Its the three unique components that make up phospholipids
What are 2 fatty accids, a glycerol molecule, and a phosphate group
The name of Nucleic Acid monomers
What are Nucleotides
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
The bonds that from between Amino Acids called
What are Peptide Bonds
The names of the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides such as glucose or fructose,
Polysaccharides such as Starch, Glucose and Cellulose
What Kind of Isomers are the compounds below:

They are Stereoisomers as they contain the same number and types of atoms but have different bonding relationships. In Stereoisomers the carbon skeleton one of the elements bonds too is different, and it usually identifiable with a single bond.
The part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic, and which part of it is hydrophobic
What are the hydrophilic phosphate heads, and the hydrophobic Fatty Acids tail
The Three unique components that make up Nucleotides
What is a phosphate group, a pentose sugar (ribose/ deoxyribose) and a nitrogenous base
The monomers of proteins and the 4 components that make them up
Amino acids, which are made up of a center carbon atom, an Amino Group (NH2) on its left, a Carboxyl Group (COOH), A Hydrogen atom below, and a side chain from the top

The process of joining monomers together into Polymers called and its products.
What is Condensation or Dehydration Reactions
It creates a polymer and releases H2O.
What are the main difference between the two type of Carbonyl Functional Groups Aldehyde and Ketones when it comes to structural formula.
The difference is that Ketone (CO) has two side chains R while Aldehyde has on of its side chains replaced with a Hydrogen (H) atom.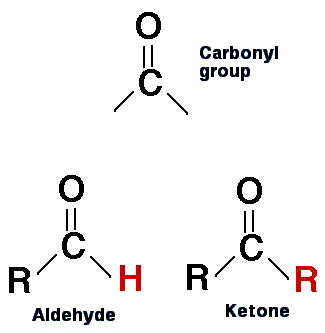
The name of the bonds that attach the hydroxyl groups of Glycerol to the Carboxyl Groups of Fatty Acids.
What are Ester bonds

The two categories of Nitrogenous Bases and the bases that make them up
Double ring nitrogenous bases are Purine Bases.
They are made up of Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Single ring nitrogenous bases are Pyrimidine Bases.
They are made up of Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T)
Note: In RNA Thymine is replaced by Uracil (U)
What are primary, secondary, tertiary and Quaternary structures
Which of the following process aren't an example of a condensation Reaction:
The formation of ester bonds
The formation of peptide bonds,
The formation of sucrose from glucose and fructose
The Formation of Glycerol and Fatty acids from Triglycerides
The formation of Glycerol and fatty acids from Triglycerides is an example of Hydrolysis where a polymer (Triglycerides) are broken down into two or more monomers (Glycerol and Fatty Acids)
What is its general pH considered?
It is generally acidic and forms peptide bonds
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carboxylgroup-56a129e15f9b58b7d0bca5e9.jpg)
The difference that defines whether a Fatty Acid is Unsaturated or Saturated
Fatty acids with only single bonds are Saturated, and those with some double bonds are Unsaturated.
If a Strand of DNA has 20% Adenine, how much Guanine does it have?
There has to be an equal amount of Adenine to Thymine, so that uses 40%, leaving 60% for Guanine and Cytosine. Those must also be equal to each other, so There is 30% Guanine in the strand.
The 7 Major Categories of Proteins and their Functions
1. Gene Expression and Regulation Proteins (Self Explanatory)
2. Motor Proteins: Initiate movement like those in our muscles
3. Defense Proteins: Protects from Disease like our immune system.
4. Metabolic Proteins: Increases rate of Chemical reactions.
5. Cell-Signaling Proteins: Enable communication and with cells and their environment.
6. Structural proteins: Supports and Strengthens structures
7. Transport Proteins: Promote movements of solutes throughout membranes.
Which of the Following is considered a dimer?
1. Ribose
2. Proteins
3. Lactose
4. Nucleotides
3. Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the two monosaccharides Glucose and Galactose
What makes up the Primary structure of Proteins
The primary structure of proteins is the linear chain of Amino Acids joined together by covalent Peptide bonds.

What is the general structure of Steroids (Lipid)
The 4 carbon bonded rings with Hydroxyl scattered within
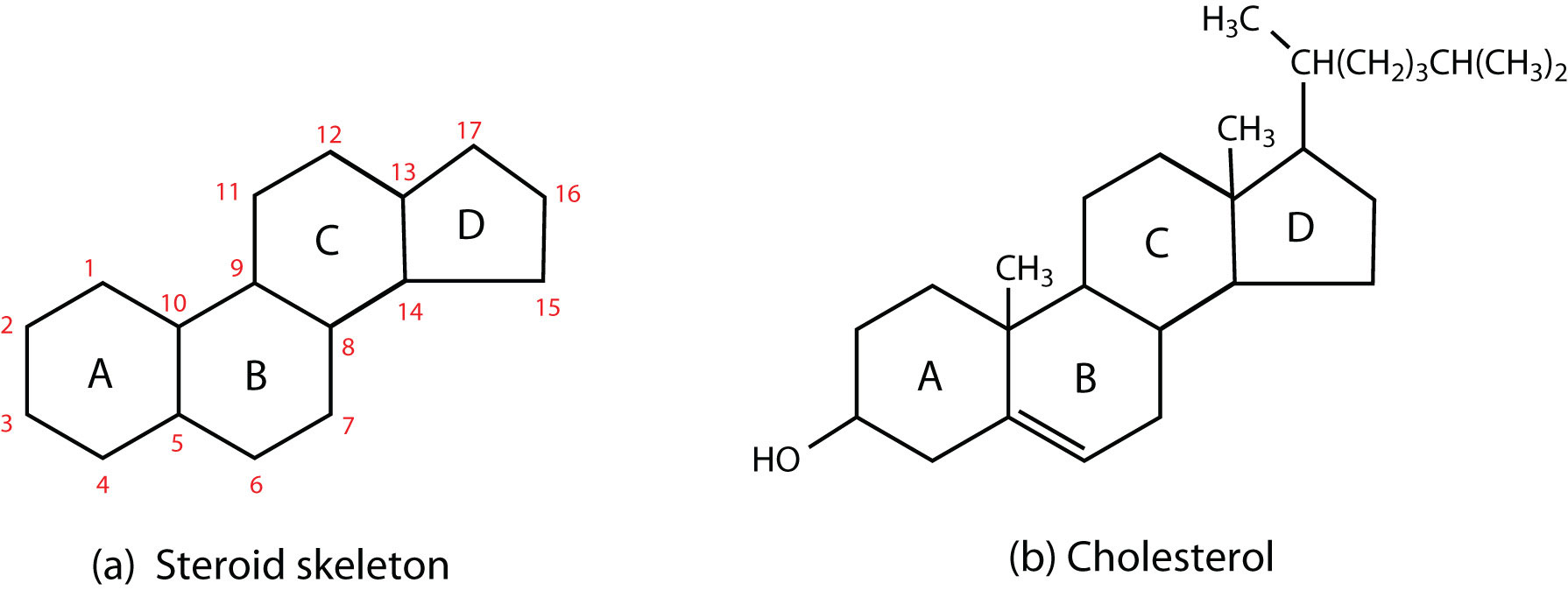
WARNING DIFFICULT QUESTION
What Types of Nitrogenous Bases can bond with each other, and what kind of bond do they form?
 Adenine bonds with Thymine/Uracil, and Guanine bonds with Cytosine
Adenine bonds with Thymine/Uracil, and Guanine bonds with Cytosine
Hydrogen Bonds join the bases together, while covalent bonds between the phosphate group of Nucleotides make up a DNA/RNA strand
WARNING DIFFICULT QUESTION
The 5 Factors that can effect Protein Structure
Hydrogen Bonds: Essential in determining secondary structures.
Ionic Bonds: Essential for Tertiary and Quaternary structures.
Hydrophobic Effects: Essential for Tertiary and Quaternary structure as amino acids avoid water
Van Der Waals Dispersion: Weak attractions among molecules that can repel for Tertiary and Quaternary.
Disulfide Bridges: Covalent Sulfhydryl bonds that form between amino acids for stability.

WARNING HARD QUESTION
When we chew a piece of bread for a while, (about a min) the flavor will begin to turn sweet, with the information you know about carbohydrates and the enzymes in our saliva, why do you suppose that is?
As we chew and the saliva covers the bread, it begins to break down the polysaccharide called starch in the bread into glucose, a sweet tasting simple sugar. This process is also known as Hydrolysis.
The two distinguishable shapes formed by the Secondary Structure of Proteins
What is the ⍺-Helix and the β-Pleated sheet