Cells come from other _______. (A part of the cell theory)
What are cells?
These types of cells have the following 4 characteristics; DNA, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes
What is all cells?
ATP breaks a chemical bond to release the energy needed for cellular activities (T or F)
What is true?
What is ribosome?
Cells are the basic _____ of life. (A part of the cell theory)
What is unit?
The DNA in the cell below is free floating in the cytoplasm.

What is prokaryotic?
This step in the diagram below shows energy being released.
What is Step 2?
This organelle is responsible for transporting proteins.
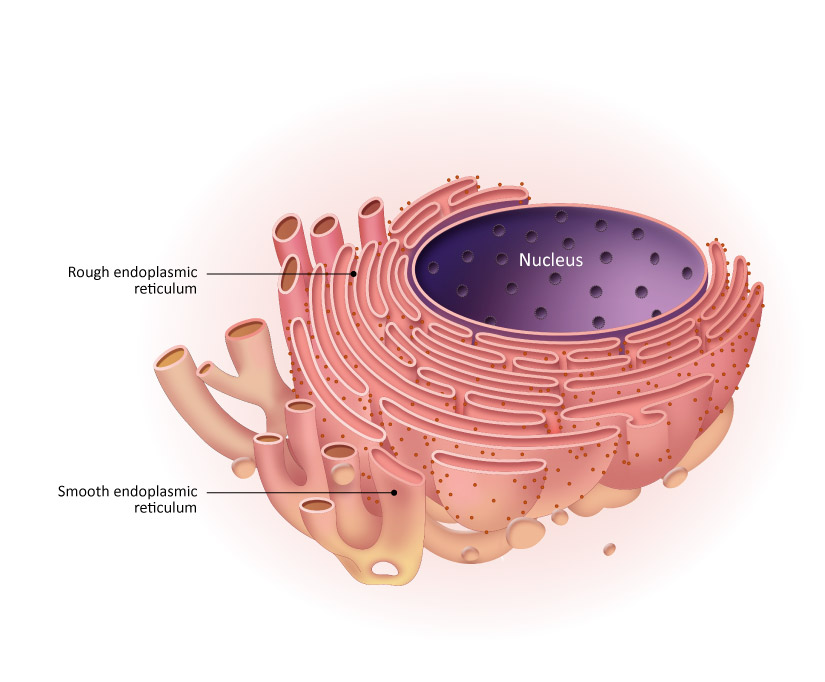
What is rough endoplasmic reticulum?
All living _________ are made up of cells. (A part of the cell theory)
What are things or organisms?
This organelles found in plants is larger and stores water for photosynthesis.
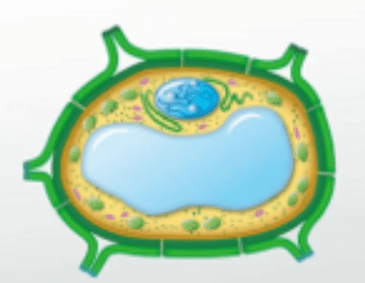
What is vacuole?
Osmosis is a type of this transport where water molecules move with the concentration gradient.
What is passive transport?
The organelle shown below conducts cellular respiration and makes ATP for the cell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_mitochondrion-5661ca005f9b583386c70c31.png)
What is mitochondria?
A well supported explanation of a part of the natural world is this scientific word.
What is scientific theory?
The two organelles found in the plant cell but not the animal cell.
What are cell wall and chloroplast?
The diagram below shows which type of cellular transport.
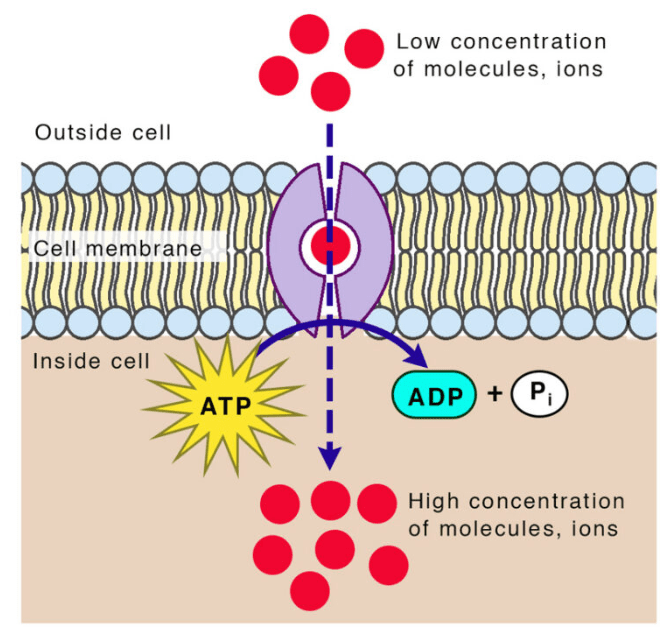
What is active transport?
Ribosomes make proteins from a strand of RNA. This organelle is where the RNA gets its instructions from.
What is the nucleus?
This is how theories change and develop.
What is new evidence?
The cell below is this type of cell.
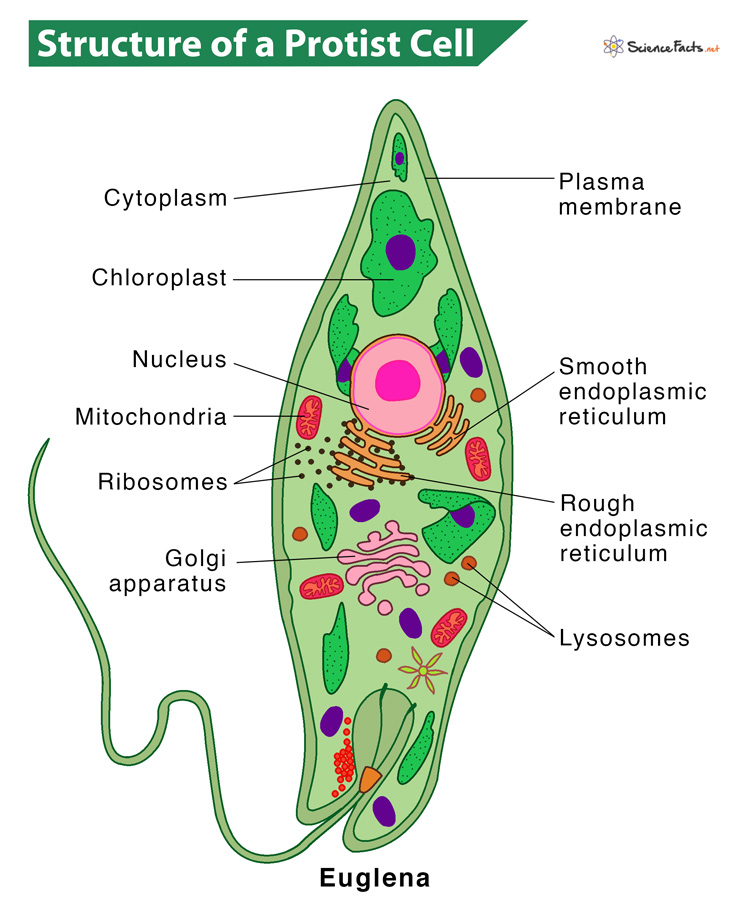
What is eukaryotic cell?
The diagram below shows this type of cell transport. Molecules are moving from an area of high to low concentration.

What is facilitated diffusion?
This organelle is found only in animal cells and helps to split the cell apart during cell division.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/conceptual-image-of-centriole--476872587-5c48c754c9e77c00019c13cb.jpg)
What is centriole?