What is variation in a species?
Variation refers to the differences in characteristics (phenotypes) between individuals of the same species.
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is the process where organisms with characteristics better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to the next generation.
What is a producer in a food chain?
A producer is an organism, usually a plant or algae, that makes its own food through photosynthesis, forming the base of a food chain.
What is the main source of energy for biological systems?
The Sun is the main source of energy for biological systems.
What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species, genes, and ecosystems in a given area.
Give one example of continuous variation in animals.
Body length in animals such as humans is an example of continuous variation, where individuals can have a range of lengths.
Give an example of artificial selection in domesticated animals.
Dog breeding is an example of artificial selection, where humans select dogs with desirable traits (e.g., size, coat color) to breed and produce offspring with those traits.
Define a herbivore and give an example.
A herbivore is an organism that feeds on plants. An example is a Vegan (ew)
Which process in the carbon cycle removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, as plants use it to make glucose.
Give one reason why an ecosystem may be destroyed.
An ecosystem may be destroyed due to habitat destruction caused by human activities, such as deforestation or urbanization.
What is the difference between continuous and discontinuous variation?
Continuous variation shows a range of differences (e.g., height, skin color) with no clear cut-off points, while discontinuous variation shows distinct categories (e.g., blood type, gender).
How does natural selection lead to the adaptation of organisms in their environment?
Natural selection leads to adaptation by favoring individuals with traits that increase their chances of survival and reproduction in their specific environment. Over time, these traits become more common in the population.
What are the trophic levels in a food chain, and where would you place a lion that eats bokke?
1st level: Producers (e.g., plants)
2nd level: Primary consumers (herbivores, e.g., bokke, zebras, deer)
3rd level: Secondary consumers (carnivores, e.g., lions)
The lion would be placed at the secondary consumer level.
Explain how the combustion of fossil fuels contributes to the carbon cycle.
The combustion of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as carbon stored in the fuels is oxidized, contributing to the carbon cycle and increasing greenhouse gases.
How can overharvesting of species lead to extinction?
Overharvesting can reduce the population of a species to critically low levels, preventing the species from reproducing and leading to extinction.
How do mutations contribute to genetic variation?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can create new alleles. These new alleles can introduce genetic variation within a population.
Explain why organisms that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to reproduce.
Organisms with traits that help them survive (e.g., better camouflage, faster movement) are more likely to find food, avoid predators, and reproduce, passing their advantageous traits on to the next generation.
Why is energy transfer between trophic levels not 100% efficient?
Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient because much of the energy is lost as heat during metabolic processes (e.g., movement, digestion), and not all parts of the organism are consumed or digested.
How does human activity affect the carbon cycle and contribute to climate change?
Human activities like deforestation, burning fossil fuels, and industrial processes release excessive amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, which enhance the greenhouse effect and contribute to global warming and climate change.
What is the role of seed banks in conserving plant species?
Seed banks store seeds of plant species for future use, ensuring that genetic material is preserved and can be used to replant species that are threatened or have become extinct in the wild.
Describe how a mutation could lead to the formation of a new allele in a population and explain its potential effect on the phenotype of an individual.
A mutation changes the DNA sequence in a gene. This can result in a new allele, which may produce a different protein, leading to a change in the phenotype. For example, a mutation in a gene for eye color might cause an individual to have a different eye color than others in the population. If the mutation offers an advantage (e.g., improved camouflage), individuals with the new allele may have a better chance of survival and reproduction.
Describe the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria through natural selection and explain how human actions have influenced this process.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria develop through natural selection when random mutations produce bacteria that can survive exposure to antibiotics. When humans overuse antibiotics, especially in agriculture and medicine, it creates an environment where only the resistant bacteria survive. These bacteria reproduce and pass on their resistance, leading to a population of antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are harder to treat.
Using a food web, explain the impact of overharvesting and introducing foreign species on the balance of the ecosystem. Give an Example.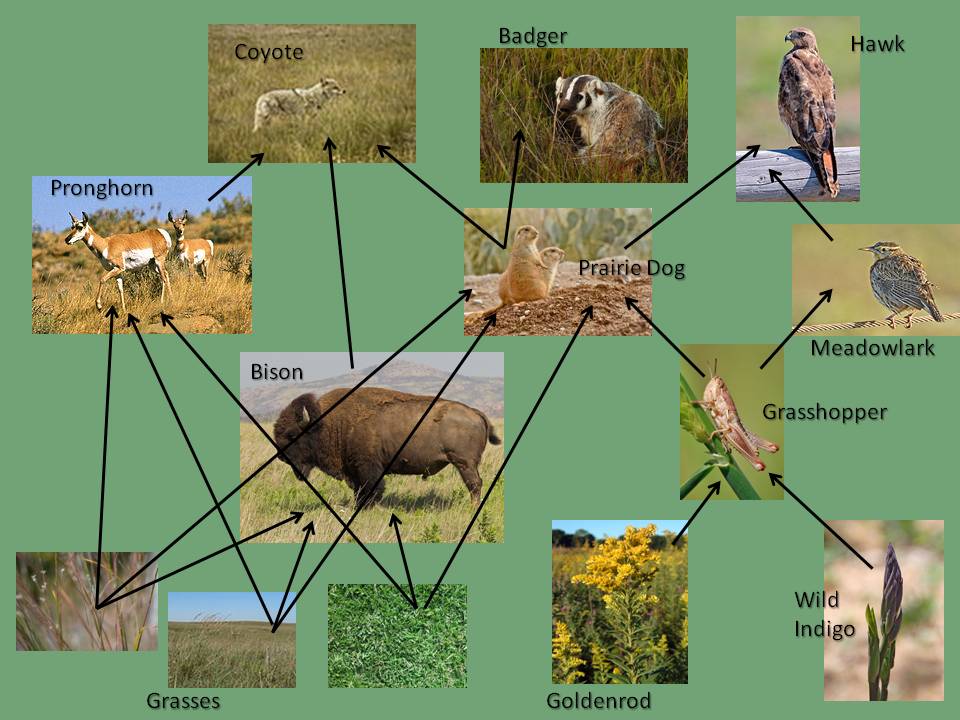
Overharvesting can reduce the population of a species, causing imbalances in the food web.
Example, if predators are overharvested, the population of their prey may increase uncontrollably. Introducing foreign species can disrupt the balance by introducing new competitors or predators, leading to the decline of native species. Invasive species may outcompete or prey on native species, altering the structure of the food web.
Explain the role of decomposition in the carbon cycle, and describe how deforestation can disturb this cycle and exacerbate climate change.
Decomposition breaks down dead organic matter, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. Deforestation disrupts this cycle by removing trees that absorb carbon dioxide, reducing the ability of the environment to store carbon, and increasing atmospheric CO2 levels, exacerbating climate change.
Describe how the introduction of an invasive species can lead to the destruction of a native ecosystem, and provide an example.
Invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, prey on native species, or introduce diseases. For example, the introduction of the zebra mussel to North American lakes disrupted local ecosystems by outcompeting native mussels for food and space, leading to a decline in native biodiversity.