What kind of bonds are present between water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
enzymatic proteins
defensive proteins
storage proteins
transport proteins
hormonal proteins
receptor proteins
structural proteins
contractile/motor proteins
What is an oligosaccharide?
A sugar (sacchar) of little/few (oligo)
What is the complimentary strand of the following sequence?
5'-AGCCUGA-3'
5'-UCAGGCU-3'
*This is RNA!
What does it mean for a lipid to be amphipathic? What does this imply for membranes?
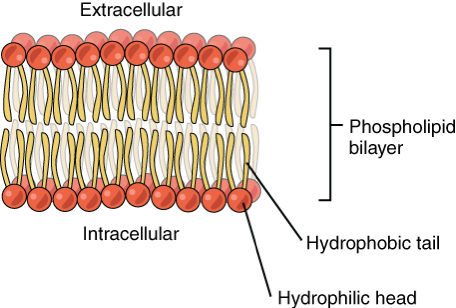 a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
hydrophilic heads are on the outside of the bilayer facing cytoplasm and outside environment
What are 2 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
1. bacteria and archaea vs everything else
2. size
3. nucleoid vs nucleus
4. complexity
What reactions synthesize and break down polymers?
 Dehydration (condensation) and hydrolysis reactions
Dehydration (condensation) and hydrolysis reactions
What are the secondary structures of proteins?
Alpha helix
Beta sheet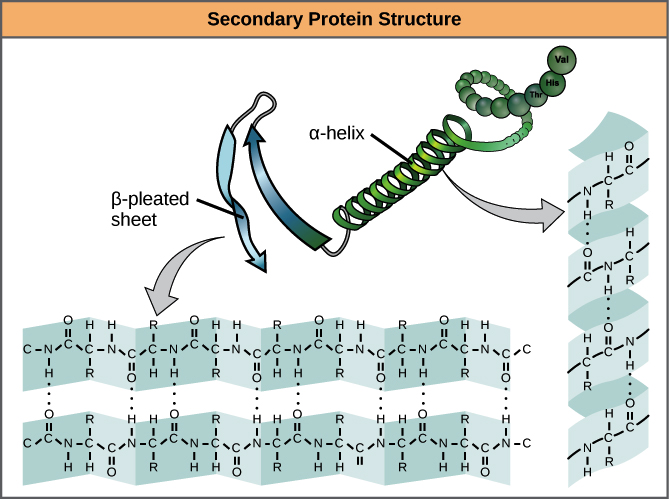
How can carbohydrates be classified?
- location of carbonyl group
- length of carbon skeleton
- arrangement around asymmetric carbons
What base pairs of DNA pair with each other? How many hydrogen bonds are between these pairs?
A-T -> 2 H-bonds
C-G -> 3 H-bonds
What is the significance of cholesterol?
Precursor for synthesis of other steroid molecules
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
- Structure: maintain cell shape, anchor cell components
- Motility: cellular movement/highways
What are the important properties of water?
1. cohesion/adhesion
2. expansion as ice
3. moderation of temperature
4. versatility as a solvent
Which environment would be most detrimental to a protein in the human bloodstream?
a. environment with a pH of 7
b. environment with glucose present
c. environment with a lot of H+ ions
d. environment with temp 35°C
c. environment with a lot of H+ ions
This is an acidic environment! Detrimental to the protein structure.
- provide carbon skeletons for complex molecules
- structural support
- energy storage
What was the discovery of Watson and Crick?
(nucleotide pairings, double helix structure)
How does soap work?
Amphipathic lipids surround the oil/dirt to form a micelle with hydrophilic heads facing the outside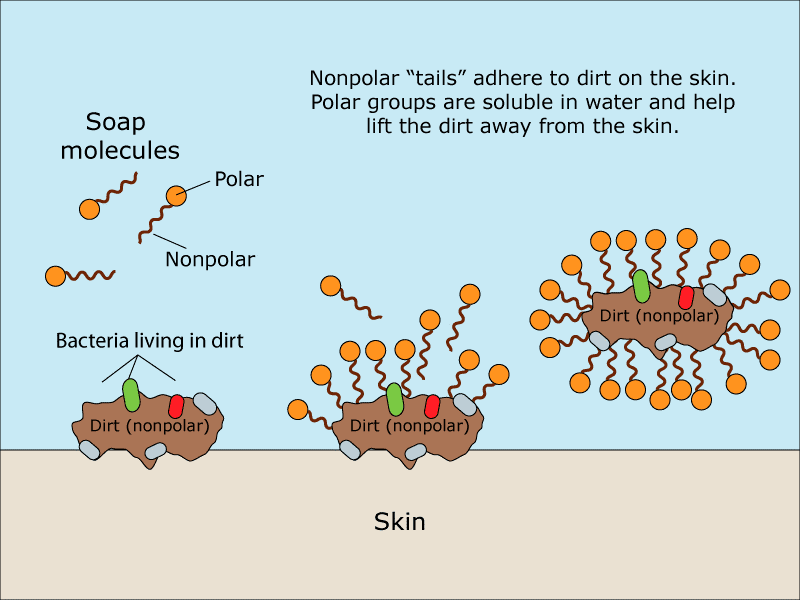
What is the function of the central vacuole in plant cells?
- store inorganic ions
- allows for large size of cell
- helps plant remain rigid
Explain the differences between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions
isotonic - environment outside the cell is the same as in the cell; there is no net movement
hypotonic - solute concentration inside the cell is greater than outside the cell; water moves into the cell
hypertonic - solute concentrations outside the cell is greater than inside the cell; water moves out of the cell 
1. transport
2. enzymatic activity
3. signal transduction
4. cell-cell recognition
5. intercellular joining
6. attachment to cytoskeleton/extracellular matrix
What is chitin?
a polymer of modified glucose molecules in the cell wall of fungi and exoskeleton of insects/crustaceans
What are the 2 types of nucleic acids and what are the monomers they are made of?
*Bonus if can describe composition of nucleotides*
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
made of nucleotides (nitrogenous base, 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group)
Would an unsaturated or saturated fatty acid be more likely to remain fluid when submerged in cold water?
Unsaturated
What organelle is considered the detoxifier of the cell?
Peroxisome
Why is carbon considered the backbone of life?
- in nearly all molecules in organisms
- has 4 valence electrons, allowing 4 different bonds -> can for complex molecules
What is an example of a disease caused by the misfolding of proteins?
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
- ALS
- Bovine spongiform encephalopathy
Why aren't starch and cellulose nutritionally equivalent?
Due to their different conformations and digestibility
Name 3 differences between RNA and DNA
T vs U
ribose has extra -OH group/is unstable
usually single stranded
RNA is used as a template for proteins/amino acids
What is the difference between a trans-fat and unsaturated fat? Why is one more unhealthy than the other?
Trans-fats are straight at the double bond, while unsaturated fats bend at the double bond
This allows for trans-fats to be compacted like saturated fats and raises your LDL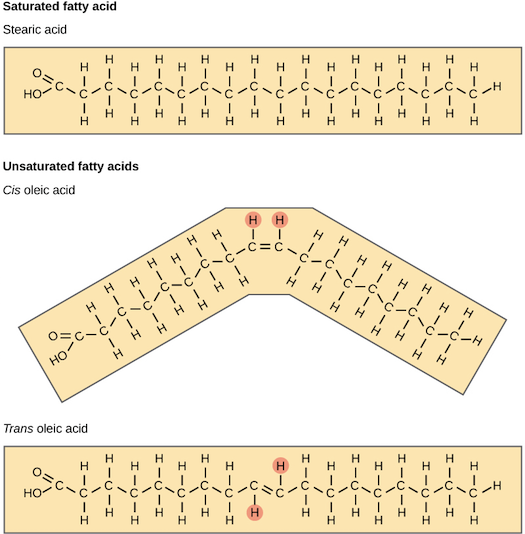
Explain the organelles involved in protein synthesis and excretion
1. Synthesis via ribosomes
2. Entrance into the rough ER
3. Modification/shipment via the Golgi