What are biotic features of an ecosystem?
What are abiotic features of an ecosystem?
Biotic - living - trees, plants, insects, animals
Abiotic - nonliving - rocks, water, soil, air, minerals
A primary consumer is also known as what?
Primary consumer = herbivore (they eat the producers)
What are the trophic levels from producer up to quarternary consumer?
producer -> primary consumer -> secondary consumer -> tertiary consumer -> quarternary consumer
What are the 3 types of biodiversity?
genetic diversity - difference in genetics of a species
species diversity - diversity of species (# different species) in a given area
ecosystem diversity - different ecosystems present in an area
What is the biggest human impact on biodiversity?
Habitat loss/destruction, habitat degradation, habitat fragmentation
A climatogrpah shows what two features, the two features that determine a climate?
temperature and precipitation
A symbiotic relationship between two species where one benefits and one is harmed?
parasitic
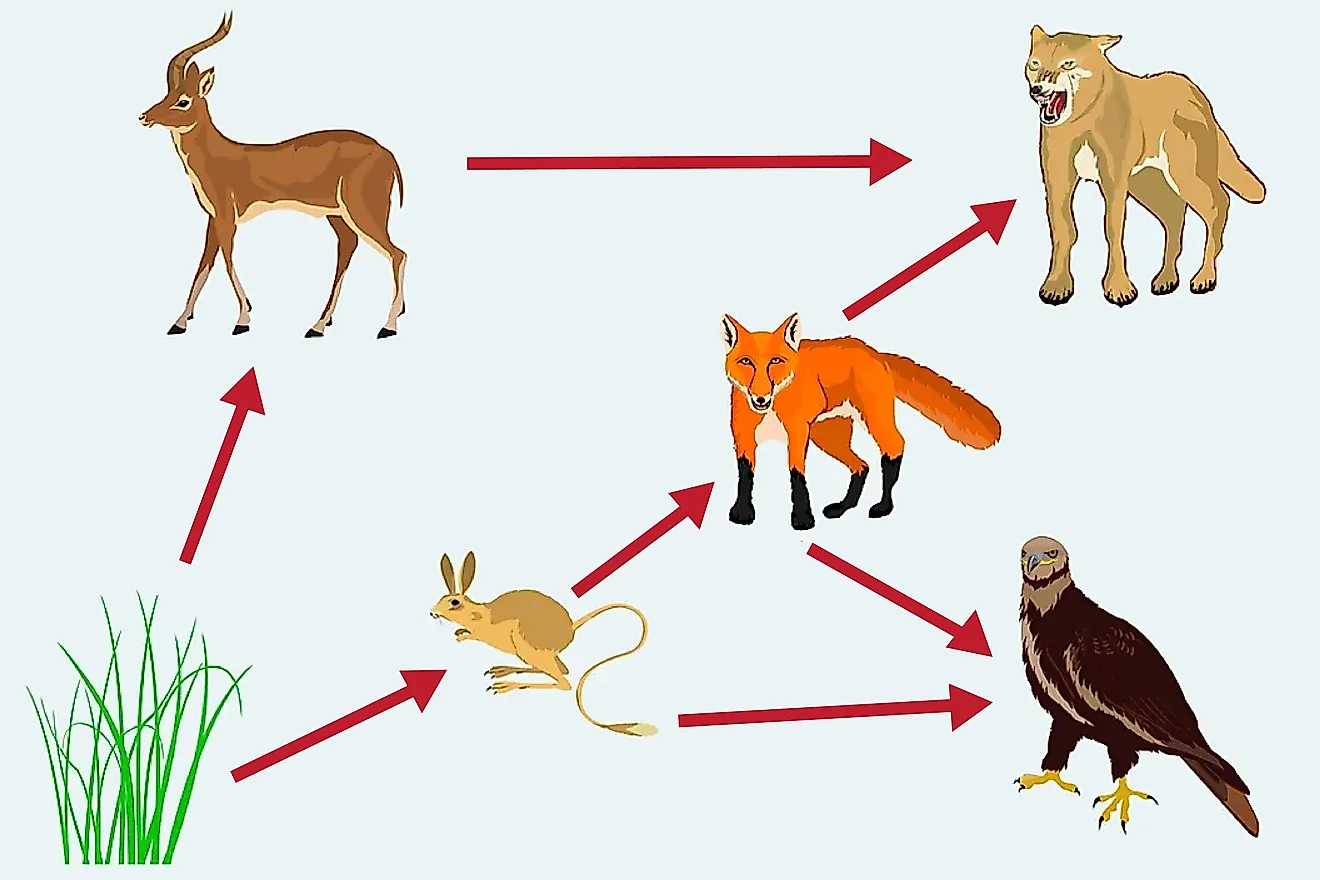
What animal is a tertiary consumer?
Cougar or eagle
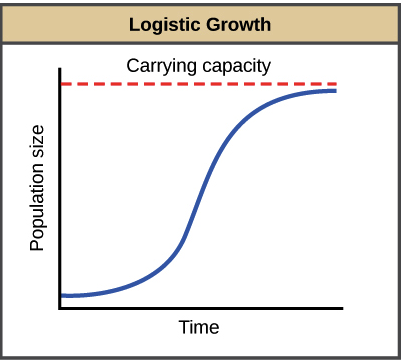
What is carrying capacity?
maximum number of organisms an ecosystem can support
What acronym do we use to remember the impacts humans have on biodiversity?
H - habitat loss/degradation/fragmentation
I -invasive species
P - population growth (human)
P - pollution
O - overexploitation of resources (overhunting, overfishing)
The main type of animals found in grasslands?
large, grazing, hoofed herbivores
A symbiotic relationship between two species where both benefit?
mutualism

If 25000kcal of energy is available to the fox, how much energy will be available to the eagle?
2500kcal
What type of growth gives you a J-shaped curve and why?
exponential growth due to no limiting factors
What is ecosystem resilience and what afffects/determines it?
The ability of an ecosystem to recover after a disturbance
The more biodiverse an ecosystem, the more resilient
A large ecosystem characterized by a specific climate is called a ?
Biome
A symbiotic relationship between two species where one benefits and one is not affected?
commensalism
 If 25000kcal of energy is available to the deer, how much energy will be available in the grass?
If 25000kcal of energy is available to the deer, how much energy will be available in the grass?
250000kcal
What happens when a population nears or exceeds carrying capacity?
The population will crash/die off if it exceeds carrying capacity until it it under it, then it will increase until it stablizies around the carrying capacity. 
When do non-native species get considered invasive species and why?
When they start to have a negative impact on the ecosystem because they have no natural predators or competitors.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather - short term day to day atmospheric conditions
Climate - long-term weather patterns averaged over years/decades
What type of species interaction is shown?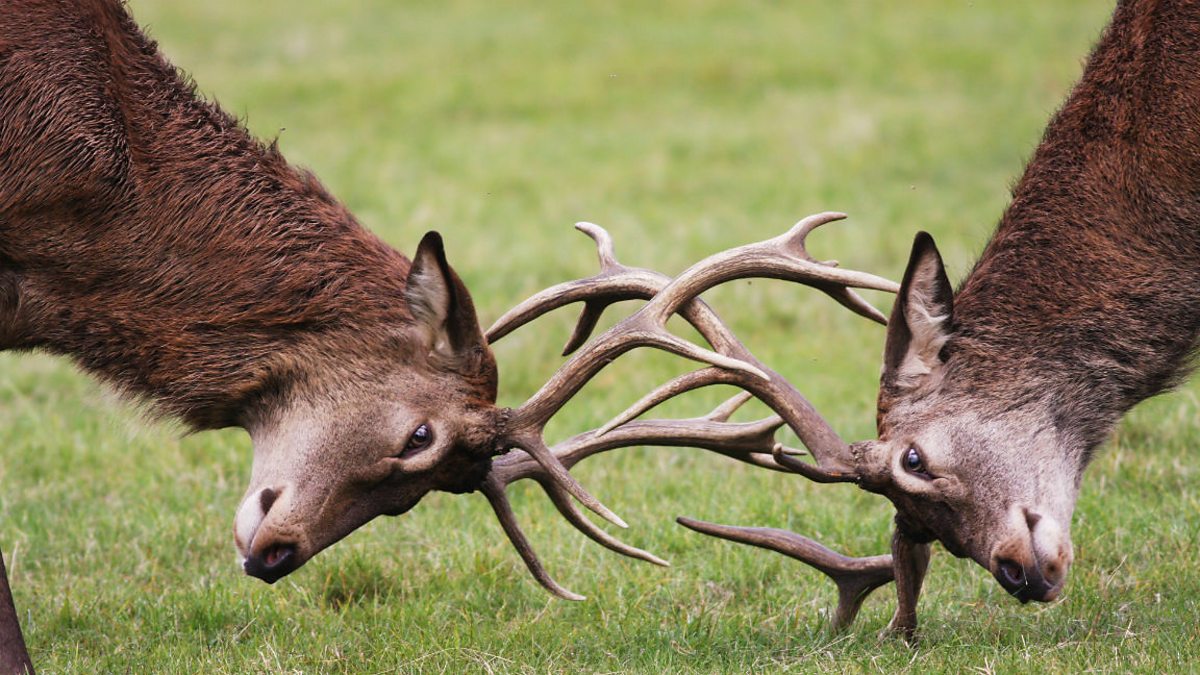
competition
What happens to the 90% of energy that is not passed up the trophic levels?
It is sued to maintain life functions, growth, and lost as heat to the environment
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession occurs in a completely barren area with no existing soil or life, like a newly formed volcanic island,
Secondary succession happens in a previously inhabited area that has been disturbed by an event like a fire or flood, meaning it already has some existing soil and vegetation to build upon
Decreasing biodiversity may have what effects? give me 2
- decreased ecosystem resilience
- increased rate of extinctions
- decrease in natural resources
- potential loss of medicinal plants/animals
-