What type of succession is occurring?
primary succession
What 3 things do plant cells have that animals cells do not?
chloroplast, cell wall, large vacuole
Photosynthesis occurs in the _____, while cellular respiration occurs in the _____.
chloroplast, mitochondria
Interphase
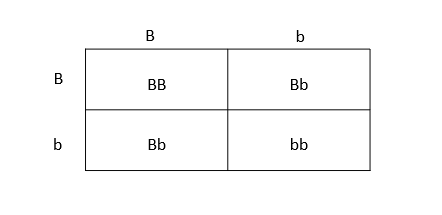
Black fur is dominant to white fur in guinea pigs. Create a Punnett square for two heterozygous guinea pigs.
Which organism would be most affected by the decline in grains? Why?

mice, because it is their only source of food
How are prokaryotes different from eukaryotes?
They do not have a nucleus.
Adding light to a plant _____ the rate of photosynthesis.
increases
What occurs during the S phase?
synthesis/replication of DNA
What is the replicated DNA sequence for TTA ATC CCA?
AAT TAG GGT
What are invasive species and how do they affect ecosystems?
nonnative species with no predators that disrupt the ecosystem
List the components of the cell theory.
The cell is the basic unit of life.
Living things are made up of one or more cells.
All cells come from preexisting cells.
What product of photosynthesis is used as a reactant in cellular respiration?
glucose
Cancer is defined as _____.
uncontrolled cell division/mitosis
What is the mRNA sequence transcribed from the DNA segment ACT CGG ATC?
UGA GCC UAG
How do dead organisms affect the carbon cycle?
Dead organisms release CO2 back into the atmosphere.
Name the type of macromolecule.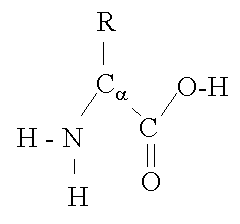
Protein
Which tubes has organisms that undergo cellular respiration?
2, 3, 4
Name the steps of Mitosis and what occurs.
P - prophase, condensing of DNA
M - metaphase, move towards the middle
A - anaphase, chromosomes separate
T - telophase, DNA decondenses, cell begins to separate
Blood types are an example of what type of inheritance?
Codominance/Multiple Alleles
Define and give an example of each:
Producers
Consumers
Decomposers
producers - autotrophic organisms, plants
consumers - heterotrophic organisms, animals
decomposers - organisms that break down dead organisms, bacteria
Define, give an example, and list the monomer for each:
Carbohydrates
Nucleic Acids
Lipids
Proteins
C - main energy source, sugar, monosaccharides
L - energy storage, fats, fatty acids
N - genetic material, DNA, nucleotides
P - structure and function, enzymes, amino acids
During exercise, this type of cellular respiration occurs and results in _____.
lactic acid fermentation, lactic acid
When does crossing over occur and what does it result in?
Meiosis I - Prophase I, increased genetic diversity
What are stem cells and how are they harvested?
Totipotent cells that can differentiate into any type of cell. They are taken from embryos.
Which level has the most energy? What happens as energy is transferred to the next level?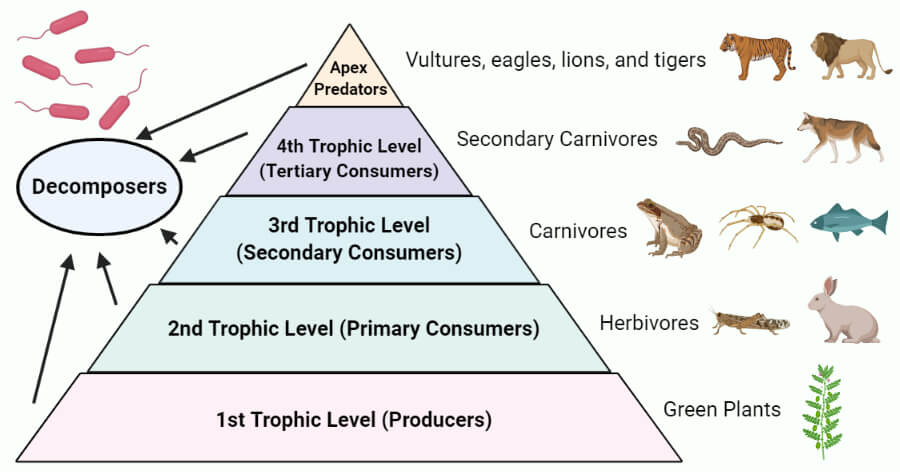
1st trophic level (producers), only 10% is passed on
Name the structure, what is is made of, and identify the purple structure.
cell membrane, phospholipids, protein
Explain how ATP releases energy.
By breaking the last phosphate bond.
Define diploid and haploid.
2n = full set, somatic cells
n = half set, gametes
How does DNA code for proteins?
DNA is transcribed into an mRNA that codes for amino acids through translation.
If producers start with 4000J, how much energy would be in the third trophic level?
40J
Explain the Miller-Urey experiment.
An experiment that mimicked early Earth by heating up water, adding a mixture of gases, and running a current through them, resulting in traces of amino acids.
Name the process, reactants, and products.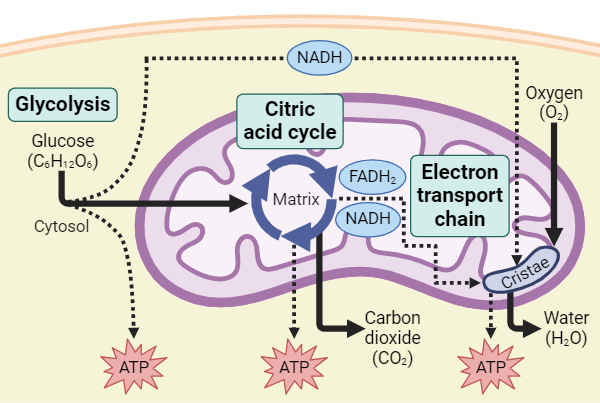
cellular respiration
glucose, O2
CO2, H2O, ATP
This is a result of which process?
Meiosis
How do transgenes help with diabetic patients?
Insulin gene is inserted into bacteria and then harvested to prescribe to patients.