This term refers to large, complex molecules made up of smaller subunits.
What are polymers/macromolecules?
What are: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids?
This macromolecule provides quick energy and can help build the structure for the cell wall.
What is: carbohydrate?
This macromolecule serves as the raw material for other macromolecules.
What are: carbohydrates?
Monomers are joined by these to form polymers. (Hint: Its what the rubber band represented).
What are: bonds?
These are the basic subunit/building blocks for polymers.
What are: monomers?
These are the three basic building blocks for carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. (Write in order).
What are: monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides?
This macromolecule is responsible for many functions such as storage of necessary materials (not energy), and can help build strong nails and hair.
What are: proteins?
These are the elements that carbohydrates provide to the other macromolecules.
What are: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O)?
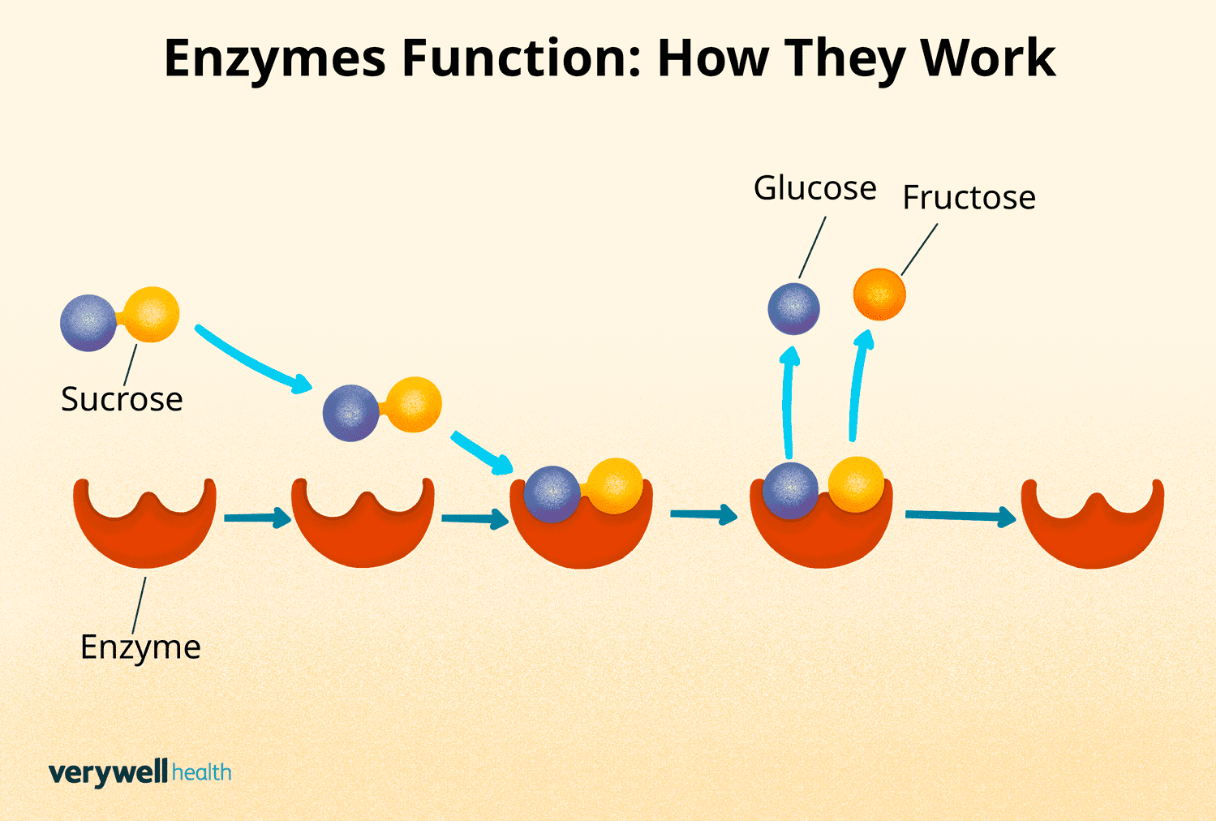 Enzymes are an example of proteins. Proteins can change shape and break down when at least one of these conditions is changed.
Enzymes are an example of proteins. Proteins can change shape and break down when at least one of these conditions is changed.
(Any 1) What is: temperature, pH, salinity?
A nucleotide is an example of this general name used to describe the basic building block of macromolecule structures.
What is: monomer?
This macromolecule is the only one that has Carbon-Phosphorus bonds.
What are: nucleic acids?
Lipids have more energy than carbohydrates and proteins because of this structural differences. (Provide 10-15 words or less stating the difference)
What are: More Bonds = More Energy?
While proteins and nucleic acids require the elements C H O, they also require other elements. List out the extra elements proteins and nucleic acids each require in addition to C H O.
What are: proteins (N, sometimes S), nucleic acids (N, P)?
Glycogen and starch are examples of this macromolecule.
What is: carbohydrate?
This is the name for the independent variable seen in the diagram below.
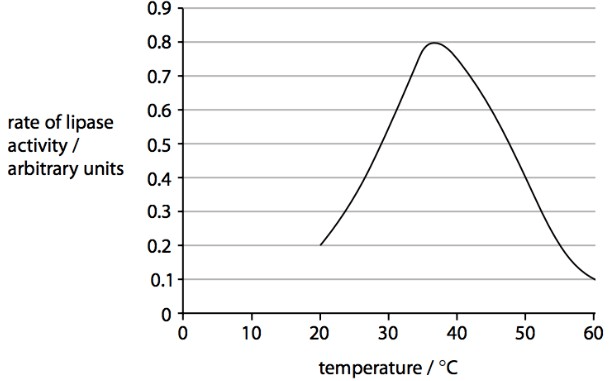
What is: temperature?
The structure shown is an example of this type of macromolecule. (Do not give the specific name of the example.)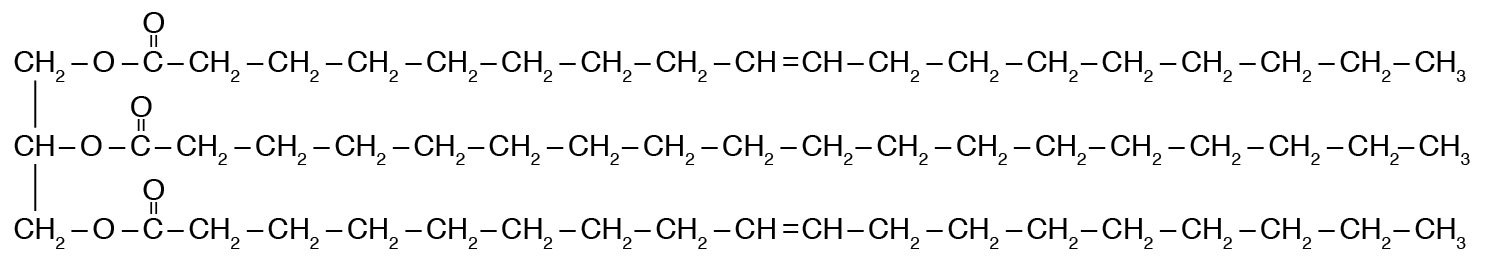
What is: Lipid?
This specific substance, an example of a protein, helps break down substances. This results in speeding up chemical reactions.
What is: enzyme?
This is how plants obtain the additional elements not obtaind from glucose. (Provide 10-15 words or less)
What is: through the roots? (Think soil lab)
Sketch the following diagram and provide a label for each space. For the bottom two boxes, use the term: high energy and low energy. 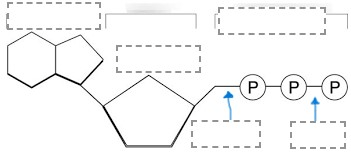
(Look at the drawing on the board**)
This is an image of two substances. Are these the same macromolecule? (Yes or no)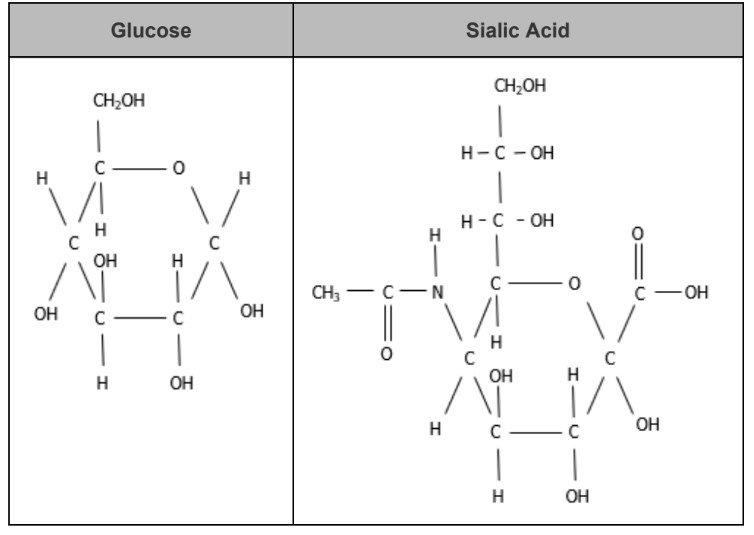
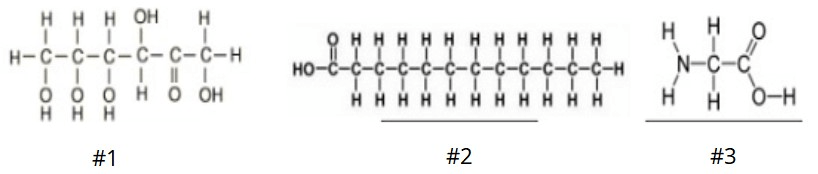 This is the identify of the 3rd macromolecule shown in the picture.
This is the identify of the 3rd macromolecule shown in the picture.
What is: protein?
Write the following on your whiteboard: nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, proteins. Now, place a number 1 - 4 in order of which the body uses first as an energy source. 4 represents the one the body does not use at all.
What is: 1) carbohydrates, 2) lipids, 3) lipids, 4) nucelic acids?
This is a diagram for photosynthesis. This letter represents the food molecule created that the plant uses to then convert to ATP.
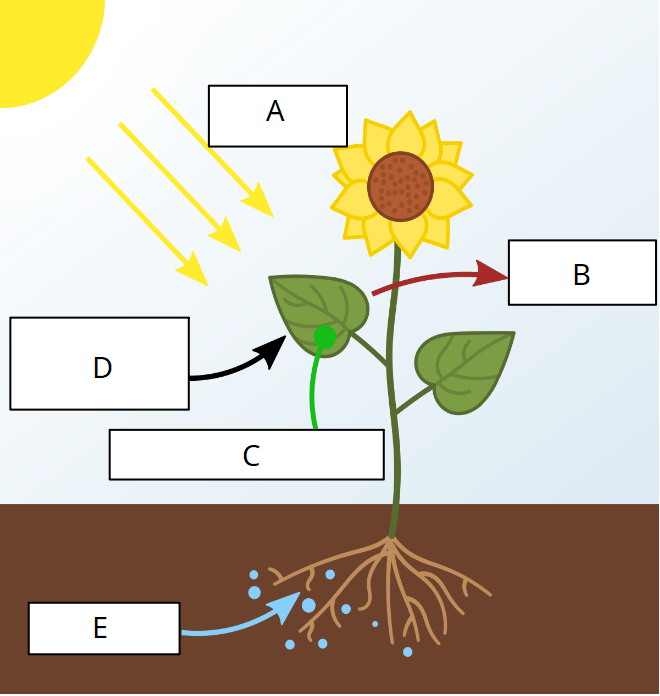
What is: letter C?
Enzymes can break down when temperature, pH, or salinity are changed. When an enzyme breaks down and loses its shape, it loses its function. This term is used to describe what happens to the shape of the enzyme. (It starts with a "D______") 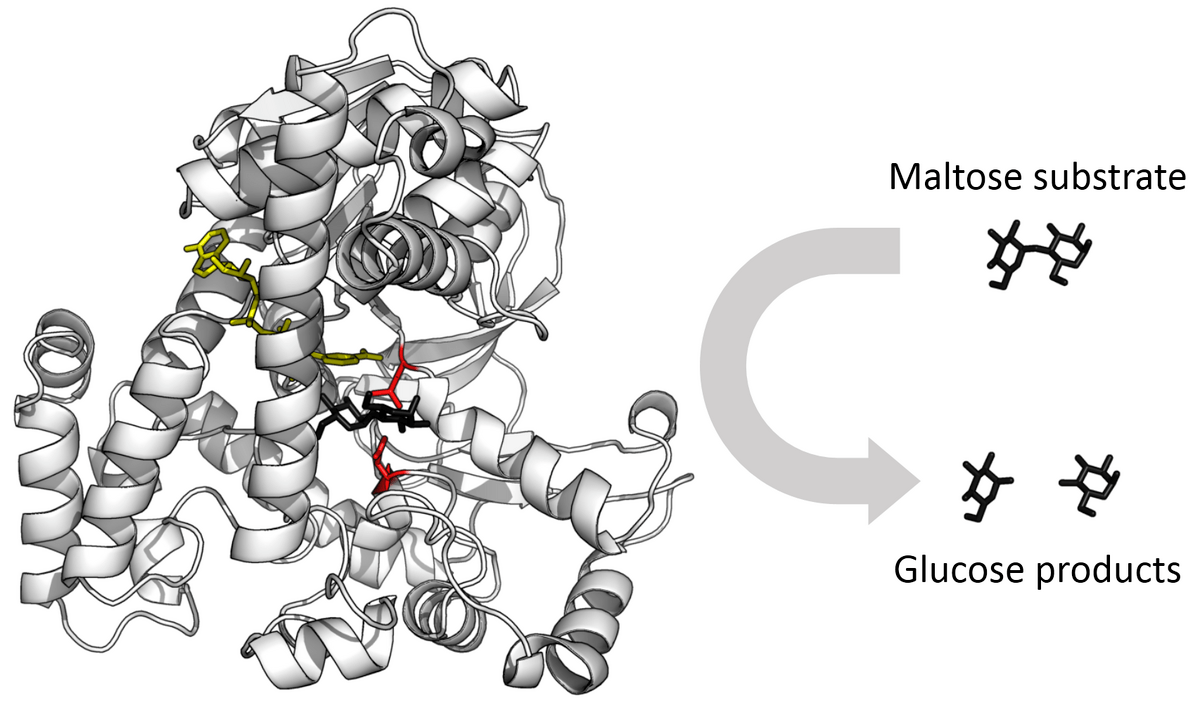
What is: denature?