In science, this is the term for a comprehensive, broadly supported, repeatedly tested, cohesive and predictive explanation for a natural phenomenon.
What is a THEORY?
These proteins speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
What are ENZYMES?
This type of cellular division produces 2 identical cells.
What is MITOSIS?
Alternative forms of a gene for a single trait, such as red or brown tails.
What are ALLELES?

Organisms which are multicellular and photosynthetic belong to this phylum.
What are Plants or Plantae?

In an experiment, the group receiving the placebo is known as
The CONTROL group

Energy is neither created nor destroyed but can change from one form to another
This is the description of what?
What is the 1st LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS?
In stable environments, this type of reproduction is most often present.

What is Asexual Reproduction?
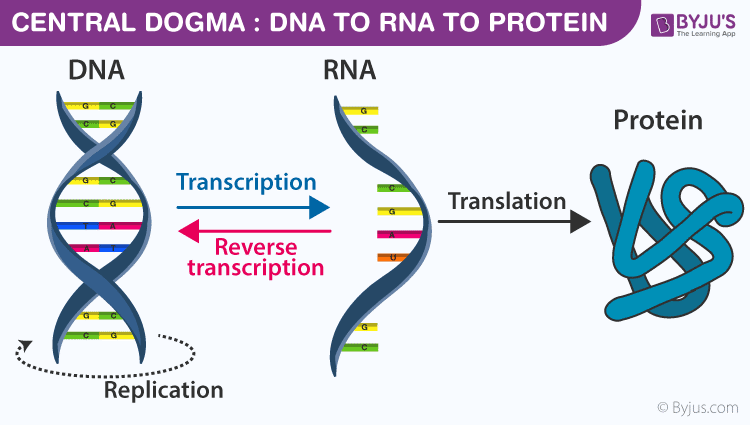
Known as the Central Dogma, this process includes the steps transcription and translation.
What is Protein Synthesis?
This type of speciation involves a geologic barrier.
What is Allopatric speciation?
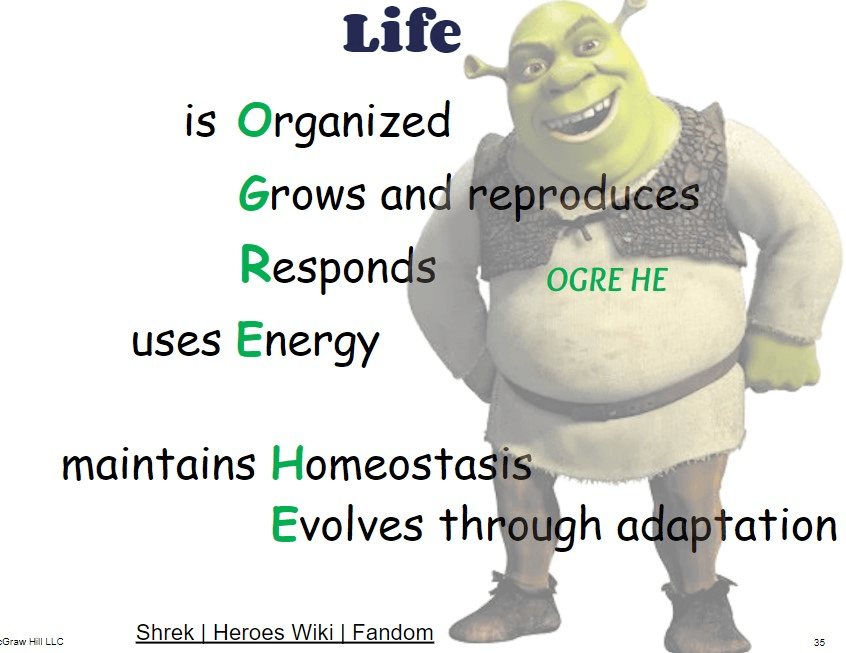
These 6 items are considered necessary for Life.
What are:
The type of reaction depicted here.
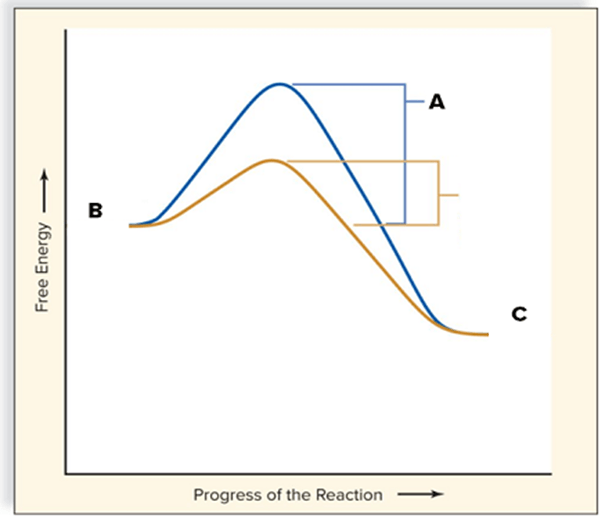
What is an EXERGONIC reaction?

This phase of cell division:

What is Metaphase?
Mutations in these cells affect the organism but not their offspring.
What are Somatic cells?
A relationship among organisms which benefits one and has no effect on the other is know as this.
What is Commensalism?
This part of the atom determines chemical interactions with other atoms (chemical bonding)
What are ELECTRONS?
This aerobic process occurs in all eukaryotes and produces ATP from biomolecules, especially glucose.
What is Cellular Respiration?
Programmed cell death, also known as this, is an essential part of normal development.
What is APOPTOSIS?
Genetic mutations resulting in all of the following codons being altered, usually resulting in non-functional proteins.
Original "PAM ATE THE BAD RED PIE"
PAM ATT ETH EBA DRE DPI E
Frameshift (specific type of insertion)
This has occurred when an organism becomes accustomed to a stimulus and over time no longer responds to the stimulus.
What is Habituation?
The correct order of classification from the most inclusive to the most exclusive from the following:
Class
Domain
Family
Genus
Kingdom
Phylum
Order
Species
Domain-Kingdom-Phylum-Class-Order-Family-Genus-Species

This is the chemical equation for Cellular Respiration
The presence of these genes promotes the cell cycle and inhibits apoptosis.
What are Proto-oncogenes?
Regulation of gene expression can occur at the Nuclear or Cytoplasmic levels. Three examples are:
Note: be able to describe
Options:
Nuclear levels:
1.Chromatin structure. (Epigenetics)
2.Transcriptional control.
3.Posttranscriptional control.
Cytoplasmic levels:
4.Translational control.
5.Posttranslational control.
This is a type of learning where an organism's behavior is paired with a stimulus.
What is Operant Conditioning?
These 5 properties make water necessary for life as we know it

1. High heat capacity and heat of evaporation
2. Good Solvent
3. Cohesion and adhesion
4. Less dense when frozen
5. Necessarily for biological reactions in cells
The increasing entropy of the universe describes this.
What is the 2nd LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS?

Aneuploidy (incorrect number of chromosomes) is the result of this process that sometimes occurs as part of sexual reproduction?
What is nondisjunction?
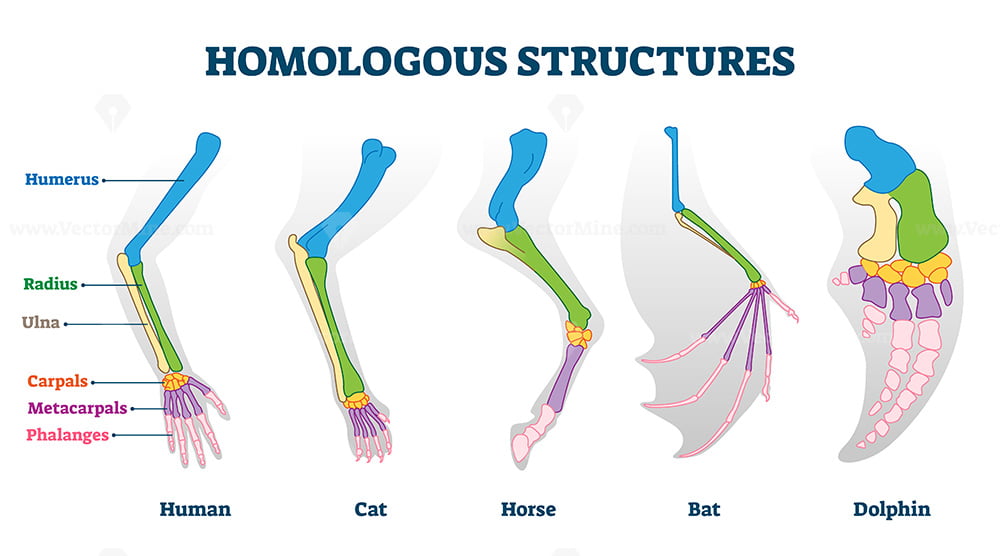
These structures have similarities in form as a result of having a shared ancestry.

What are Homologous structures? (1/2 for ancestral traits)
This type of selection favors features which improve the chances of mating. This often leads to male competition and female choice. (easy as it sounds)

What is Sexual Selection?
A group of substances helping to maintain homeostasis by having the ability to absorb (react with) excess H+ or OH- ions in a solution.
What are BUFFERS?

This is an endergonic process occurring only in specific cell types which is responsible for the conversion of photon energy to chemical energy.
What is PHOTOSYNTHESIS?

The type of inheritance represented in this pedigree.
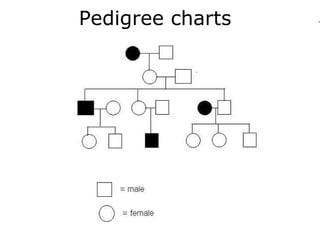
What is Recessive?
This refers to the reproductive success of an individual relative to other members of a population.
What is Fitness?
This type of mating system leads to increased parental care, especially paternal (daddy) care.
What is Monogamy?

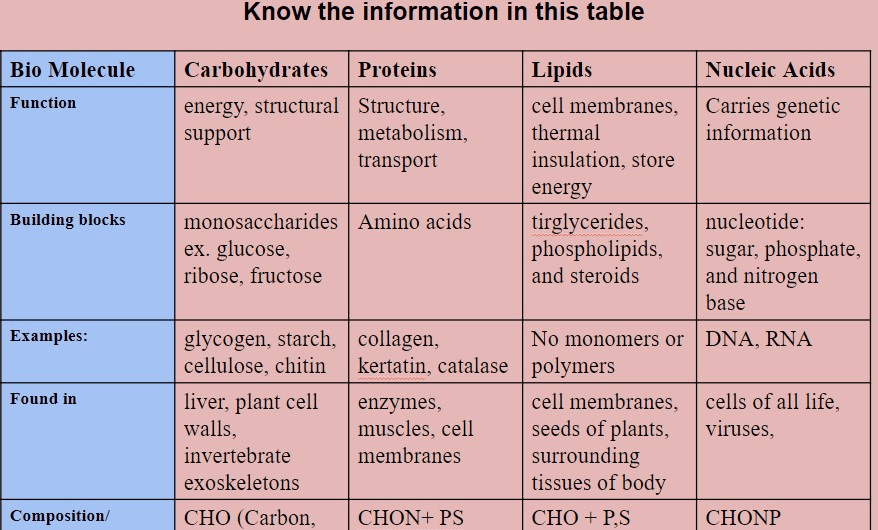
This biomolecule is characterized by being required for cellular membranes, and functions as long-term energy storage and insulation.
What are LIPIDS? (fats ok although this is a more specific term)
This is an anaerobic process, that has proved quite useful to humans, especially in the production of foods, that metabolizes glucose to either lactate or alcohol and CO2.

What is FERMENTATION?
This refers to abnormal cell growth as a result of a malfunction of the cell cycle where the abnormal cells are confined to an area and do not invade other tissues.
What are BENIGN TUMORS?
Phenotypic variation, competition for resources, and differential reproductive success are observations consistent with this type of evolutionary force.
What is Natural Selection?
These are 2 proposed biological reasons for the different reproductive behaviors of males vs. females.
What are
1. # and size of gametes
2. energy investment (pregnancy and child rearing)

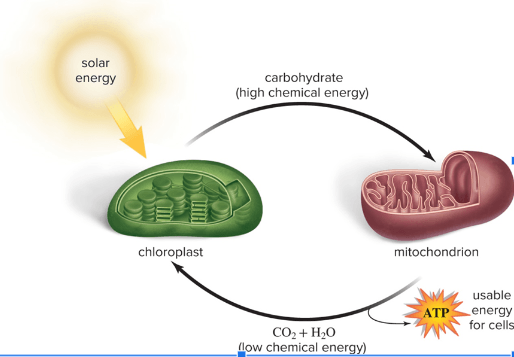
Endosymbiotic theory proposes the origins of which eukaryotic cellular components?
What are MITOCHONDRIA and CHLOROPLASTS?
Dehydration synthesis, anabolic, energy requiring, non-spontaneous reactions can be grouped under this term
What are ENDERGONIC REACTIONS?
The three main sources of genetic variation among sexually reproducing organisms.
What are CROSSING-OVER, INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT, and FERTILIZATION?
•One incidence of crossing over per chromosome =
4,951,760,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 genetically different zygotes possible.
This type of evidence for evolution
What is Biochemical?
Helping others at a cost to oneself if there is a reasonable expectation that the behavior will be paid back later.
What is Reciprocal Altruism?
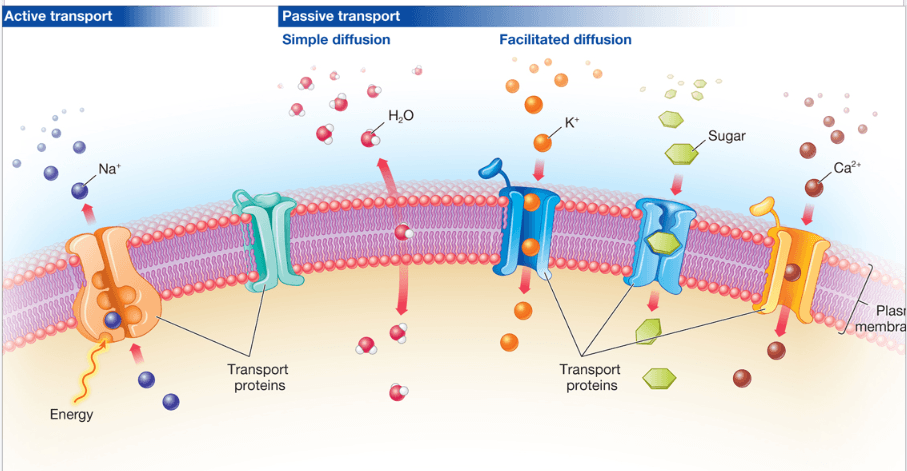
This is the term for the transportation of small to medium-sized polar molecules by proteins embedded in the cell membrane.
What is FACILITATED TRANSPORT or
FACILITATED DIFFUSION
Heating over 100 C, adding strong acids or bases or adding certain solvents can cause this in proteins.
What is to DENATURE?
If an individual with a dominant phenotype is crossed with an individual with a recessive phenotype, 4 of their 9 offspring show the recessive phenotype. This would be the genotype of the first parent. (use letter "A")
What is Aa, Heterozygous?
In a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 16% of the individuals are homozygous recessive.
This (what) is the frequency of the dominant allele.
p2+2pq+q2=1 and p+q=1
What is 0.6 or 60%?
The reproductive success of self as well as relatives which may explain seeming acts of altruism.
What is Inclusive Fitness? Kin Selection