What are the two types of data and what is an example of each?
Quantitative- there are 30 apples
Qualitative- the apples are crisp and red
Give an abiotic factor that can affect a biome's climate.
precipitation, temperature, humidity, soil composition, bodies of water, terrain, wind
What are density-independent factors? Give one example.
Density-independent factors affect all populations regardless of population size and density.
Examples: weather, natural disasters
What are the 3 parts of cell theory?
- all living things are made of cells
-cells are the basic structure of life
-all cells come from other cells
Draw an atom. What are the 3 subatomic particles that make up atoms? What are their charges?
Proton- positive; electron- negative; neutron- neutral/0/no charge
What is a dependent variable? What is an independent variable?
Dependent- what is observed and measured in an experiment
Independent- what we manipulate/change during an experiment to see how it effects the DV
How do greenhouse gases affect Earth's global temperature and why?
Greenhouse gases increase Earth's global temperature because they lock in thermal energy from the sun and reradiate heat.
What are density-dependent limiting factors? Give two examples.
Density-dependent limiting factors operate strongly when population density reaches a certain level. They depend on how many are in the population.
Examples: disease, competition, food, water, space, mates
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy, passive transport does not.
When we use prior knowledge to assess/understand a current situation and make a decision on how to proceed, we are making an_______.
Inference!
What do enzymes do?
Lower activation energy, speed up reactions, can be reused again.
What is the month that gets the highest amount of precipitation?
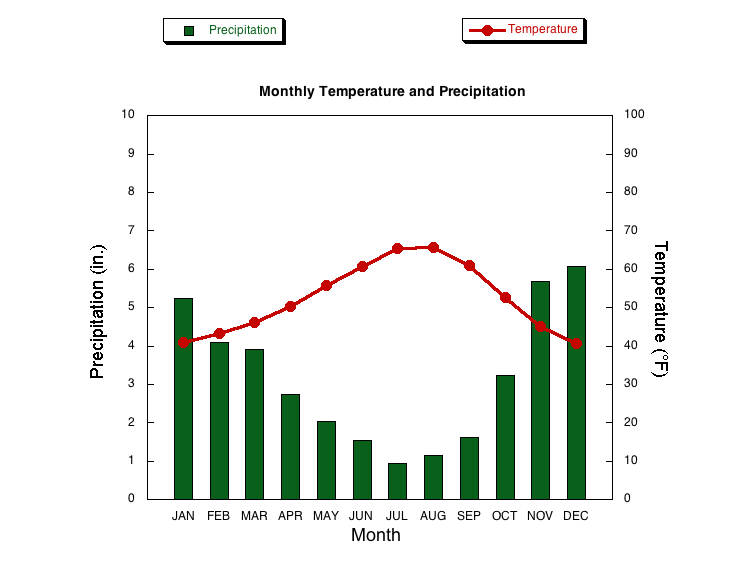
December
What causes our oceans to be more acidic?
Too much carbon in the atmosphere causes our ocean to take in carbon. Carbon causes the water to become more acidic.
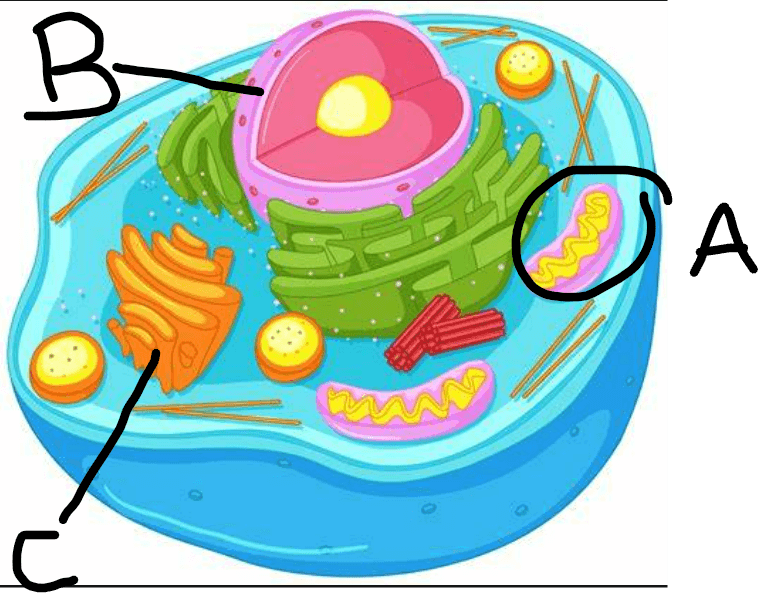 What is A, B and C?
What is A, B and C?
A= mitochondria
B= Golgi Apparatus
C= Nucleus
What is photosynthesis and how could it benefit our planet?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy. It helps take CO2 out of the atmosphere.
Acids vs. bases- which has a high pH? which has a low pH? which has a higher concentration of H+? which has a lower concentration of H+?
Acids- low pH, high concentration of H+
Bases- high pH, low concentration of H+
What are the 2 processes that primary producers use to collect energy?
chemosynthesis and photosynthesis
What is a keystone species? Give an example we discussed in class.
A keystone species plays a vital and unique role in maintaining structure, stability, and diversity in an ecosystem
Sea otters!!
Put the following terms in order from least complex to most complex:
-organ
-cell
-organ system
-tissue
Cell, tissue, organ, organ system
True or false: Two different species of earthworms are placed into a terrarium. One species survives while the other species will decrease to zero.
Bonus 100 pts: What is the principle that describes this?
True- the competitive exclusion principle
What are the three groups that make up an amino acid? Which group is different from one amino acid to another?
Carboxyl group, amino group, and the R group (this changes)
What percentage of energy is transferred to each trophic level? What happens to the rest of the energy?
10% is transferred to each level; energy can be lost as heat and used in biological processes
Describe the relationship between CFCs and the ozone layer.
Extra 100 points:
True or false- CFCs have been banned worldwide.
CFCs are harmful chemicals that break up and destroy parts of the ozone layer.
True!
Then, provide 3 differences.
- Eukaryotic cell- animal, human, plant, fungi
- Prokaryotic cell- bacteria
- Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller
- Prokaryotic cells are generally less complex
- Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus
Pancreas cells make a lot of enzymes (which are proteins). Which type of organelle makes proteins?
Ribosomes
Describe why water molecules are polar. What type of bond is in a water molecule? What type of bond is between molecules of water?
Covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen allow for electron sharing. Electrons are more attracted to oxygen due to a higher positive charge in the nucleus of oxygen. This shift in electrons causes oxygen to have a more negative charge and the hydrogens to be slightly positive.
Photic- sunlight reaches (photosynthesis can happen)
Aphotic- sunlight does not reach (photosynthesis cannot happen)
We have to dive down, use a submarine, etc.
Draw one graph that shows exponential growth.
Draw one graph that shows logistic growth.
Define carrying capacity.
Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals of a particular species that a particular environment can support
What are the two types of electron microscopes? Which one allows us to see 2D images and which allows us to see 3D images
Scanning electron microscope- 3D
Transmission electron microscope- 2D
Provide 2 similarities between plant and animal cells. Provide 2 differences between plant and animal cells.
A Venn diagram might be useful!
Similarities:
-both have a nucleus
-both have membranes
-both have vacuoles
-both have mitochondria
Differences:
-plant cells have a cell wall
-plant cells have chloroplasts
-plant cells have a large central vacuole