A good hypothesis is ____
What is falsifiable and testable ?
The amount of _________ in an atom of a specific element will always stay the same.
What are protons?
This is an example of an __________ compound.
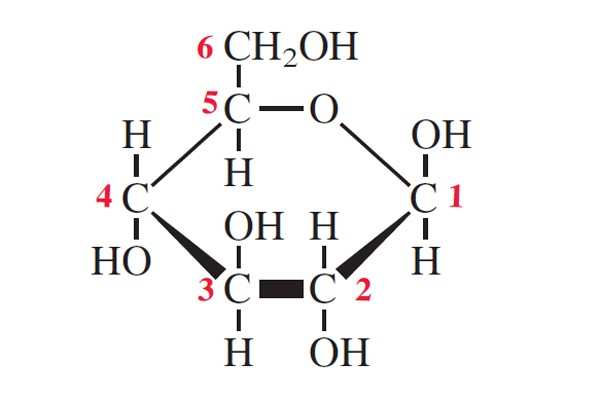
What is organic?
a bimolecular layer of lipids and proteins
what is plasma membrane?
What reaction is this ?
What is dehydration synthesis?
The emergent property at this level, in the organization of life, is a collection of two or more types of tissues.
What is the organ?
Define an isotope.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
This macromolecule has a variety of functions including: structural, enzyme, transport, etc.
What is protein?
What type of reaction is taking place?
What is Dehydration synthesis
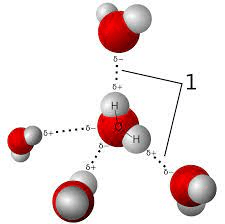
What are H-bonds
The genetic information in a bacterial cell is ___________.
What is free floating?
Fluorine will bind with__________in order to become stable.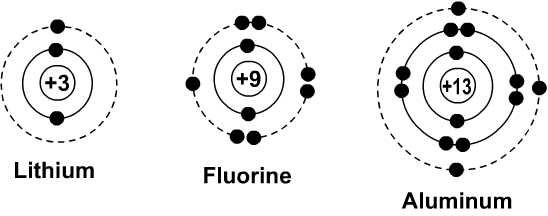
What is Lithium?
What does the structure of a polypeptide monomer include?
the structure of an amino acid has a variable R group, an amino group(NH3+), a carboxyl group(COO-), and a Hydrogen
The plasma membrane plays a dynamic role in cellular activity by...
What is regulating the movement of material in and out of the cell?
In Chapter 2, what is the primary difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
The primary difference is that ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of ions, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Properties of life include
1. Order
2. Reproduction
3.________
4. Energy processing
5. ________
6. Response to the environment
7. ________
Growth and development, Regulation, Evolutionary adaptation.
Polar Covalent bonds cause partial charges to occur because...
one of the atoms in the bond is more electronegative/electron greedy and has a stronger pull on their "shared electrons"
What are the primary differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA: double stranded, thymine pairs with adenine, stays inside the nucleus
RNA: single stranded, uracil pairs with adenine, mainly active outside the nucleus
How does structure determine function when it comes to the endoplasmic reticulum ?
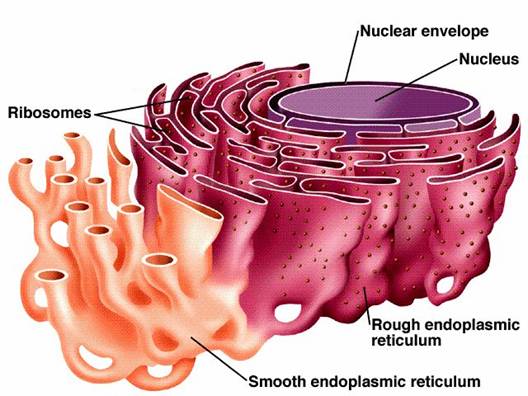
The ER is divided into the rough ER and the smooth ER. The rough ER has ribosomes that carry out protein synthesis. The smooth ER focuses on lipid synthesis and detoxification.
How does the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) change when moving down the pH scale, as discussed in Chapter 2?
When moving down the pH scale (towards lower pH values), the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) increases by a factor of 10, indicating increased acidity.
How does a Eukaryotic cell having a variety of membrane bound organelles affect its functioning
Each organelle can be specialized for a specific task, allowing the cell to seamlessly carry out a variety of different functions simultaneously. Structure determines Function!
The chemical bonds ranked from weakest to strongest are as follows:
Hydrogen bonds<Ionic bonds<Covalent bonds
A monomer of nucleic acid is called a nucleotide but a nucleotide also contains what macromolecule as part of its structure?
what is a carbohydrate? (pentose sugar)
The cytoskeleton helps organize the cell's structure and activities via these 3 different types of protein rods
What are microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments?
These are all examples of what level of protein structure?
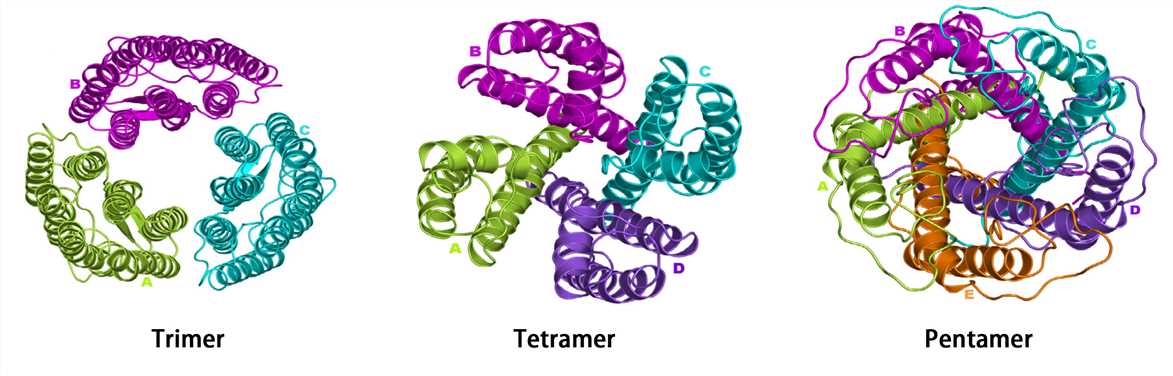
What is Quaternary structure?