Name the chemical elements that could possibly be found in a carbohydrate molecule.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Name the chemical elements that could possibly be found in a lipid molecule.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Name the chemical elements that could possibly be found in a protein molecule.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur
List the two types of nucleic acid molecules that nucleotides are monomers of.
DNA and RNA
Name the chemical elements that could possibly be found in a nucleic acid molecule.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
Identify what type of carbohydrate molecule this is.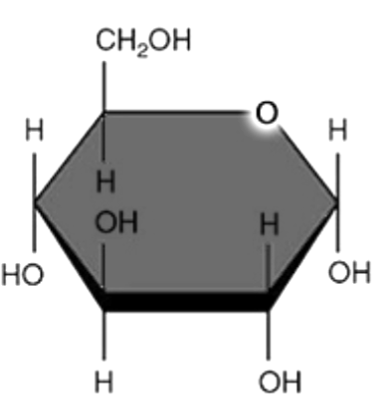
Monosaccharide
Name the type of lipid shown here: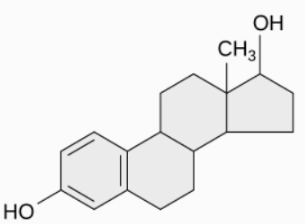
Steroid hormone / Lipid hormone
State the name of the specific type of chemical bond which links amino acids within a protein.
Peptide bonds
List the types of nucleotide bases which may be found in DNA, AND list the types of nucleotide bases which may be found in RNA.
DNA: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
RNA: Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
State the locations in a eukaryotic cell where DNA may possibly be found.
Nucleus
Identify what type of carbohydrate molecule this is. 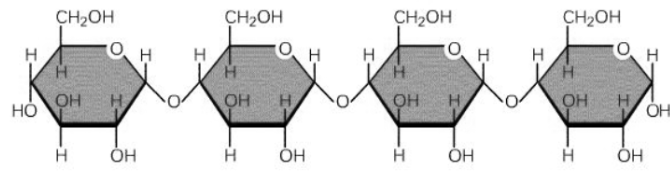
Polysaccharide
Identify the specific type of lipid shown here.
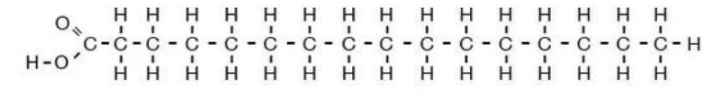
Saturated fatty acid
State the number of amino acids shared by all living organisms on Earth.
20
Identify which of the molecules shown here is deoxyribose, and identify which one is ribose.
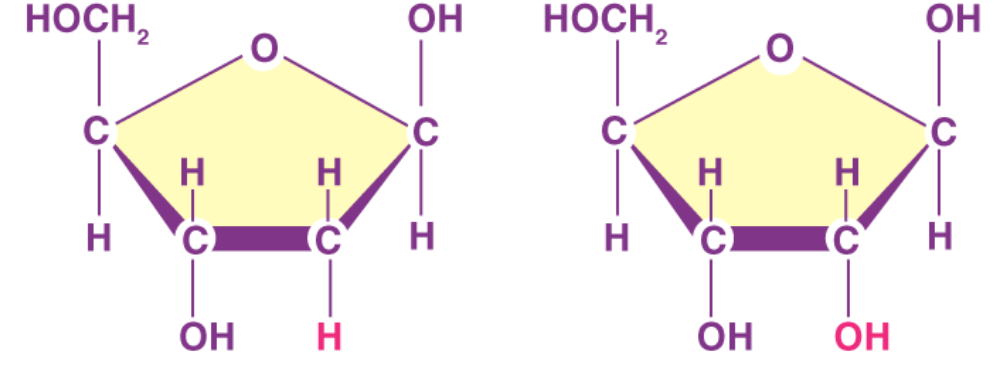
Left = deoxyribose, right = ribose
The nucleotide sequence of one strand of a DNA molecule reads CAT TAG TAC. Provide the sequence that would be found on the opposite strand.
GTA ATC ATG
Provide the name of any specific disaccharide molecule.
Various answers (ex. sucrose, lactose, maltose)
Shown below is adipose tissue, the tissue in humans (and other animals) responsible for storing fat. What type of lipid molecule is the main type found in human fat?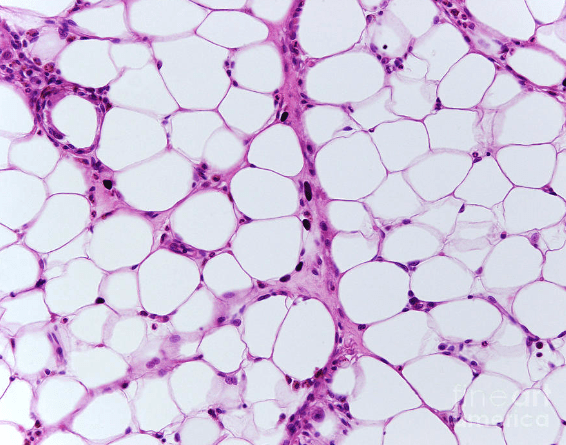
Triglycerides
This is the term for the process by which extreme heat or extreme high/low pH may cause a protein to lose its shape, and therefore cease its normal functions.
Denaturation / Denaturing
On the whiteboard, circle and name the three parts of this nucleotide molecule.
Left = phosphate group, middle = pentose sugar (deoxyribose), right = nitrogenous base (adenine)
DNA pulled from an organism's cells is found to have a nucleotide base content that is 15% thymine. How much of this organism's nucleotide base content would be made up of cytosine?
35%
Name the specific type of chemical bond which links together the monomers shown in this diagram. 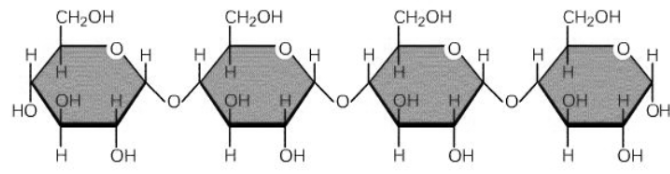
1,4 glycosidic bond
Name the specific type of lipid which is regarded as the least healthy for human heart and cardiovascular health.
Trans-monounsaturated fatty acids
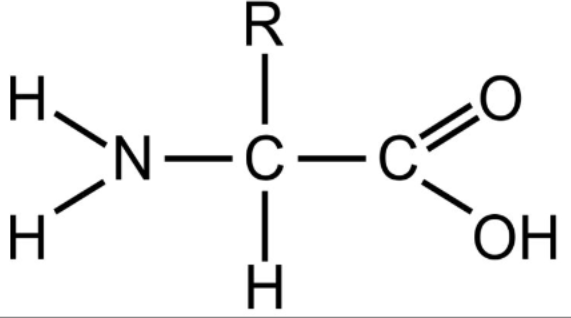
Draw the generalized structure of an amino acid on the whiteboard.
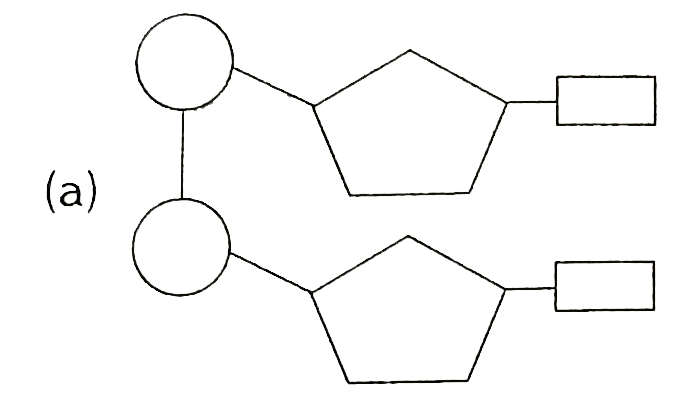
Using the simplified drawing style we learned for illustrating nucleotides (i.e. with circles, pentagons, and rectangles), draw a dinucleotide molecule on the whiteboard.
Shown here are three possible arrangements for nucleotide bases on the opposite strands of a DNA molecule, or the bases on a strand of DNA and a strand of RNA during transcription. Which of these three represents the normal and expected arrangement, and which ones represent errors that should not normally occur?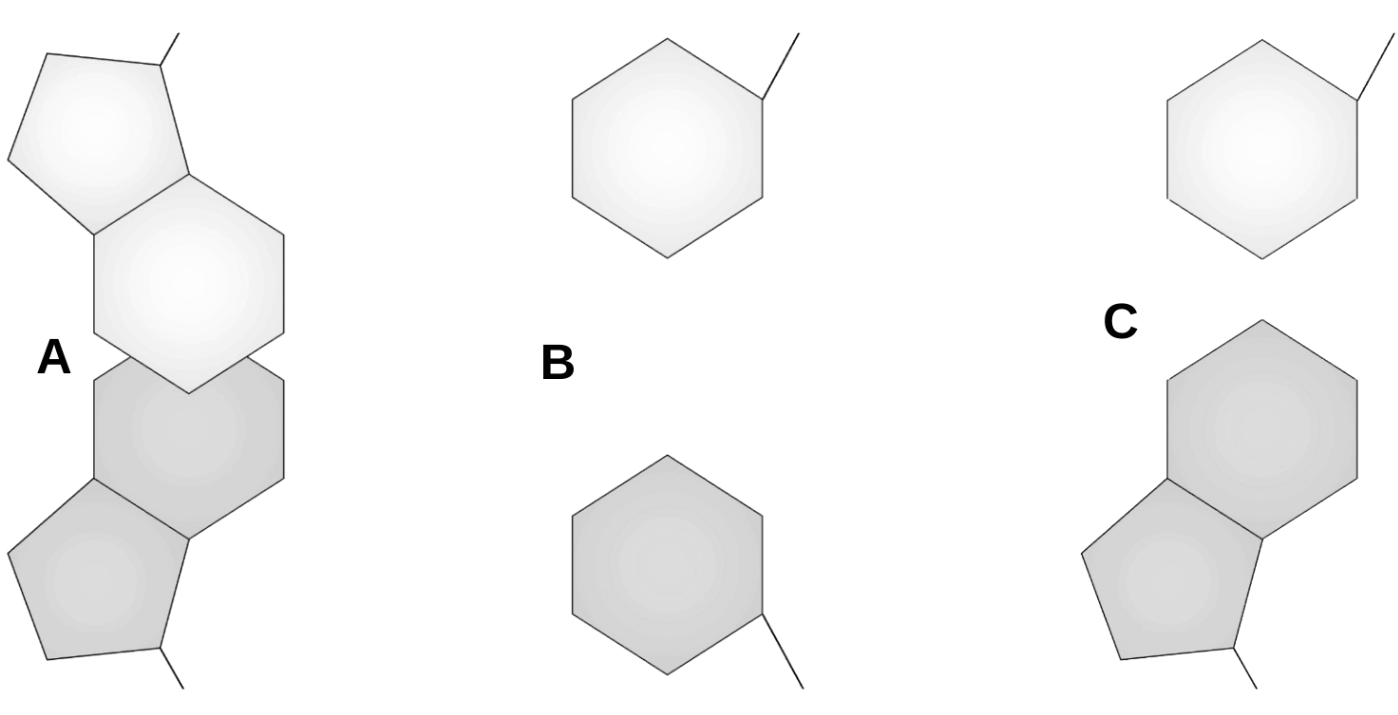
C = normal (purine-pyrimidine pair)
A = error (purine-purine pair)
B = error (pyrimidine-pyrimidine pair)