Biology is
What is the scientific study of life?
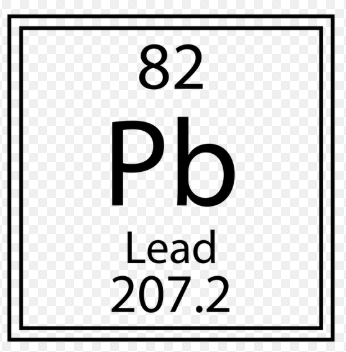 How many protons are in this molecule
How many protons are in this molecule
What is 82?
Describe hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions
What are hydrophobic means "water fearing" it will not mix with water or other polar solvents, hydrophilic means "water loving" they will mix with water and other polar solvents
Organic chemistry
What is the study of carbon-based compounds
The four type of macromolecules
What are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
The 7 characteristics of life
What is Order/Organization, Reproduction, Growth & Development, Respond the environment, energy processing, Regulation, & evolutionary adaptation?
Name the three subatomic particles and give their respective charges
What is proton (positive), neutron (neutral), electron (negative)
List the emergent properties of water
What is cohesion/adhesion, solvency, high specific heat, ice is less dense than liquid water
Which functional group contains carbon and hydrogens only
What is a methyl group
The bonds associated with all of the macromolecules
What are Carbohydrates (Glycosidic), Lipids (ester linkage), Nucleic acids (phosphodiester bond), Protein (peptide bond)?
What are the hierarchical divisions from smallest to largest
What are atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs & organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems.
The difference between isotopes and ions
What are isotopes is a difference in the number of neutrons, ions is a difference in electrons.
If given the [H+] how would you find the pOH
What is -log[H+]=pH, then 14-pH= pOH
A functional group that can act as a base an pickup H+
What is amine
Name the monomers of each macromolecule
What is carbohydrates (monosaccharide), lipids (n/a), nucleic acids (nucleotide), proteins (amino acid)
Can an organism produce offspring with another organism of the same genus
What is yes?
Define bond capacity
What is the number of electrons that an atom can lose, gain, or share to make a chemical bond?
Determine how you would find molarity
Mol of solute divided by L solution
Isomers name the three types and give the definition
What is the Structural isomer have different covalent arrangements of their atoms, cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements, enantiomers are mirror images of each other
Purines vs. Pyrimidines
Purines are a double-ringed structure (Adenine, Guanine), Pyrimidines are a single-ringed structure (Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil).
A theory
What is a broad framework or model for explaining natural phenomena, that generates a specific testable hypothesis?
Name the 4 types of bonds discussed in class and whether they are intramolecular or intermolecular
What is hydrogen bonding & van der Waals (intermolecular), ionic & covalent bonding (intramolecular)
How does a buffer work
What is the addition of small amounts of acid or base (weak)?
Vitalism vs. Mechanism
What is vitalism the belief that non-living matter is composed of different compounds than living matter? Mechanism the belief that non-living matter is composed of the same compounds as living matter
The classification of amino acids
What is hydrophobic, hydrophilic, positively charged, negatively charged?