What two chemotherapeutic drugs were primarily tested in this study?
Cisplatin and paclitaxel
The drug palbociclib (palbo) was used in many of the figures. What was its role?
palbociclib causes a G1 delay, thus slowing proliferation rates
What overall theory explains why aneuploid cells resist chemotherapy?
Slower proliferation (particularly G1 delays) shields them from drugs that act in specific cell-cycle phases
Why did they use HCT116 cells in addition to MEFs?
HCT116 is a human colon cancer cell line to confirm the mechanism in a human model
What feature of aneuploid cells do the researchers believe leads to drug resistance?
G1 delay / slowed proliferation
What did Figure 1D show about p53’s role in drug resistance?
Resistance to cisplatin in trisomic cells remained when p53 was inactivated, showing the effect is largely p53-independent
Why might combining palbociclib (palbo) with standard chemotherapies be risky for patients?
Palbociclib causes G1 arrest, making cells less sensitive to drugs that target dividing cells.
What secondary analyses did they perform using public datasets and why?
They analyzed the CCLE (Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia)/Broad Institute's RNAi screening to correlate aneuploidy, proliferation, and drug response
What gap in knowledge were the authors trying to fill?
Whether drug resistance in aneuploid cells arises from specific gene copy changes or from general features of the aneuploid state
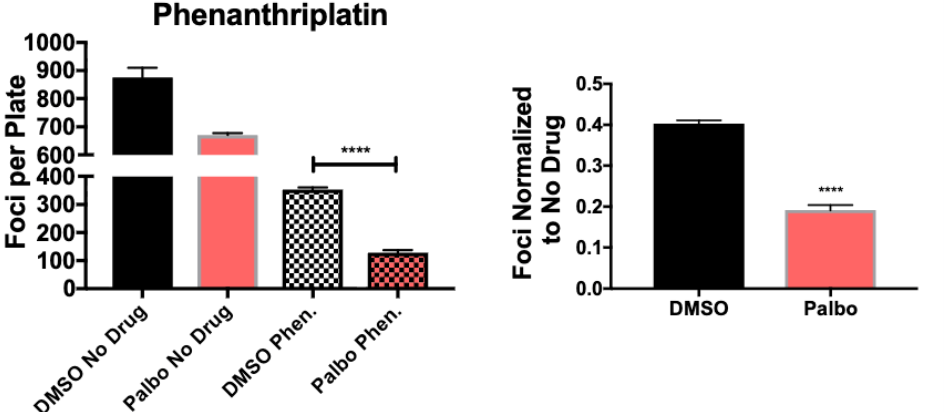
In Figure 4C, what TYPE of drug did researchers use that kills cells in G1, and what was the result?
Phenanthriplatin is a Platinum drug like Cisplatin
G1-arrested cells were more sensitive to it, showing phase-specific drug effects
Can euploid cells with G1 delays show chemotherapy resistance?
Yes, the resistance comes from slower proliferation not aneuploidy
What did the authors conclude about DNA repair in G1-delayed cells?
Resistance was not due to increased repair but to less damage formation.
What mechanism do the researchers use to generate MEFs?
Robertsonian Translocations
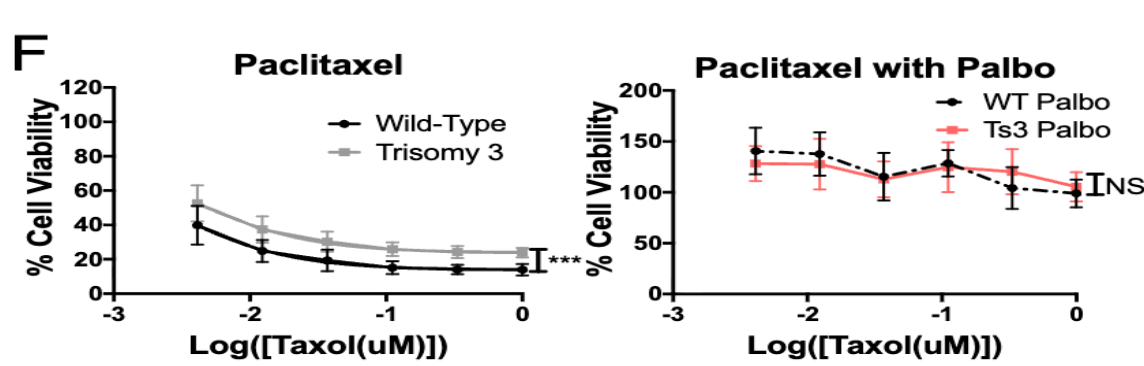
What was the main takeaway from Figure 5F?
When aneuploid and euploid cells were slowed to the same growth rate, their resistance to paclitaxel was equal, proving that resistance comes from slow proliferation
How does this study help explain why aneuploidy is linked to poor cancer prognosis even though it slows growth?
Because slow-growing aneuploid cells can better survive chemotherapy cycles, recover, and repopulate the tumor
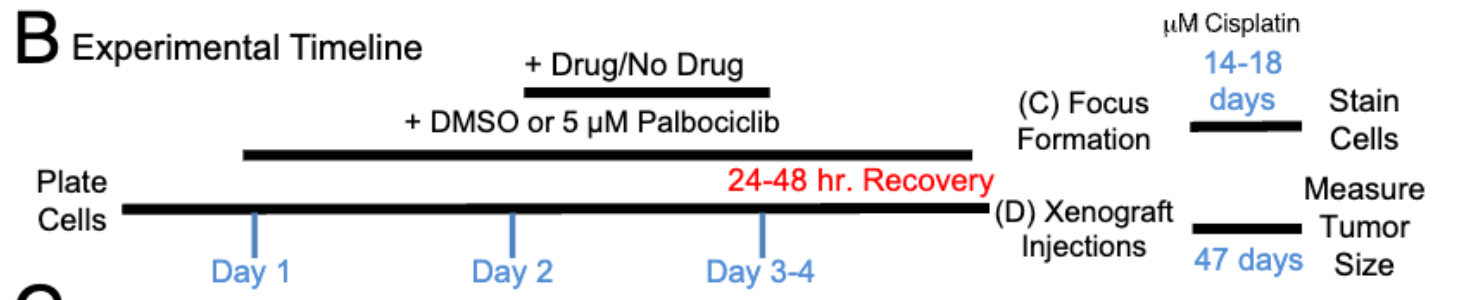 In Figure 3, what did the focus formation assay measure?
In Figure 3, what did the focus formation assay measure?
The ability of cells to survive treatment and reenter the cell cycle long-term
What types of Chemotherapeutics are Cisplatin and Paclitaxel respectively
Alkylating and Plant Alkaloid
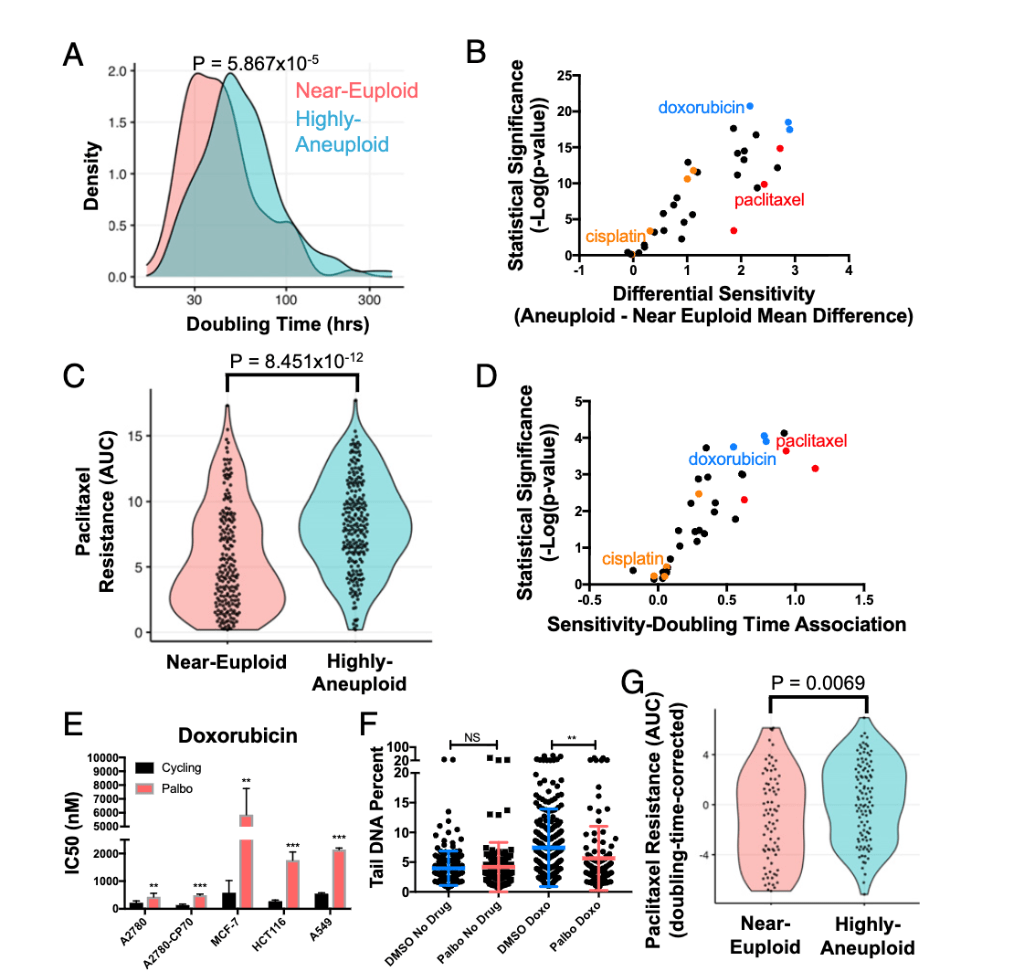 In Figure 6, the CCLE analysis, what relationship did the authors find between aneuploidy, proliferation rate, and drug response?
In Figure 6, the CCLE analysis, what relationship did the authors find between aneuploidy, proliferation rate, and drug response?
High aneuploidy and slow proliferation strongly correlated with resistance to many chemotherapies, especially those targeting cell division
What gene on chromosome 16 might explain extra resistance in Ts16 MEFs?
ERCC4, involved in nucleotide excision repair and cisplatin response
If you were a researcher continuing this project, what one new question would you ask and how would you test it?
Be Creative!