What is an organic compound?
A compound made of primarily carbon atoms.
What functional groups are typical for a carbohydrate?
1) Alcohol and aldehyde or ketone
2) Acetal and hemiacetal
List some functions of proteins.
antibodies, enzymes, build and repair muscle
What are the monomers of lipids?
Glycerol and fatty acids
What are 2 examples of Nucleic Acids?
DNA and RNA
What is the difference between reactants and products?
Reactants are the starting materials for the reaction and products are what is made during the reaction.
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
In this type of reaction, water is used to break down a larger molecule (often a polymer) into smaller units.
Water molecules are held together by what type of bonds?
What are hydrogen bonds?
Why the terms "proton" and "Hydrogen ion" can be used interchangeably?
Because proton is all that is left if Hydrogen atom loses its only electron.
What is a monosaccharide?
The simple sugar, like glucose or galactose, which when bonded together create larger di, tri, etc. saccharides.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
What are some functions of lipids?
Insulation, Protection, Long term energy, energy storage, cell membranes, hormones, waterproof coverings.
Nucleic Acids are made of thousands of monomers called this.
What is nucleotide?
What is the difference between an endothermic and exothermic reaction?
Endothermic reactions absorb more energy than they release. Exothermic reactions release more energy than they absorb.
Describe the difference between condensation and hydrolysis reactions
Condensation is when a water is removed to synthesize or make a bigger molecule. Hydrolysis is when water is added to break a molecule into smaller parts.
Water is a polar molecule. Describe what makes it a polar molecule.
One part of the molecule has a slight positive charge (hydrogen side) and one part has a slight negative charge (oxygen side).
What is a polymer?
Long molecules assembled from small repeating units (Monomers) bonded to each other.
List the 3 polymers of glucose
Starch, glycogen and cellulose
What are the characteristic functional groups of protein?
An amide, and amine, and a carboxylic acid
Give some examples of lipids.
fats, oils, waxes, steroids, butter, olive oil
Which is the function of Nucleic Acids?
To store and carry genetic information.
What is the difference between a catalyst and an enzyme?
An enzyme is a type of catalyst that speeds up reactions in living things.
Two or more substances physically but not chemically combined.
What is a mixture?
Bond formed between 2 amino acids
What is a peptide bond?
This type of lipid has three fatty acid tails.
What is a triglyceride?
Describe the molecular structure of a nucleotide.
Sugar molecule attached to a phosphate group and also attached to a base.
Explain how an enzyme works (include the terms substrate, bonds, active site, products and reusable).
An enzyme works by binding the substrates at the active site and weakening the bonds therefore allowing the reaction to occur faster to produce the products. Once the products are made, the enzyme does not get used up and can be reused.
Scale used to measure acids and bases. Describe the range and where acids and bases fall on this scale.
The pH scale measures acids and bases. It runs from 1-14 with acids being from 1-6.9 and bases being from 7.1 - 14. Seven is neutral.
Describe the difference between a molecule and an ion
Molecule is composed of atoms which are covalently bonded to obtain stable electron configuration. Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that lost or gained electrons.
Plants make this polysaccharide.
What is cellulose?
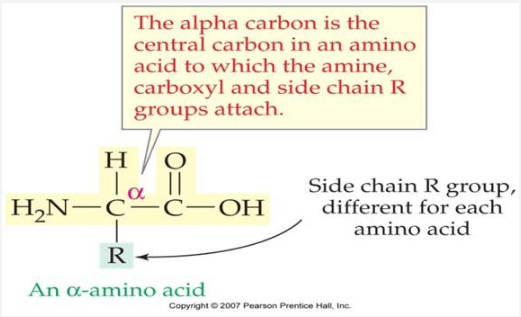
Draw a generic structure of an amino acid.
Center Carbon attached to a hydrogen, amine group, carboxyl group and R group which is specific to each amino acid.
What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated fat?
Saturated fats have all single bonds and are solids at room temperature. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond and are liquids at room temperature.
Are nucleic acids polymers? Explain how you know this.
Yes because they are large molecules made up of smaller repeating units.
What 2 things affect enzymes and how do they affect them?
Temperature and pH affect enzymes. If temperature and pH are not at the right conditions, the enzyme will get denatured which means it will change shape and the substrates will no longer recognize the enzyme.
Water is the universal solvent. Why is this important to living organisms?
Water dissolves many different substances in the body and allows for chemical reactions to take place in the living things.