Chemistry
Water and
Carbon
Large Molecules
_____ ____: All living things are composed of cells.
What is Cell Theory?
_____: a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical reactions.
What is an element?
______ have the same chemical formula but different structures.
What is an Isomer?
What are the four classes of macromolecules?
What is Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids?
Define the term Biology.
Biology is defined as the scientific study of life.
What are the three domains of life?
What is Archaea, Eukarya, and Bacteria?
Atoms are made of 3 types of subatomic particles. What are they?
What is Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons?
What is the difference between the solvent and the solute?
Solvent: the dissolving agent
Solute: the dissolved substance
The bond between two monosaccharides is called a _____ ______.
What is a glycosidic linkage?
Solutions with water as the solvent are called ______ solutions.
What is aqueous?
What does the Evolutionary Theory state?
Species come from other species, and species change over time.
The ____ ____ is the number of protons in each element, while the ____ ____ is the number of protons AND neutrons in an element
What is the Atomic Number/Mass Number?
Acids have a pH _____ than 7, while acids have a pH _____ than 7. _______ are solutions of acids and bases that resist changes in pH.
What is less than, greater than, and buffers?
What is dehydration synthesis? What is Hydrolysis?
Dehydration Synthesis: Building of a macromolecule -> water lost
Hydrolysis: Breaking down a macromolecule -> water gained
What is the outermost shell of an atom called?
What is the valence shell?
What are the metabolic pathways through which energy flows in an ecosystem?
What is Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration?
What are the three OR four types of bonds discussed in lecture? (Hint: 2 bonds fall under the same category)
What is Nonpolar/polar covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and weak bonds?
What is a functional group?
What is this image showing?
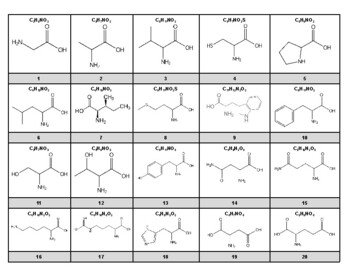
What is an amino acid structure?
Genes consist of DNA, a ____ ____ made of monomers called nucleotides.
What is a nucleic acid?
What are the fundamental properties of living systems? (Hint: there are 4 of them)
1. Living systems require energy and matter.
2. Living systems span multiple levels of complexity, acquiring emergent properties w/increasing complexity
3. Living systems are organized around the transmission and expression of genetic information.
4. Living systems are the result of evolution
Chemical reactions are said to be ______ and are determined by their ______ and ________.
What is reversible/reactants/products?
What are the four emergent properties of water important to life?
1. Moderation of Temperatures (High specific heat + heat of vaporization)
2. Cohesion of water molecules = surface tension, Adhesion to polar molecules
3. Solid is less dense than liquid
4. Solvent for aqueous solutions
Why are lipids biologically important? (List 2+ reasons)
Energy storage
Long term energy reserves in mammals
Insulation
Phospholipid bilayer
Hormones/steroids
______ bonds can form between atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements; ______ bonds are attractions between anions and cations.
What is a covalent bond? What is an ionic bond?