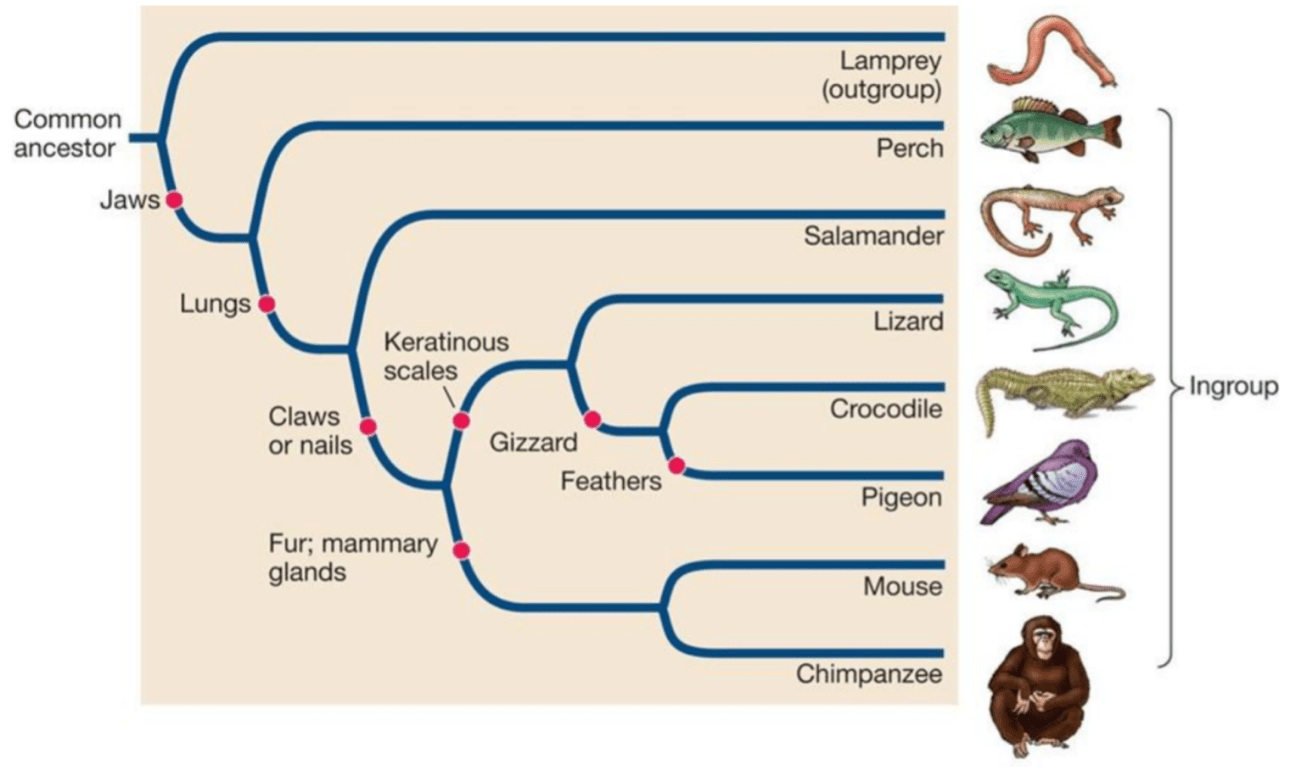
Crocodile and pigeon & mouse and chimpanzee
Which is ultimately the most important factor for generating distinct species?
a. morphological traits
b. interbreeding
c. the niche an organism inhabits
d. reproductive isolation
e. species isolation
reproductive isolation
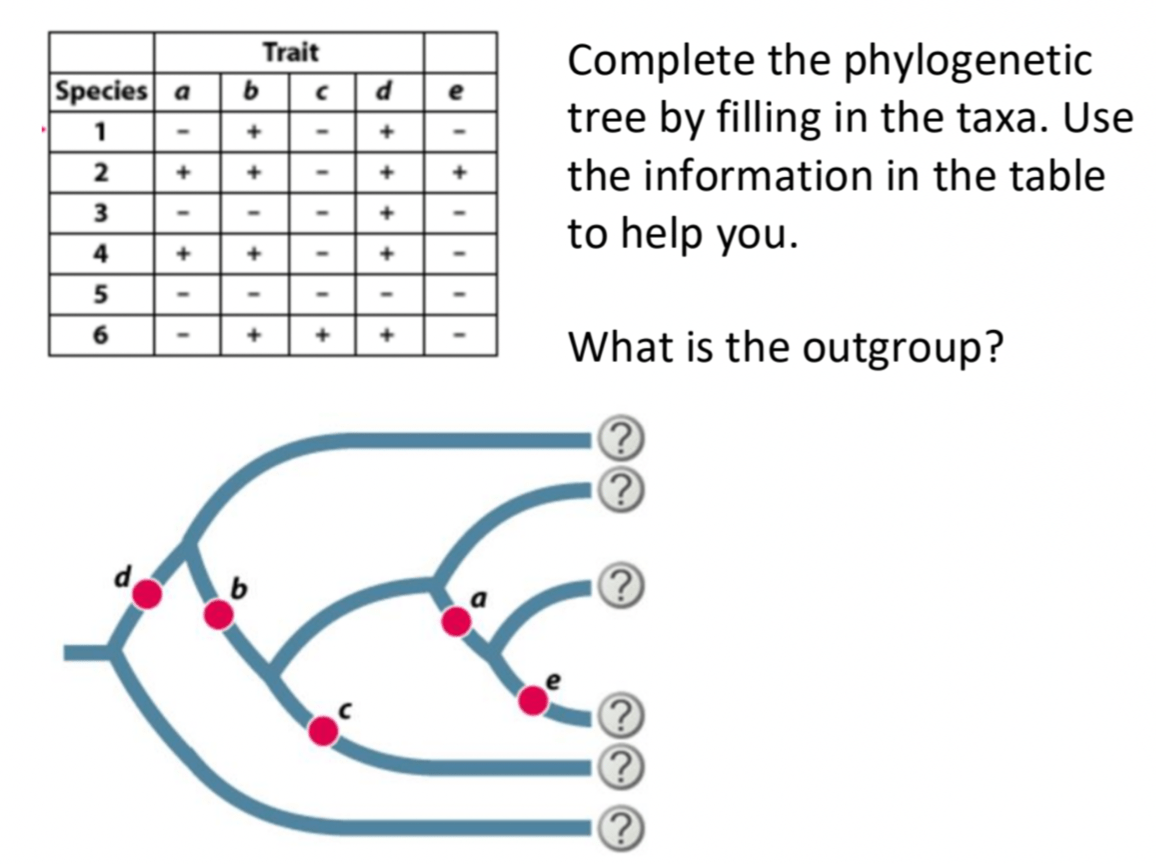
from top to bottom: 3, 1, 4, 2, 6, 5
5 is the outgroup
p + q is always equal to 1... if q is 0.44, find p2
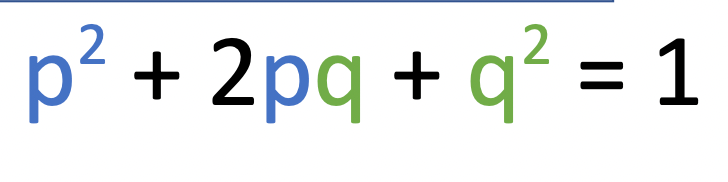
p2 = 0.33
What is this called?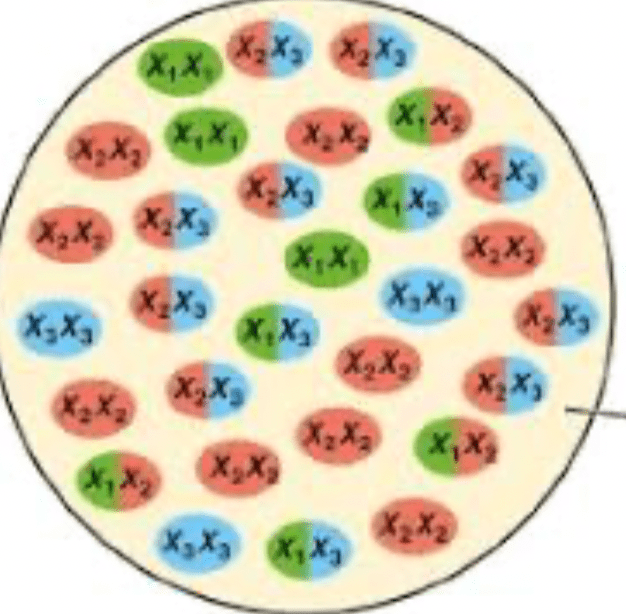
Gene pool
What is the limitations of fossils in determining phylogenetic relationships?
It fragmentory/ missing for some groups
A biologist has identified two groups of salamanders with very similar physical features on opposite banks of a river. Which investigative approach would help determine whether the groups are the result of allopatric speciation?
a. Look for ways that the salamanders could migrate from one side to he other.
b. Compare the gene pools of the two populations to see if there are any alleles not shared by both groups.
c. Move several individuals from one side to the other and observe their ability to survive.
d. Compare the complete genomic sequences of individual salamanders from each group.
b. Compare the gene pools of the two populations to see if there are any alleles not shared by both groups.
Give an example of prezygotic isolating mechanisms
Mechanical isolation, pollen incompatability, temporal, behavioral, or anything else that works

White flowers: 500 white flowers /2,000 flowers in total = 0.25 (25%)
Red flowers: 1-0.25=0.75 or 75%
Which of the following means evolution is NOT occurring?
a. Selection among genotypes
b. Nonrandom mating
c. Large population
d. Mutation
c. Large population
Why can frog calls be used to determine phylogenic relationships, but not bird songs?
bird songs are typically learned, in order to be used in phylogenetic analysis the trait MUST be inherited or culturally transmitted
If allopatric speciation is the most prevalent mode of speciation, what do you predict about the geographic distributions of many closely related species?
The presence of geographical barriers among populations ensure that they begin to evolve independently and mechanisms of reproductive isolation will appear among them
How often do populations in nature fit the conditions of Hardy-Weinburg equilibrium?
never!