What is defined as the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element?
An Atom
Which type of chemical bond forms when electrons are shared between atoms?
A Covalent Bond
What is the pH value of a neutral solution, such as pure water?
7
Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain which two elements?
Carbon and Hydrogen
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions are known as ______.
Enzymes
Which subatomic particle has a positive charge and is located in the nucleus of an atom?
A Proton
Which type of chemical bond results from the transfer of electrons between atoms?
A solution with a pH value less than 7 is classified as a(n) ______.
Acid
Large organic molecules composed of many smaller subunits are called ______.
Macromolecules or Polymers
Which molecule is the basic subunit (monomer) of proteins?
Amino Acids
Which subatomic particle has no charge and is found in the nucleus of an atom?
A neutron
Which weak attraction occurs between a slightly positive hydrogen atom (like in water) and a slightly negative atom?
A Hydrogen Bond
A solution with a pH value greater than 7 is classified as a(n) ______.
Base
Which macromolecule serves as the primary source of energy for living organisms?
Carbohydrates
Name two factors that can affect the rate at which an enzyme functions.
Temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration
Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are known as ______.
Isotopes
The attraction between water molecules is best described as ______.
Cohesion
Lipase is an enzyme that breaks down lipids in the digestive system of humans. It functions best at a pH range of 4-5. When a person takes an antacid tablet, the pH increases to 7 in certain areas of the digestive system. What effect would likely be caused by a change in pH?
Lipase would denature, therefore less lipids would be digested.
DNA and RNA are examples of which type of macromolecule?
Nucleic Acids
The substances present at the beginning of a chemical reaction are called ______.
A pure substance composed of only one type of atom is classified as a(n) ______.
element
The attraction between water molecules and other polar substances is called ______.
adhesion
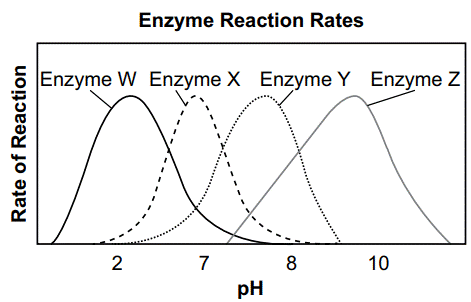
Which enzyme would most likely reach its maximum reaction rate in pure water?
Enzyme X - functions best at a pH of 7
Which macromolecule is made of one or more chains of amino acids and is important for growth and repair?
Proteins
The substances produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called ______.
Products