The largest level of organization
biosphere
Subatomic particles found outside the nucleus of an atom
electrons
Anaerobic metabolism requires the presence of what?
oxygen
Which body system that functions to produce gametes and nurture offspring.
reproductive system
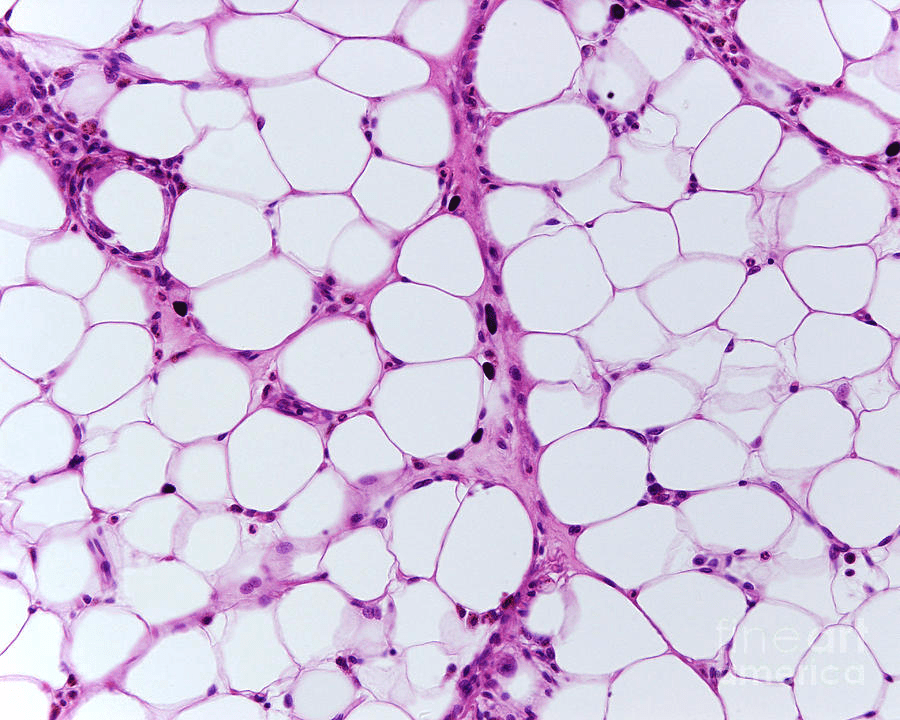
adipose
Which Domain do we belong to?
Eukarya
The ability of water molecules to stick together is called what?
cohesion
What is the second step of cellular respiration and where does it take place?
Krebs/Citric Acid cycle ; mitochondria
This membrane lines the lungs, heart, and digestive organs
serous membranes
This membrane lines the cavities of joints
synovial membranes
After analyzing data, what is the next step in the scientific method?
draw conclusions
Amino acids are monomers of which biomolecule
protein
The primary function of this organelle is lipid synthesis and detoxification
smooth ER
Describe the function of a ligament
connect bone to bone
Define facilitated diffusion
Movement of molecules with the aid of a transport protein
In an experiment, the observed change or response in the system that is caused by the manipulation of another variable is the __________.
the dependent variable
Define nonpolar and polar covalent bonds
nonpolar = electrons shared equally
polar = electrons shared unequally
What are the function of lysosomes
contains enzymes that degrade/recycles debris
This specific tissue type absorbs excess interstitial fluid
lymph
Explain how acids and bases interact with hydrogen
acids donate hydrogen
bases accept hydrogen
List at least 5 of the 7 characteristics of living things
What is
1) use energy, 2) homeostasis, 3) highly organized, 4) evolution, 5) DNA, 6) reproduction, 7) made of cells
What are the four polysaccharides?
What is starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin
The 4 components of the plasma membrane (cell membrane)
phospholipid bilayer, channel proteins, glycocalyx, and cholesterol
This specific tissue type can be found in the lining of the trachea
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What reactions do our muscle cells perform, and under what conditions?
Lactic acid fermentation, in the absence of oxygen