The four major nerves that serve the brachial plexus?
What is axillary, median, ulnar and radial
The membrane that surrounds groups of fascicles in a nerve
What is the perineurium
What activates the nociceptors?
What is pain receptors are activated by extremes of pressure and temperature as well as chemicals released from injured tissues.
True or false, the withdraw reflex is monosynaptic
What is false, it is polysynaptic
Longest and thickest nerve of the body, innervating the hamstring, adductor magnus and most muscles in the leg and foot.
What is the Sciatic Nerve?
Contains autonomic nerve fibers that join ventral rami in thoracic region
What are Rami Communicantes?
Tell us what referred pain is
What is pain from a body region that is perceived coming from a different body region
This keeps the knee from buckling when standing upright
What is a Knee-Jerk Reflex?
What are the levels of autonomic nervous system?
What is
Hypothalamus: controls the overall integration of ANS
Brainstem: reticular formation. Regulate pupil size, heart, blood pressure
Spinal cord: reflexes for urination, defecation and erection.
Describe the structure of nerve
What is
endoneurium: loose CT that enclose axons and their myelin sheaths. Schwann cells
Perineurium: CT WRAPPINGS THAT BINDS GROUPS OF AXONS INTO BUNDLES CALLED FASCICLES.
Epineurium: a tough fibrous sheath , encloses all fascicles to form the nerve.
Sensitive to changes in temperature. Hint: this is a type of stimulus
What is a Thermoreceptor?
This produces muscle relaxation in response to a tension to help prevent damage due to excessive stretch. This is also polysynaptic.
What is a Tendon Reflex?
The 3 levels of neural integration
What is receptor level, circuit level and perceptual level
State the role of schwann cells in regeneration of nerve fiber
What is
Schwann cells engulf myelin fragments and secrete chemicals that recruit macrophages, which dispose of debris and release chemicals that stimulate Schwann cells to divide
How is referred pain different from visceral pain?
What is referred pain refers to pain stimuli arising in the part of the body that are perceived as coming from another part. While visceral pain results from noxious stimulation of receptors in the organs of the thorax and abdominal cavity. Stimulation of dull aching.
The 5 different components of the reflex arch
What is the receptor, the sensory neuron, the integration center, the motor neuron and the effector
Name Cranial Nerve 7,8,9 and 10
What is
7) Facial nerve
8) Vestibulocochlear nerve
9) Glossopharyngeal nerve
10) Vagus nerve
Name the highlighted sections
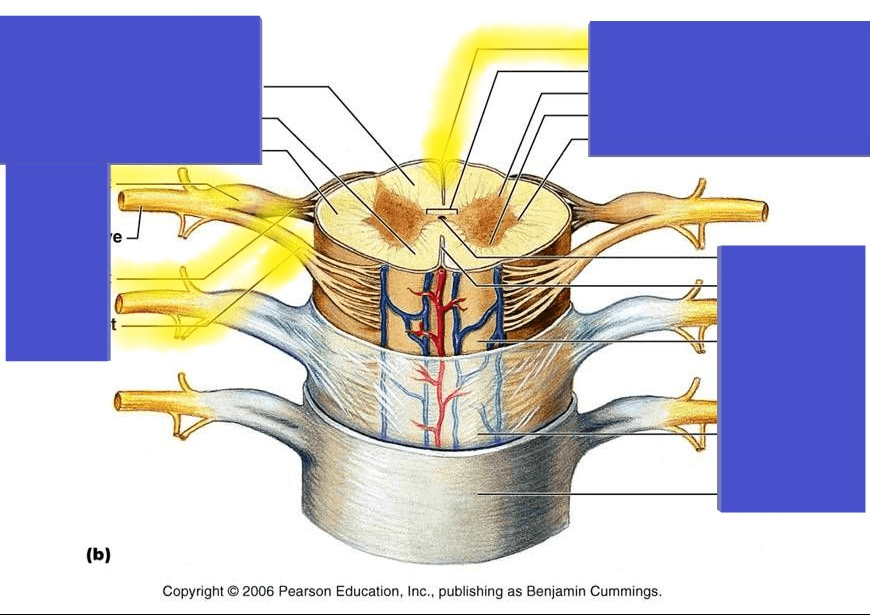
What is: Posterior median sulcus, dorsal root ganglion, dorsal root, ventral root
Name the 5 stimulus types of sensory receptors
What is mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, chemoreceptors and nociceptors.
Differentiate between stretch reflex and the tendon reflex
What is stretch reflex are monosynaptic and ipsilateral and tendon are polysynaptic.