Bonds that are important for the structure and function of biological molecules.
What are covalent and non-covalent bonds?
The determinate of the function of a biomolecule.
What is confirmation/ 3-dimensional architecture?
What is pH = -log [H+]?
The monomers for carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides/ simple sugars?
The bonds that facilitate base pairing in DNA.
What are hydrogen bonds?
This type of biomolecule is primarily responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information in living organisms and comprises these building blocks.
The calculation for [H+] when given the pH.
What is 10-pH ?
A mechanism for cells to condense the storage of important substances.
Bonds formed between amino and carbonyl groups to form chains of amino acids.
What are peptide bonds?
A close fit between biomolecules that allows interactions.
What is structural complementarity?
The Henderson Hasselbach equation.
What is
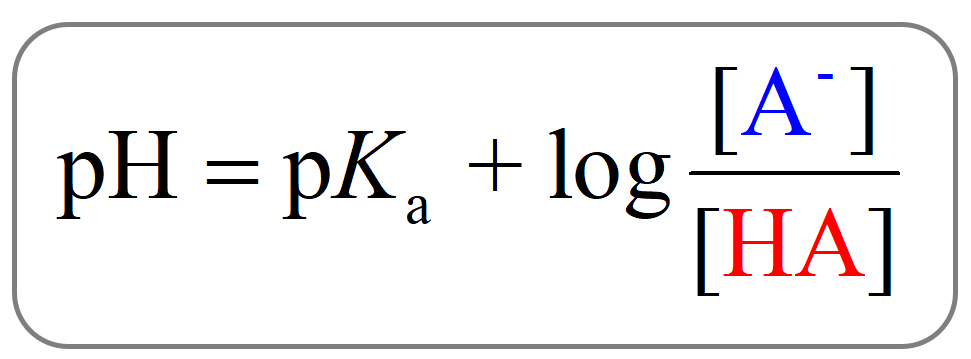
The purpose of hyperventilation.
To raise CO2 levels in the bloodstream.
The effect of introducing conditions that would disrupt bonding properties.
What is denaturation/ loss of function?
Water has a high dielectric constant and the ability to form many hydrogen bonds to allow it to do this more easily.
What is the ability to readily dissolve many species and interact electrostatically with charged solutes?
The buffer region of a solution's pH that a group can resist deprotonation.
What is +/- 1 of the groups pKa?
Living organisms require a constant investment of energy so they can continue to exist in this specific way.
What is a dynamic steady state?
DNA polymerase carries out replication following the DNA strand in a specific manner due to this property of nucleic acid.
What is directionality?
The protonation/deprotonation of a group in a solution depends on these two things.
What is the pH of the solution the group is in and the buffer region of the group?
The attractive and repulsive forces between two charged species.
What is electrostatic force?