The term for only a subset of genes establishing a new population.
What is the founder effect?
Individuals with a particular phenotype survive to sexual maturity at higher rates than those with other phenotypes.
What is viability selection?
Genotypes have different phenotypes in different environments.
What is phenotypic plasticity?
In a two locus system, this it the multilocus genotype of a gamete
What is its haplotype?
Metabolism, reproduction, evolution, and homeostasis are all examples of this defining feature of organisms.
What are properties of life?
When divergent species mate but produce inviable or unfit offspring.
What is post-zygotic isolation?
We are currently in the 6th one of these in the history of life on earth.
What is a mass extinction?
The amount of DNA found in a cell.
What is the C-value?
Occurs when a population is more fit in its local environment than others.
What is local adaptation?
Heterozygotes have higher fitness than either homozygote.
Dapnia growing neck teeth in the presence of predators is an example of this.
What is environmental variation?
Population structure, Genetic Drift, Selection
What are processes that cause LD?
This model of multicellularity may have higher conflict because it requires independent cells to come together.
What is the Coming Together model?
Isolation, divergence, and reproductive isolation.
What are the three stages of allopatric speciation?
The northern white rhino is considered this because only two individuals, Najin and Fatu, remain alive.
What is functionally extinct?
A research approach to identify genome variation that is associated with a trait.
What is GWAS?
Inbreeding and highly structured populations can both have this genetic consequence.
What are more homozygotes than expected?
Explains why yellow elderflowers increase in fitness when rare.
What is negative frequency dependent selection?
Examples include: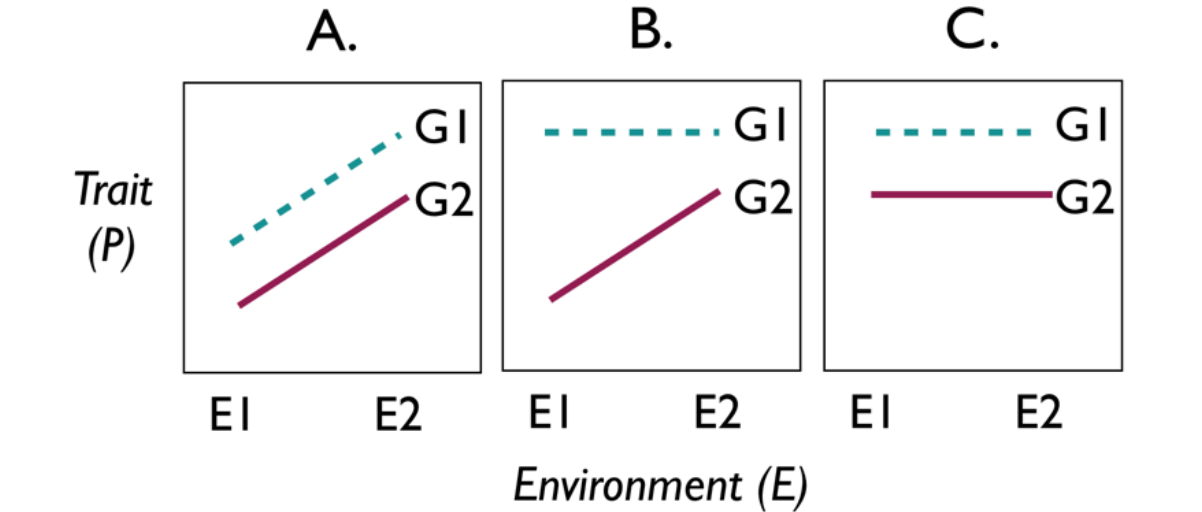
What are reaction norm plots?
The frequency of any chromosome haplotype can be calculated by multiplying the frequencies of the constituent alleles
What is a condition that must be true under LE?
This hypothesis proposes that early life relied on a single molecule capable of both storing genetic information and catalyzing chemical reactions.
What is the RNA world?
This form of speciation occurs when adjacent populations diverge despite being connected by a narrow zone of hybridization.
What is parapatric speciation?
Often caused by predation, competition, or climate change.
What is background extinction?
These organisms have large, expanded genomes.
What are multicellular eukaryotes?
Decreases in the fitness of a population resulting from mating with genetic relatives.
What is inbreeding depression?
Copies of a deleterious allele are eliminated from a population by selection at the rate they are created by mutation.
What is mutation-selection balance?
Increases the variation around a trait.
What is disruptive selection?
Recombination
What is why LD decreases over time?
This hypothesis explains how eukaryotes gained complexity.
A population of organisms that is considered distinct for purposes of conservation
What is an Evolutionary Significant Unit?
This mass extinction, also called the “Great Dying,” wiped out more than 96% of all species on Earth.t
What is the End-Permian mass extinction?
Most genes change too fast or aren’t universal, making this a challenge for tracing deep evolutionary relationships.
What is finding conserved genes across all life?
1-H_I/H_T
What is Wright's F-statistic, FIT, that shows the inbreeding of individuals relative to the total population.
Positive frequency dependent selection, selection on dominant alleles, and underdominance may result in this.
What is reduced genetic variation?
Comprised of additive and non-additive variance.
What is genetic variation?
A way to detect alleles that underwent recent selection
What is examining patterns of homozygosity?
This pair of processes—key to major transitions in evolution—explains how groups of units come together and divide labor to create new levels of biological organization.
What are aggregation and specialization?
Characterized by an interbreeding population with cohesive gene pool
What is the biological species concept?
Research shows past survival of older species doesn’t predict future extinction, because extinction is driven by this.
What is fitness in the current environment?
Genome size varies widely among species without matching organismal complexity because much of it consists of this “extra” DNA.
What is non-coding DNA?