What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What is the primary reactant of glycolysis?
Glucose
Is the release of an electron from an electron acceptor molecule oxidation or reduction?
Oxidation
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
What does ETC stand for?
Electron Transport Chain
What are the four building blocks of life?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytoplasm
What step is Oxidative Phosphorylation in cellular respiration?
Last Step
How many ATP is produced in the Krebs Cycle?
2
In Chemiosmosis, H+ ions move down the concentration gradient. Is energy required for this process?
No
What base does RNA have that DNA does not?
Uracil
In glycolysis what is glucose converted to?
Pyruvate
What is the product of OP?
ATP
What is the first chemical reaction in cellular respiration to create ATP?
Glycolysis
What step comes after the Krebs Cycle?
Electron Transport Chain
What bond is used in Lipids?
Ester Bond
What does lysis mean in Glycolysis?
To split
Where does OP take place?
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
What is the total number of ATP produced in cellular respiration?
38
Where does the Electron Transport Chain take place?
Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria
What is this functional group?
-COOH
Carboxyl Group
What is the molecular formula for Glucose?
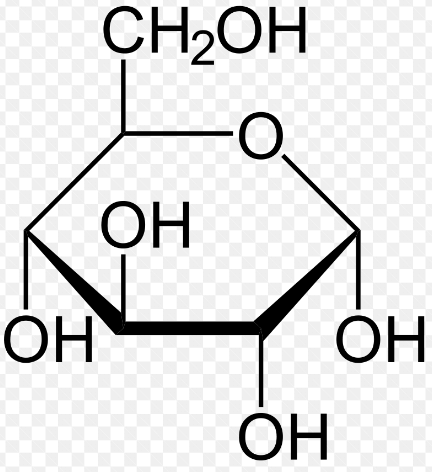
C6H12O6
What molecules carry high potential energy electrons?
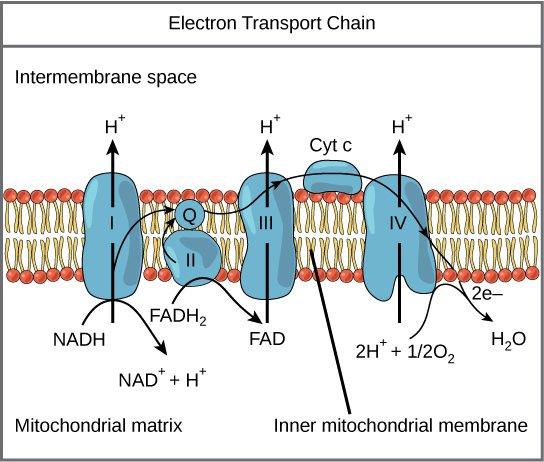
FADH2 and NADH
What are the three components of ATP
Adenine, Ribose, and 3 Phosphate Groups
What is the name of the embedded protein that provides a channel for hydrogen ions to pass through the membrane?
ATP Synthase