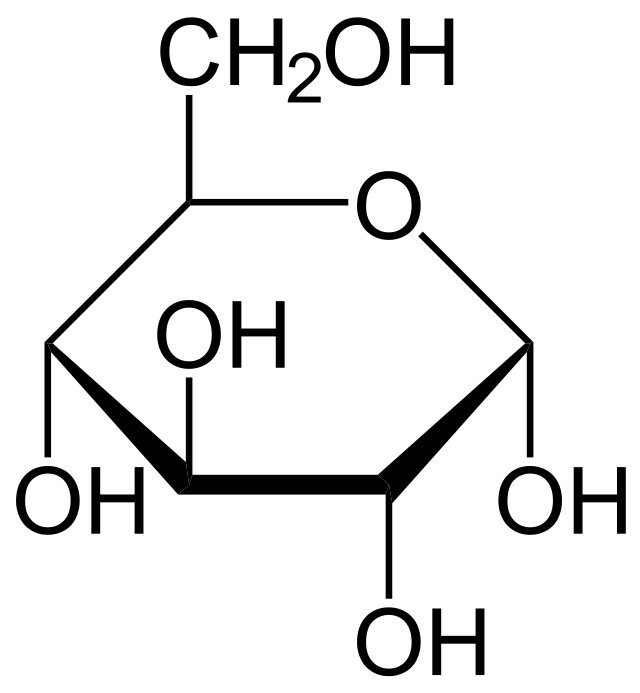
Monosaccharide
Monomers of a lipid
Glycerol
Fatty acids
Monomer of proteins
Amino acids
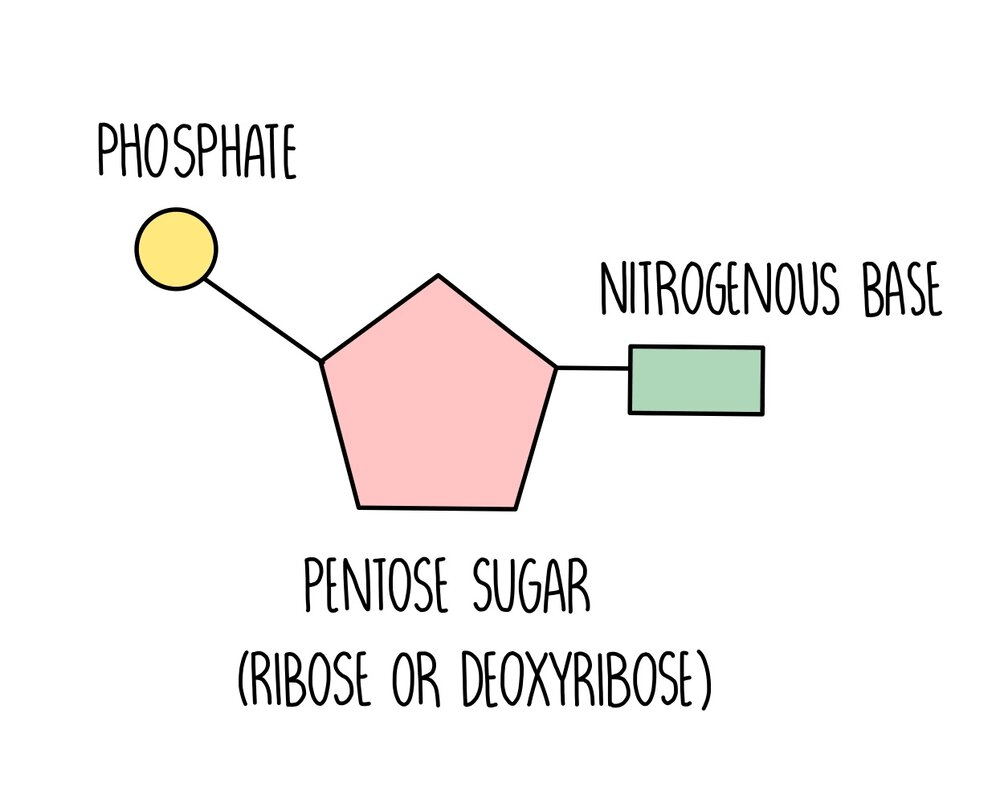
Monomer of a nucleic acid
Nucleotide
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
By lowering the activation energy
Polymer of carbohydrates
Polysaccharide
What elements are found in lipids?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
What are two functions of proteins?
Construction material for the body
Enzymes
Regulate cell processes
Immunity (antibodies)
DNA
RNA
What three letters do enzymes typically end with?
-ase
Draw a glucose molecule
What are three functions of lipids?
Insulation
Long-term energy storage
Chemical messenger
Waterproof coating
Cell membrane
Polymer of a protein
Polypeptide
Two functions of nucleic acids
Storing/transmitting genetic information
Instructions for making proteins
What are two different reactions that enzymes can facilitate?
Synthesis
Decomposition
This polysaccharide is how animals store extra carbs
Glycogen
What specific lipid makes up the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
Which protein carries oxygen in red blood cells?
Hemoglobin
Name two differences between DNA and RNA
Double vs. single stranded
Different sugars (Deoxyribose vs. ribose)
One nitrogen base (Thymine vs. Uracil)
Temperature
pH
Salinity
What are two functions of carbohydrates?
Quick energy
Structure (Cell wall)
What is this called?
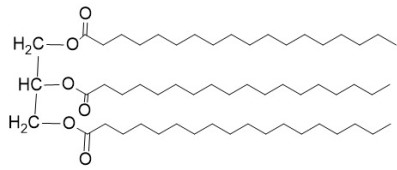
Triglyceride
What type of bond holds amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
Draw and label the three parts of a nucleotide
What is represented in the diagram by 'd'? Is this synthesis or decomposition?
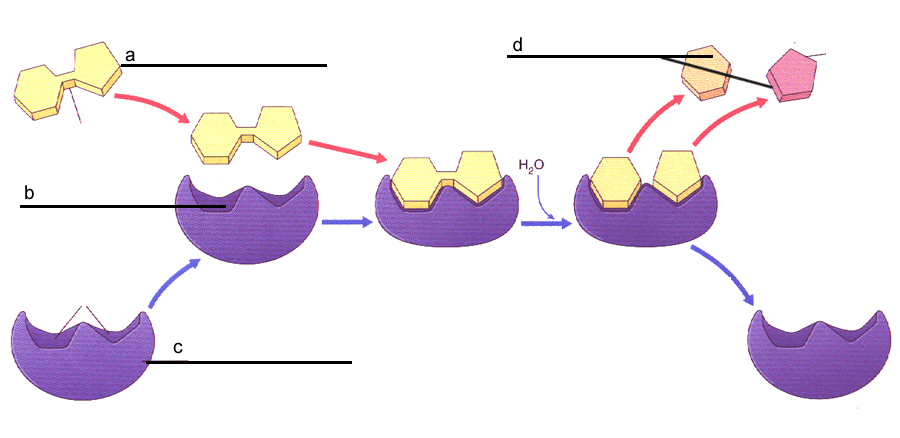
Products
Decomposition