The smallest unit of life.
What are cells?
The two categories of cells.
What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic?
Two parts: The type of microscope we used in lab (name?) allowed us to see (living OR dead) cells.
What are: light microscope & living cells?
Chemical bonds gain, lose, and transfer this subatomic particle.
What are electrons?
This is the atomic number of the element above.
What is 6? (Carbon: 6p+)
The largest level of organization we discussed.
What is the biosphere?
The TWO places DNA is located in eukaryotic cells.
The nucleus and ribosomes.
The difference of an object/structure compared to those in the same field of view.
What is contrast?
This is the difference between an anion and a cation.
anion: a negative ion
cation: positive ion
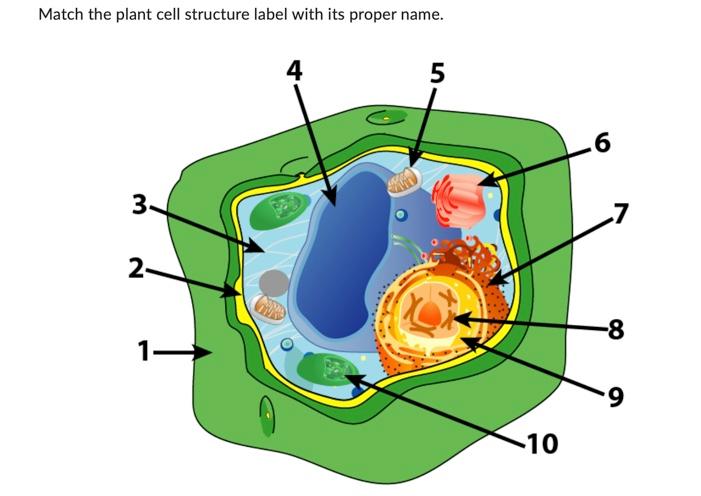
The name & function of organelle #4.
Name: Central vacuole
Function: water storage
The THREE levels of organization below an organism.
What are organ system, organs, and tissues?
This organelle is the powerhouse of the cell.
What is mitochondria?
The ability to see fine detail; a measure of clarity.
What is resolution?
The mass number of an atom with 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons.
What is 7? (add 3p+ and 4n = 7)
This is the name of organelle #5.
What is endoplasmic reticulum?
The definition of biology.
What is the scientific study of life?
These FOUR components are the same in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What are: ribosomes, DNA, cytoplasm, and cell/plasma membrane?
This type of microscopy uses specific molecules that can show different cellular components (e.g., structures, protein, organelles).
What is fluorescence microscopy?
This is the number of covalent bonds Oxygen (atomic number: 8).
What is two?
This is the name & function of organelle #6.
Name: Golgi apparatus
Function: factory - shipping, receiving, and sorting of vesicles
What are: atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere?
Name TWO tenets of the Cell Theory.
Every living organism consists of one or more cells.
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Cells are individually alive even as part of a multi-celled organism.
All living cells arise by division of preexisting cells.
Cells contain hereditary material (DNA), which they pass to their offspring during processes of reproduction.
 This image was taken with a/an ____________ microscope.
This image was taken with a/an ____________ microscope.
What is an electron microscope?
This is the definition of a hydrogen bond.
What is: a weak attractive force between a hydrogen atom and either an oxygen or nitrogen atom that are in other molecules or within the same molecule.

The type of bond shown between two elements (explain).
What is an ionic bond? This is because an electron is being transferred (stolen) from one element to a more electromagnetic element.