What are the three domains of Life?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes, and Eukarya is eukaryotic. The four kingdoms in Eukarya are Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What are the four elements that makeup 96% of your body?
C, H, N, O
Why is pH is an important concept in biological systems?
pH is important in biological systems because even if the pH even slightly changes in cells, it can be very harmful.
What are the four ways carbon skeletons can vary in?
length, branching, double bond position, and rings
What is a monomer and polymer?
Monomer- the subunit that serves as the building blocks for polymers
Polymer- a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds.
What is an emergent property? Give an example of an emergent property in biological systems.
Emergent property- a property that results from the arrangement and interaction of parts in a system.
An example- sheets of endothelial cells combine to form tubes called capillaries which transports blood.
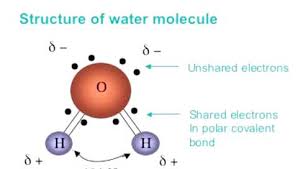
What is greater? The electronegativity of a hydrogen atom or the electronegativity of an oxygen atom?
Also - what is electronegativity?
the electronegativity of an oxygen atom.
Electronegativity- the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself. (oxygen in a water molecule)
Draw a water molecule and show how it is a polar molecule (show charge distribution)
Structural Isomers- one or two or more compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
Geometric Isomers- one of several compounds that have the same molecular formula and covalent bonds between atoms differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
Enantiomers- one or two compounds that are mirror images of each other and that differ in shape due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon.
What type of bond is formed between monosaccharides to make polysaccharides
glycosidic linkages
Compare and contrast eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
Prok: Small, simple (no organelles)
Euk: Membrane bound organelles, Larger
Both: DNA, cell membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm
What is an atom? Draw a basic atomic structure labeling the subatomic particles.
- An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element.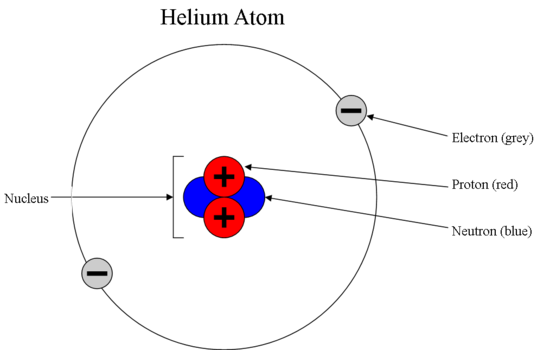
Compare hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic. What chemical property differentiates hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules?
Hydrophilic - water loving, polar
Hydrophobic- water fearing, non-polar and nonionic
Draw methane, propane, and butane on the board with the correct number of carbons and hydrogens.
-
What two types of chemical reactions are involved in the synthesis and breakdown of polymers?
1. dehydration synthesis
2. hydrolysis
List the 10 levels of biological organization from macro- to microscale.
Biosphere, Ecosystems, Communities, Populations, Organisms, Organs, Tissues, Cells, Organelles, Molecules
What bonds enable a gecko to climb a wall?
Van der Waals - weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges.
How do the properties of water allow the ocean to moderate global temperature?
Water has a high specific heat so it can absorb a lot of heat from the atmosphere without changing its temperature much. This also cools the temperature of the atmosphere.
What is ATP? What is the important functional group in ATP?
A special phosphate- containing molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), is the primary energy transferring molecule in the cell. Consists of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups.
Compare and contrast saturated vs. unsaturated fats.
Saturated fats and unsaturated fats are both hydrophobic but saturated fats have as many hydrogens as possible whereas unsaturated fats contain a double bond between carbons, giving them a kink in their shape.
What are the seven properties associated with life? Explain each.
Order, Response to Environment, Evolutionary Adaptation, Growth and Development
List and describe the 4 types of chemical bonds.
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen bonds, and van der waals
State the four emergent properties of water and explain them.
Cohesion/Adhesion
Ability to Moderate Temperature
Expansion Upon Freezing (insulation)
Versatility as a Solvent
Write the 7 biologically important functional groups on the board and their properties.
Hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, methyl
What are the four main classes of macromolecules? Explain them.
Carbohydrates/Polysaccharides
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Lipids