At least two characteristics of life.
What are organization, using DNA, metabolism, growth, etc?
The basic unit of life.
What is the cell?
The type of subatomic particle that forms chemical bonds.
What are electrons?
At least two of the types of organic molecules.
What are carbohydrates, lipids (fats acceptable), proteins, and nucleic acids?
At least 1 component of the cell theory.
What is living organisms are made up cells, that cells are the building blocks of life, that cells come from pre-existing cells, that cells contain DNA, etc.?
The command and control center of the cell.
What is the nucleus?
The study of life.
What is Biology?
The ability to break down molecules and build up molecules.
What is metabolism?
Three levels of classification smaller than the organism.
What are chemistry, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems (variations possible)
Electronegativity.
What is the strength of an atom to pull additional electrons towards the atom?
This specific type of organic molecule (ignore numbers and letters)
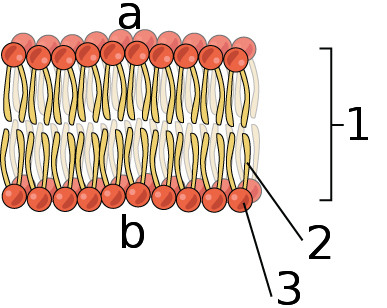
What is a phospholipid?
The reason it took so long to find and describe cells.
What is the size of cells being too small to see with the naked eye?
The part labeled D
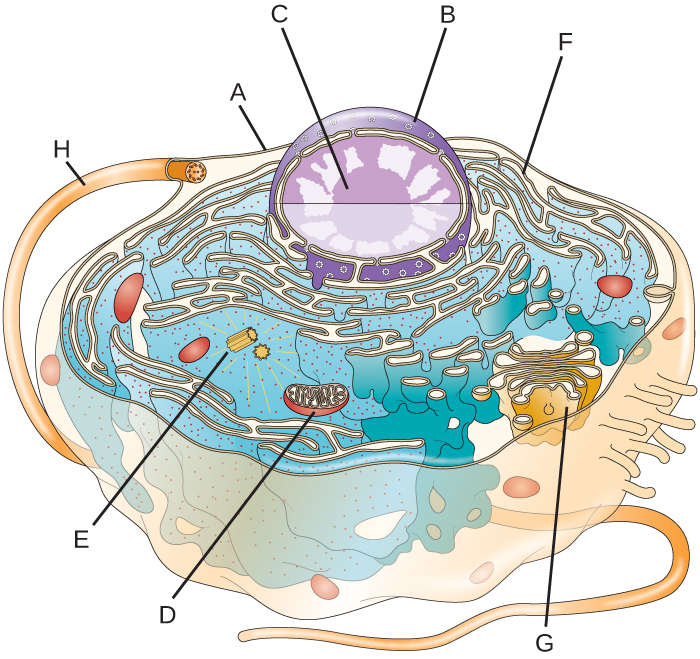
What is the mitochondria?
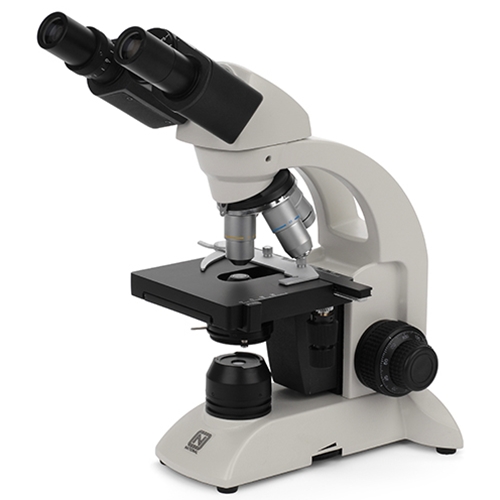
What is a compound light microscope?
1 difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
What is sexual reproduction for genetically different offspring while asexual reproduction for genetically identical offspring (other answers possible)?
1 example of how organs and organ systems work together to allow an organism to survive.
Lots of possible answers, What is that ants have an exoskeleton (organ system) and various muscles (each muscle an organ) that work together to allow ants to move to move food from the countertop or floor?
The type of bond for carbon with carbon (multiple possible answers)
What is a non- polar covalent bond (single bond for ethane, double bond for ethene and triple bond for ethyne also acceptable)?
The process used to join amino acids to make proteins (process also used for other organic molecules).
What is dehydration synthesis for proteins?
1 problem if cells are large in size with small surface area.
What is the amount of time it takes to move stuff through the cell?
The part labeled A and 1 function of the part labeled A.

What is the plasma membrane and regulate what enters or leaves the cell (other answers possible)?
Design an experiment based on the TV show Wipeout (American Ninja Warrior also acceptable) (copyrighted I'm sure!) where you also come up with a hypothesis.
So many options!
Two different ways to obtain energy and one way to break down/ use energy (various options possible)
What is photosynthesis (autotroph), eat other stuff (heterotroph) or decompose dead materials.
What is use mitochondria, break down glucose, , other terms coming up later in the semester:electron transport chain, glycolysis, respiration
The three domains and 1 identifying characteristic of each domain.
What is bacteria with the nucleoid, eukarya with the nucleus and the archaea with the nucleoid but unique structures in the cell membrane?
How water interacts with polar, electrically charged molecules.
What is the partial negative charge on oxygen attracts positive charges while the partial positively charged hydrogen attracts the negative charges?
A description of how the phospholipid bilayer forms (various answers possible).
What is the hydrophilic heads face the interior of the cell and the exterior space, both of which have water, while the hydrophobic tails hang out together in the center to be protected from water?
Two organelles present in plant cells but not in animal cells and two organelles present in both plant and animal cells.
What is chloroplasts and vacuoles only in plant cells, while mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum and nuclei are present in both?
A description of how and why antibiotic resistance emerges when a patient fails to take the full course of antibiotics (this also happens consistently with livestock)
What is the antibiotic kills off most of bacteria but does not kill off all of the resistant bacteria (they would die but are harder to kill) so when the antibiotic is removed too early the resistant bacteria have all the space in the world to make more bacteria. (other answers possible)
The definition of homeostasis and 1 specific example of how homeostasis functions in an organism.
What is maintaining internal conditions where after a meal the body releases insulin to cause glucose to be taken into cells to lower blood glucose levels back down to typical levels (other answers possible)
Emergent properties.
What is a situation where the whole is more than the sum of its parts (A key term for us)
Hydrolysis.
What is the addition of water to break a large molecule into 2 smaller molecules?
What is adenosine for the nucleotide base, tri and phosphate for the presence of 3 phosphates?
The life (or formation) cycle of a protein for the plasma membrane (simple version here, more details later in semester)
What is instructions taken from the DNA in nucleus, instructions leave nucleus to find a ribosome (or rough endoplasmic reticulum) to make the protein, protein send to Golgi apparatus for additional modifications, vesicle from the Golgi transports protein to plasma membrane and after a while the protein breaks down, is packaged into a vesicle to return to a proteosome for breakdown and recycling.
More later in the semester : )? : (?
6 steps of the scientific method in a reasonable order.
Make an observation, Ask a question, form a hypothesis, design an experiment, gather data, analyze the data, report your findings, etc.
