Primary Succession always starts with this form of substrate or ground cover
Rock
This is the starting energy source that producers use
What is sunlight?
The maximum number of individuals that can be supported in an ecosystem with a defined amount of resources
What is carrying capacity?
Name and give an example of this type of factor: Not alive and never was alive.
Abiotic Factor: Examples include water, nutrients, CO2, rock, sun, heat, climate, etc...
This pyramid is correctly displaying what rule?
What is the 10% rule?
This form of succession can take hundreds of years or longer
Primary succession
This term refers to organisms that only eat herbivores (and sometime plants in addition)
Secondary Consumer
Competition and predation are examples of this type of limiting factor
What is density dependent?
This is another term for producers/plants and means that the organism can make its own food
What is an autotroph?
When organisms have a set amount of food, we see this type of population growth
What is logistic growth?
Name 2 different events that would lead to secondary succession
Forest fires or clear cutting/deforestation
(Both remove mature plants from an environment leaving soil/dirt/ ash behind )
This is the amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to another
What is 10%?
Give an example of a Density Independent limiting factor
Natural Disaster (like forest fire, earthquake, flood, etc...) or seasonal changes
This is the ecological hierarchy from smallest to largest.
Individual, population, community, ecosystem
(Technically you can include Biome and Biosphere after ecosystem - but we didn't discuss those as much in class this year)
Remora fish attach themselves to sharks; they receive free rides, protection, and leftover food scraps. The shark is neither helped nor harmed.
What type of relationship is this?
Commensalism
These are the pioneer species for primary succession AND the reason why they are the first species present.
Lichens and Moss because they can grow on rocks and help break down rock into useable soil.
If a fox eats a sparrow that eats a grasshopper that eats grass with 1543 kCal of energy, the fox is getting this much energy.
What is 1.543 kCal ?
This term refers to an organism which is introduced to an area and negatively impacts the native organisms
What is an invasive species?
Explain why there are less predators at the top of a food web.
There is not enough energy available to support larger population.
Describe how biodiversity is measured
Species Richness: the number of different species
Species evenness: How proportional species are to one another or how balanced their distribution is.
What are 3 major differences between primary and secondary succession?
1. Primary starts on rock secondary is soil
2. Pioneer species for primary are lichen and moss while secondary is annuals and grasses
3. Primary takes a lot longer (200-1000 years) and secondary is around 150 years or less.
Draw a complete food web for the following ecosystem. The grasshopper and ground squirrel are both herbivores. The grasshopper is eaten by the scorpion. The squirrel and the scorpion are both eaten by the kit fox. The squirrel is also eaten by the golden eagle.

Explain the difference between density dependent and density independent factors and give an example of each.
Density dependent factors dependent on the population size (meaning the degree in which they impact the population is directly related to the population size) EXAMPLES: Competition, Predation, Disease, Space, Limited Resources
Density independent factors are not influenced by population size. EXAMPLES: Weather/Climate patterns, natural disasters, most human impact actions
A more diverse community can withstand shifting environmental conditions and maintains more stable populations
Draw an example of a graph that would show logistic growth and give an example of a factor that would cause this type of growth.
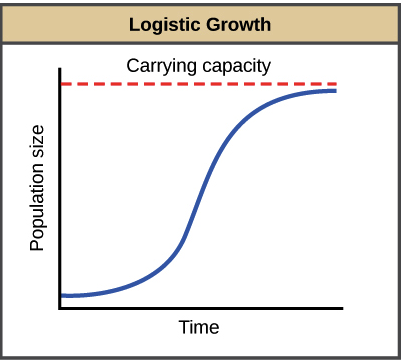
Factors: Any density dependent factors (Competition, predation, limited resources, space)