Short-term, immediate energy.
What are carbohydrates?
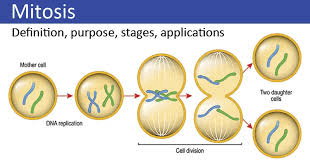
First phase of mitosis, chromosomes condensed.
What is prophase?
The purpose for mitosis.
The purpose for meiosis.
What is create identical cells to replace old, damage cells, or growth?
What is create reproductive cells?
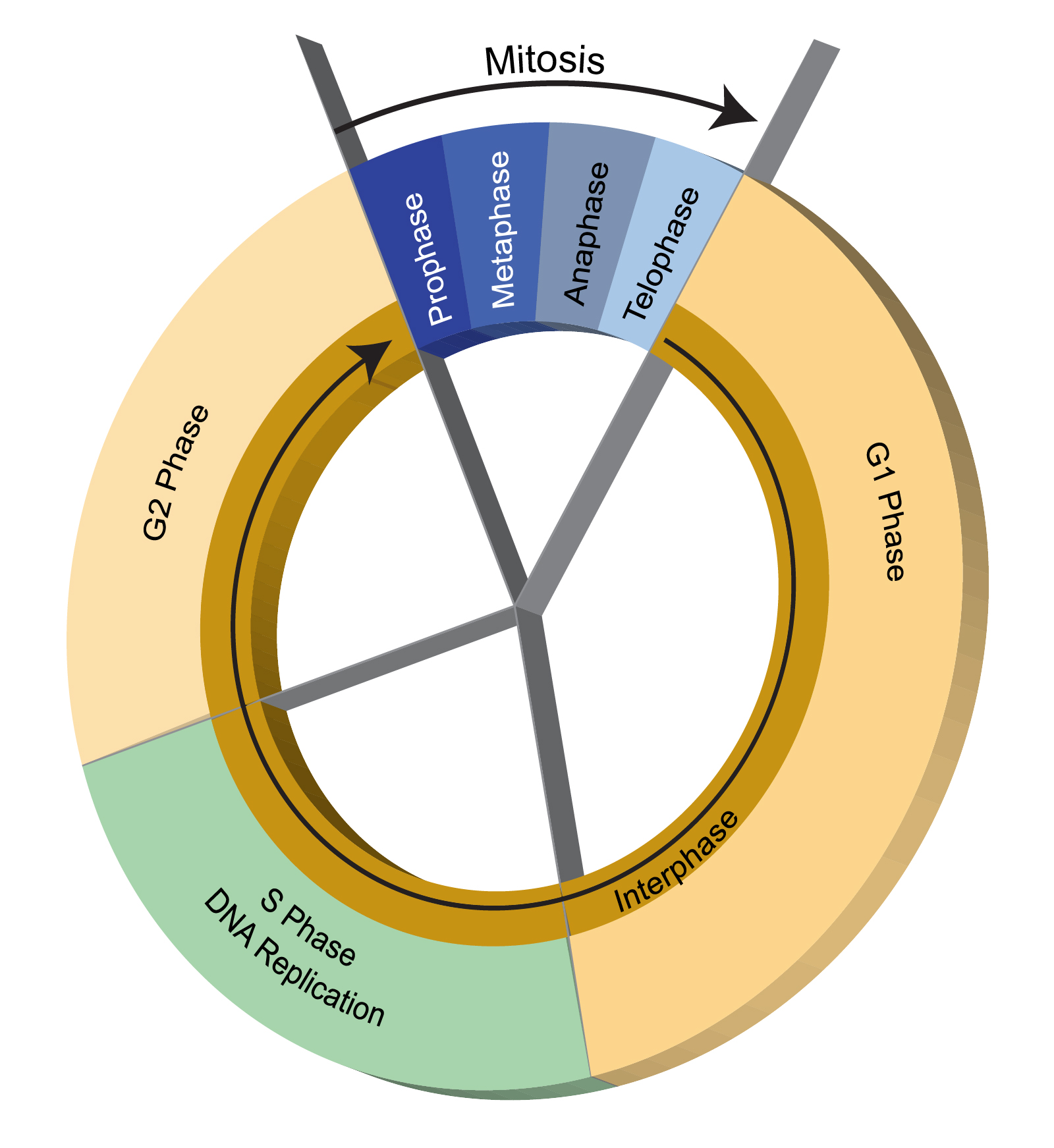
The longest part of the cell cycle, where most cell activity takes place.
What is interphase?
DNA/chromosomes are located in the _____________ of the cell.
What is the nucleus?
In RNA,
__________pairs with __________,
__________pairs with __________,
What is cytosine & guanine, adenine & uracil?
Made up of long chains of amino acids.
What are proteins?

Second phase of mitosis, chromosomes line up in middle of cell.
What is metaphase?
Cells creates in mitosis are called ____________ cells.
Cells created in meiosis are called ______________.
What is daughter, gametes?

The phase where cell growth occurs.
What is G1?
In DNA,
_____ pairs with _______
_____ pairs with _______
What is adenine & thymine, cytosine and guanine?
1st step in the protein synthesis, takes place in the nucleus
What is transcription?
Long-term energy storage (think polar bear hibernating), also makes up cell membranes.
What are lipids?

Third phase of mitosis, chromosomes separate, move away from each other towards poles of cells.
What is Anaphase?
Occurs in meiosis, genetic material is swapped between paired chromosomes.
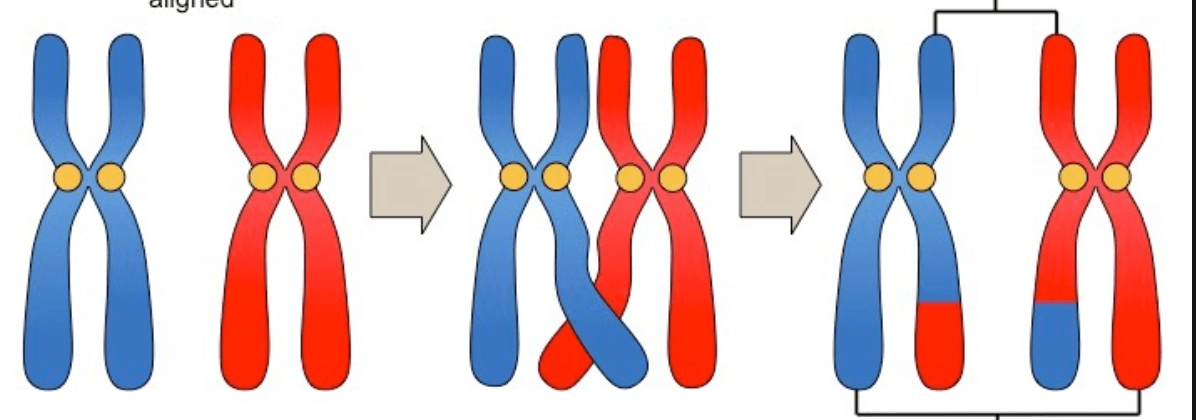
What is crossing over?

The phase where DNA is replicated (synthesized)..
What is S phase?
Examples of Point mutations.
What is substitution, deletion, insertion?
Transcription makes _________________ from a strand/segment of _____________
What is mRNA, DNA?
Stores genetic information.
What are nucleic acids?

Fourth phase of mitosis, nuclear envelope starts forming, cytoplasm starts dividing.
What is Telophase?
Meiosis creates 4 _____________ cells with ____________ number of chromosomes.
What is non-identical (or reproductive), haploid (n)?

The phase where more cell growth and preparation for cell division occurs.
What is G2 phase?
Mutations that do not cause any change in the protein.
What is silent mutations?
The second step in the process is called ________________ and takes place on the ___________________________
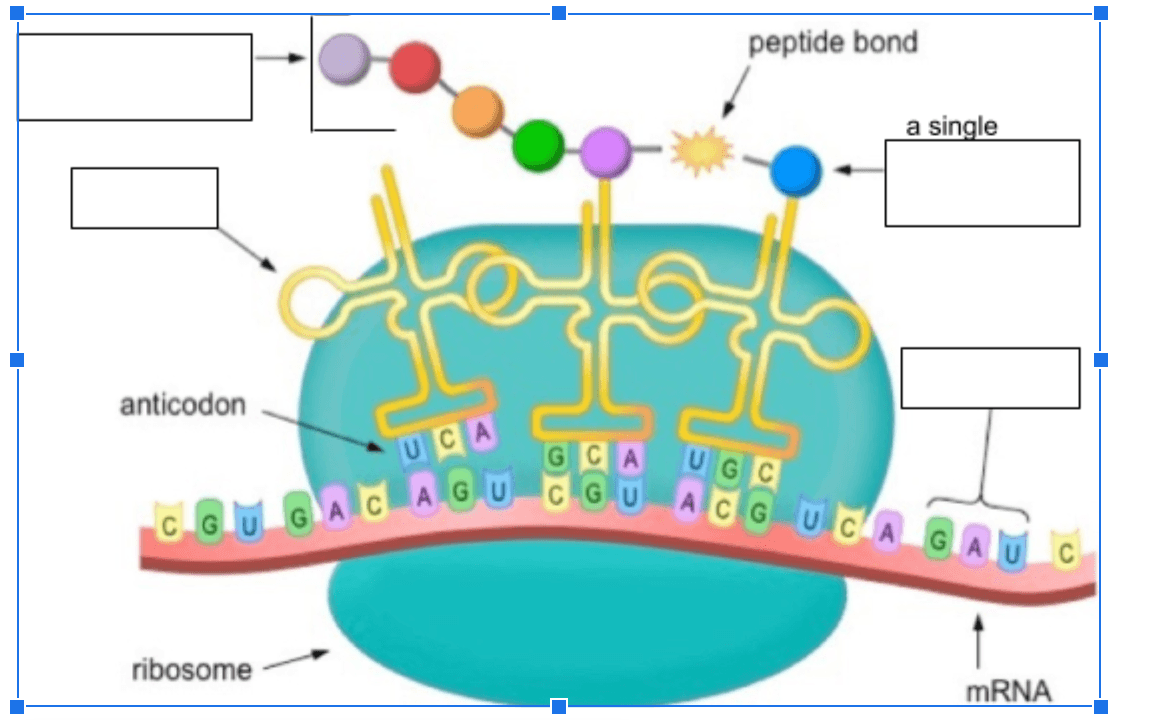
What is translation, ribosome?
Monosaccharides, Amino acids, Nucleotides.
What are monomers?

Occurs after mitosis, cells divide.
What is Cytokinesis?
Mitosis creates ___ (number) cells.
Meiosis creates ___ (number) cells.
What is 2,4?

The phase where cell division occurs.
What is mitosis/meiosis/cytokinesis?
True/False
Substitution mutations are always harmful.
What is false?
______________ brings ___________ __________ (a monomer) to the mRNA
What are tRNA, amino acids?
The 2 sides of a DNA molecule are made up of a _______________ ________________ backbone.
The rungs are made of _________________ bases.
What is sugar-phosphate. nitrogen/nitrogenous?
Mitosis creates _______________ cells with the _____________ number of chromosomes.
What is identical, diploid?
When fertilization occurs, the sperm and egg create a ____________.
What is a zygote?
The phase after cell division (mitosis/meiosis/cytokinesis).
What is interphase?
True/false:
Frameshift mutations are usually serious.
What is true?
The end product of protein synthesis.
What is a protein?