What are four types of aquaculture systems?
•Closed – Fully contained ponds that are separate from natural bodies of water. Bioreactor
•Open – Fish held in by nets but within a natural body of water.
•Ranching – Wild fish are caught and raised up to market weight.
Hatcheries – Fish are hatched then released into the environment
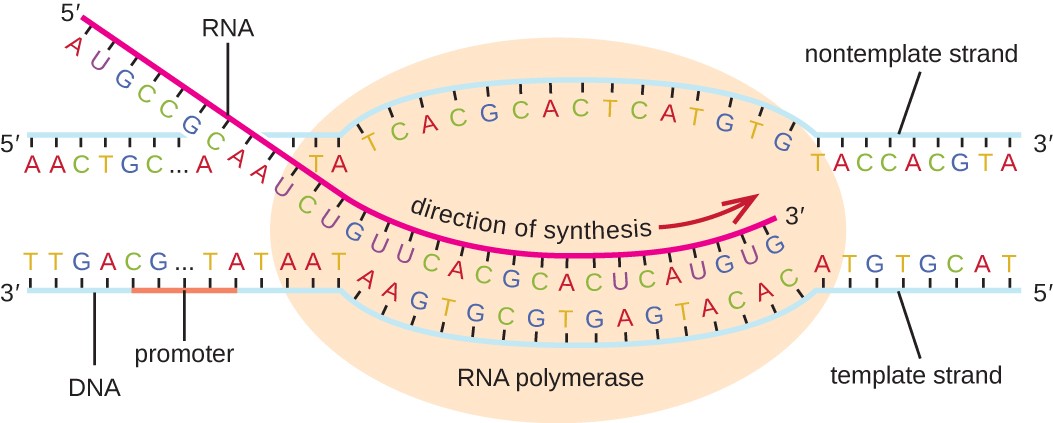
Based on the ppt slides, what is needed for a a cell to transcription in a cell?
(hint: 3 things)
-RNA polymerase
-Promoter
-Transcription Unit
Where did we acquire Taq Polymerase?
Thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus from thermal springs of Yellowstone National Park.

AUG is what type of codon?
A start codon
this type of fish farming involves farming fish and plant together where fish waste become the fertilizer for plants, works in a closed system where 99.5% of the water is recycled, and one-tenth of water is needed for growing in the ground.
Aquaponics
RNA synthesis follows the same base-pairing rules as DNA, except that ________substitutes for _________.
uracil, thymine
What should you include in a PCR reaction tube?
- Template DNA.
- DNA polymerase.
- Primers.
- Deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs)
- Buffer

What does glycerol in a sample of dna help with when deciding to run an agarose gel?
it makes the sample dense so it can sink in the wells
-Disease
-Bacteria
-Dense and crowded environments
-Water flow rates
-Waste build-up
-Large marine animals
(Complicated life cycles
Various nutrient requirements)
what is the post-transcriptional modification of the mRNA strand.
(Hint: 2 things that are added)
-A modified guanine
nucleotide added to
the 5′ end (5' cap)
-50–250 adenine
nucleotides added
to the 3′ end (poly A-tail)

List 2 examples PCR can be used for.
-Examples:
-Covid testing, genotyping, mutation detection, sequencing, microarrays, forensics, and paternity testing.
what do initiation factors do at the beginning of translation?
-they bring the large ribosomal subunit to complete the translation initiation complex

Bioluminescent fish contain these type of genes that can help us detect the presence of genes in cells, tube or organism.
Reporter Genes
Nucleotides are added to the ______ end of the
growing RNA molecule
-3'
What's unique about Quantitative PCR?
(Hint: 2 things)
-Florescent probes
-Real time method
-qPCR requires the use of fluorescent dyes or probes, while PCR does not. These probes allow you to quantify the amount of target DNA present in your sample.
-The main difference between PCR and qPCR is that qPCR is a real-time method, while PCR is not. This means that with qPCR, you can monitor the amplification of your target DNA in real-time as it is happening.
Gel green is used for what?
-non-toxic green fluorescent nucleic acid dye designed for staining DNA in agarose gels.
(A term)
___blank____ is the exploration of biodiversity for new biological resources of social and economic value.
An example of this is the use of byssal fibers from mussels can be used to make water resistant adhesive.
Bioprospecting
Accurate Translation requires two steps
1. correct match between tRNA and an amino acid done by ____ enzyme.
2. a correct match between the tRNA anticodon and a mRNA codon
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
__Blank___ is used to determine the precise order of the nucleotides in a stretch of DNA.
Most common method is....
-Sequencing
-Sanger
Sanger sequencing uses ddNTPs to stop the synthesis of DNA at random intervals. By determining the length of all the strands, the sequence can be determined.
In the termination of translation what does the release factor do?
- adds a water molecule to the A site instead of an amino acid.