What types of organisms does the cell theory apply to?
Give an example of an organism that is a prokaryote.
Bacteria
This structure produces proteins and can be found on the Rough ER or free-floating in the cytopasm.
Ribosome
This organelle uses sunlight to make glucose for the cell and is only found in plant cells.
Chloroplast
Describe how prokaryotes and eukaryotes are DIFFERENT.
Prokaryotes do NOT have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes have a NUCLEUS and membrane-bound organelles.
Unicellular organisms are made of one cell while multicellular organisms are made of many cells. Examples:
Unicellular = bacteria, amoeba, euglena, yeast
Multicellular = some protists, fungi, plants, animals
Give an example of characteristic of a prokaryote that is NOT related to its structure.
Prokaryotes are bacteria that are simple, unicellular organisms that can live anywhere. Some bacteria can move and others cannot. Some bacteria are helpful while others can cause disease. Bacteria were the first cells on earth.
Describe the DNA found in prokaryotic cells
In prokaryotic cells the DNA is a small circular chromosome.
What structure is made of proteins and gives the cell its shape,
Cytoskeleton
Which process occurs in the chloroplast that helps make food (glucose)?
Photosynthesis
Identify the type of cell shown below and cite evidence to support your claim.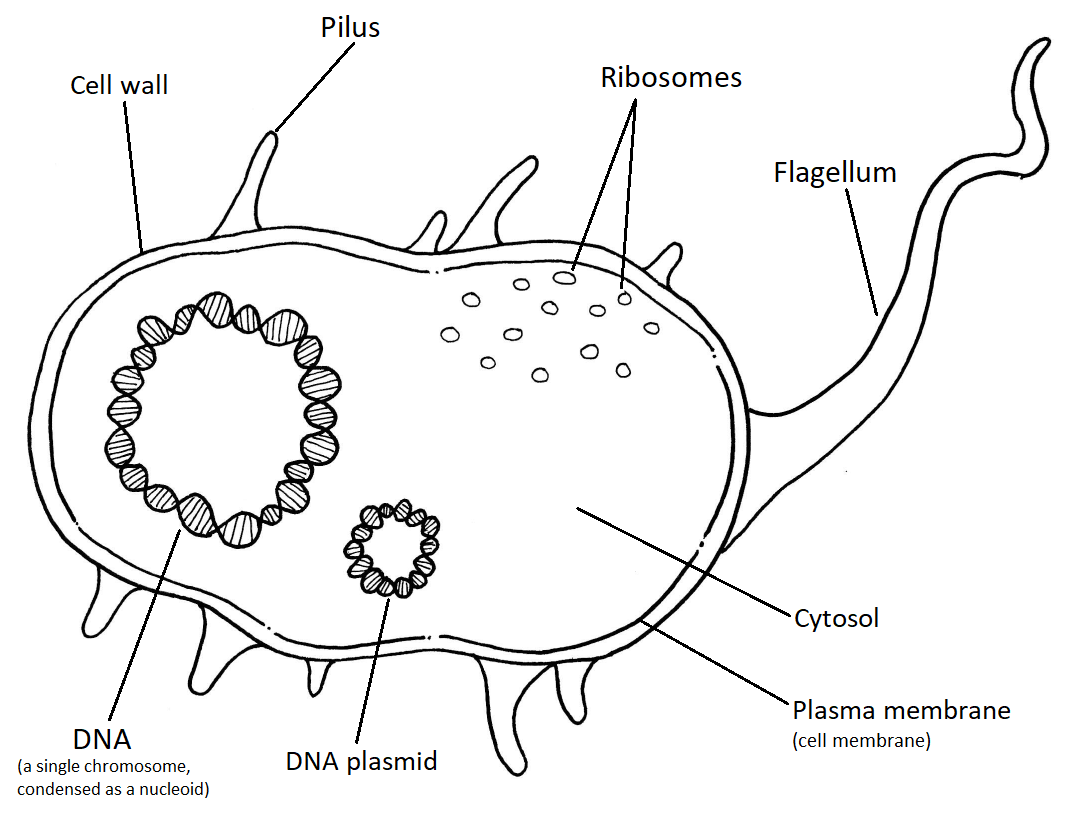
The cell shown is a prokaryote because the cell does not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. The cell contains a small circular piece of DNA that is floating in the cytoplasm and not surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
DAILY DOUBLE
Give TWO examples of structures found in cells that provide protection and support or give the cell its shape.
Cytoskeleton - protein fibers that act like the backbone of the cell and help give the cell its shape
Cell wall - found in bacteria and plants and help protect and support.
Coccus (spherical)
Bacillus (rod-shaped)
Spirillum (spiral)
Thread-like DNA present when the cell is NOT dividing.
Chromatin
Proteins are packaged and sorted here to be sent around the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
What process occurs in the mitochondria that helps provide energy for ALL cells?
Cellular Respiration
Give THREE examples of structures ONLY found in PLANT cells. Make sure to describe the function of each structure.
1. Chloroplast - makes glucose
2. Cell Wall - protects and supports
3. Large Water Vacuole - stores water needed for photosynthesis and helps provide support to help plants stand up straight and NOT wilt.
Identify the three parts of the cell theory.
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Draw and label a prokaryotic cell.
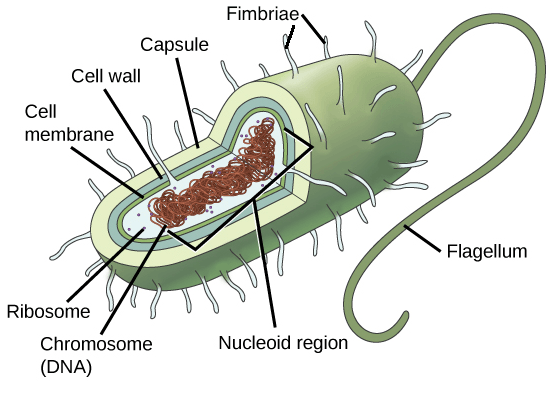
Daily Double
Condensed or "coiled-up" DNA present when the cell is dividing.
Chromosomes
This structure makes ribosomes.
Nucleolus
What form of energy do mitochondria produce?
Mitochondria produce energy for the cell in the form of ATP.
Give THREE examples of structures found in animal cells that are NOT found in plants cells and explain the function of each structure.
Animal cells have:
1. Centrioles - present during cell division that help separate the copied DNA
2. Lysosomes - contain enzymes that help break down food and worn out organelles
3. Many small water vacuoles.
4. Cilia/flagella - aide in movement
Identify the four structures found in every cell and describe the function of each structure.
All cells have:
1. DNA - controls the cell; carries the instructions for making proteins
2. Cytoplasm - jelly-like material where reactions occur
3. Cell Membrane - controls what can enter and leave the cell
4. Ribosomes - make proteins
Bacteria play many roles in the environment:
1. Take nitrogen out of the atmosphere and convert to a form plants can use (nitrogen fixation).
2. Break down dead organic matter (decomposer)
3. Help to recycle nutrients
This eukaryotic organelle is only present in animal cells during cell division and helps separate the two copies of the DNA into each new cell.
Centrioles
This is sometimes called the stomach of the cell because it contains digestive enzymes that breaks down food and worn-out organelles. Don't forget ENZYMES are PROTEINS.
Lysosome
Identify the types of cells where mitochondria and chloroplast are found.
Mitochondria are found in ALL eukaryotic cells and chloroplast are found in plant cells.
Describe how cilia and flagella are different and give an example of a type of organism or cell that has a cilia or flagella.
Cilia - short hair-like projections that help the organism move (i.e. Paramecium) or move materials (i.e. cells lining the trachea.
Flagella - long whip-like projections of the cell membrane that help cells (i.e. sperm) or organisms (Euglena) move.