(Sanger/HGP/Etc)
(Sanger/HGP/Etc)
(Illumina/Contigs)
(Phylogenetics/genomics)
(SNPs, Odd ratios)
What is a ddNTP?
A nucleotide lacking a hydroxyl group necessary to continue strand polymerization with other nucleotides
What is the N50, conceptually?
The size of the contig at which 50% of the genome can be found in contigs greater than it in size.
Find the hamming distance between these two organisms:
Human: 5' AGGTACCTAGA 3'
Mouse: 5' CGGATGGTAGC 3'
6
Can SNPs be used as evidence for biological races?
No, since the portion of the genome accounting for differences by region only makes up around 15% of SNPs. 85% is global variation between people, meaning it's plausible for individuals even from the same region to be more different than individuals from different regions.
Green = A
Blue = T
Yellow = G
Red = C
Find the synthesized strand sequence
5' ATGGCCCTTAAG 3'
 Blue = A
Blue = A
Red = T
Green = G
Yellow = C
What is the synthesized strands sequence?
5' AATGAC 3'
What is the amino acid sequence for the following sequence of RNA:
5' CCGUGAGGAAUGGGUGUGAGUUAGUUGGGU3'
Met(start)-Gly-Val-Ser
What are the types of SNPs, and what are their significance/effect
Silent SNPs affect noncoding regions or are synonymous and still code for the original amino acid. May affect regulation or translation speed.
If non-synonymous in a coding region, can be missense (changes the amino acid) or nonsense (changes it to a stop codon).
Green = A
Blue = T
Yellow = G
Red = C
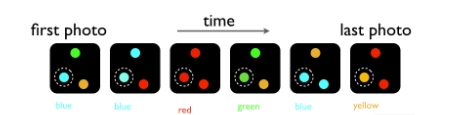
Find the template strand sequence
5' CTTAAGGGCCAT 3'
 Blue = A
Blue = A
Red = T
Green = G
Yellow = C
What is the template strands sequence?
5' GTCATT 3'
What is a realistic length of a real gene in the genome?
400+ amino acids.
Not ~20! That is the average expected length assuming random codon assembly based on a stop codons proportion of the total codon pool it makes up.
Find the odds ratio and determine if the A allele is protective, a risk factor, or no association.
Healthy Heart Disease
A 117 53
G 440 200
No association, odds ratio is 1
What is the difference between hierarchical shotgun sequencing and whole genome shotgun sequencing?
Whole genome shotgun sequencing involved fragmenting the entire genome into little pieces, and sanger sequencing each of these small fragments and aligning them together.
Hierarchical genome sequencing mapped larger fragments to chromosomes, fragmented those, and then sequenced those.
Describe pair end sequencing and why it helps with assembly of contigs
Pair end sequencing allows for techniques like scaffolding, where we have a known length of basepairs between two contigs we can use as a reference for placing other contigs. This is helpful when trying to sort out repeats. In addition, if one of the pair is found in one contig, and the other is found in another contig, then we easily overlap these two contigs
Give 3 features hinting that something may be a gene sequence.
CpG islands
Promoters
Codon preference
Intron/exon boundaries
Describe a haplotype block and why it is important in SNP products like 23 and me.
A haplotype block is a combination of nearby genotypes that tend to be inherited together. Meaning, by knowing one SNP in that area, we can potentially infer several others. This allows a sort of shortcut so you do not have to check all SNPs in the genome.
How many years would you be washing your hands if you decided to sing the entire human genome, to the tune of the 'Alphabet Song' if the song takes 20s to complete and has 26 letters.
73.18 years
How does a quality score help differentiate if a nucleotide difference is due to a sequencing error or a mutation.
Quality scores are calculated based on luminescence after addition of fluorescent bases. If its a sequencing error, it will be one base from one strand fluorescing a different color compared to all the other strands fluorescing a similar color. This will lower the quality score. A mutation in the organisms genome will be present in all fragments being sequenced, so there will be no disagreement in the fluorescence, so the quality score will be unaffected.
Describe a process used for phylogenetics, a process used for phylogenomics, and how they differ.
(Hint: Hamming distance alone is not a process, it's a tool that can be used for sequence comparisons in either process)
MSA/SuperMSA is an example gone over for phylogenetics whereas feature-frequency profile is the example gone over for phylogenomics.
MSA is "multiple sequence alignment" and involves aligning a gene or multiple genes between organisms. This is phylogenetics since it's looking and comparing a specific part of the genome. Feature-frequency profiling involves creating many combinations of 20 basepairs and seeing how many times they occur in the entirety of an organisms genome vs another. Since this is looking at the organisms whole genome, it is phylogenomics
Describe how the use of haplotype blocks can be problematic with services like 23 and me. Why isn't it fullproof?
The inferences of other SNPs based on the tag SNP are often regionally biased. It may be true for a group from European descent that a certain base at the tagSNP ensures the other SNPs will be something predictable, but that same tagSNP in another regional group may come with a different combination of SNPs at the other positions.