DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing strand, what chemical group is present at the 3' end that allows for this addition, and what bond is formed?
hydroxyl group (-OH) and a phosphodiester bond.
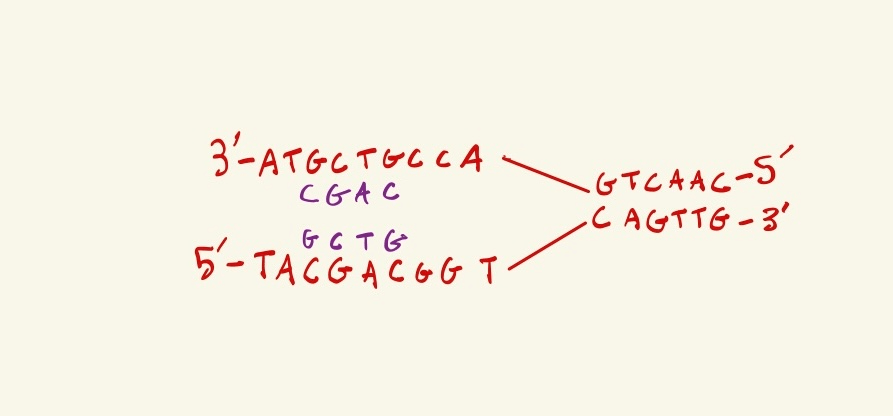
Above is DNA being actively replicated, the replication fork in moving towards the right. What are the next two nucleotides that will be synthesized in the LAGGING strand?
TA
1. Label the 5' and 3' ends of the new DNA strands being created
2. You find that the bottom strand is lagging, because the new DNA strand created from the bottom template strand can only be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction, so it goes away from the replication fork, thus the new DNA would have to be discontinously made, as the new DNA sections opening up are far to the left.
Which enzyme creates RNA primers in initiate synthesis?
Primase
Write the complementary strand of 5’- GCTAG -3’ in the 5’-3’ direction. (Hint- go backwards)
5’ - CTAGC - 3’
DNA strands run antiparallel no matter what, the answer above is just reversed
5'- GCTAG -3'
3'- CGATC -5' --------->>> (written backwards) 5'- CTAGC -3'
Whose genome is smaller, prokaryotes or eukaryotes
prokaryotes
Instead of using a primer like in DNA transcription, how does RNA polymerase know where to go?
RNA polymerase instead recognizes and binds to a specific DNA sequence called the promoter which is not transcribed itself, but rather serves as a binding platform for the transcription machinery to initiate RNA synthesis.
You are studying two types of bacteria, bacterium alpha and bacterium beta. You isolate DNA from both bacterium and you run tests to find their base composition. Bacteria alpha has a adenine composition of 22% and bacteria beta has a adenine composition of 18%. Based off of this limited information, predict which bacteria, alpha or beta, has a higher melting point.
Bacteria Beta
Explanation: After calculating percent composition of each type of base, bacteria beta seems to have a higher composition of guanine/cytosine, which are stronger due to them pairing with three hydrogen bonds instead of two, thus requiring a higher temperature to melt.
Give the 6 nucleotide long primer generated from the strand below. The primer is started at the highlighted nucleotide. Make sure to include polarity as well.

5' - CACAGU - 3'
1. Start by labeling the new strand's polarity, remember new strand has to be complementary AND antiparallel to the template strand. We know new strand's polarity will be 5'-3' so now start with the highlighted and create your sequence going to the right. Make sure your putting uracil instead of thymine because it is a primer, primer is made of RNA.
Which enzyme joins together okazaki fragments at the end of DNA replication?
DNA ligase
Write the non-template/coding strand for the RNA sequence 5’- AUGCGG -3’
5’- ATGCGG -3’
What is the amount of origin of replications in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Prokaryotes - 1 origin
Eukaryotes- multiple
What is the function of the sigma factor in RNA transcription?
Sigma factors recognize the promoter and then guide RNA polymerase to itself, those two bind to form the holoenzyme on the promoter to get RNA synthesis started.
You have three samples of DNA, and the percent composition of each type of base in each DNA sample is shown down below. The three organisms from which it came from is an RNA virus, a single stranded DNA, and a tiger. It is unknown which sample belongs to which organism. Use the info below to match which sample belongs to which animal
Sample A
Adenine(A): 14% Cytosine(C): 36% Thymine: 14% Guanine: 36% Uracil: 0%
Sample B
Adenine(A): 30% Cytosine(C): 20% Thymine: 0% Guanine: 20% Uracil: 30%
Sample C
Adenine(A): 28% Cytosine(C): 12% Thymine: 33% Guanine: 17% Uracil: 0%
Sample A- Tiger
Sample B- RNA Virus
Sample C- Single Stranded DNA
Which strand of DNA would be most impacted if DNA ligase was missing during DNA replication?
The lagging strand would be most impacted as it is crucial for joining the many okazaki fragments that are causes by the discontinious synthesizing.
Identify key differences between DNA Polymerase III vs DNA Polymerase I
DNA Polymerase III - synthesizes new strands of complementary DNA in both leading and lagging strand
DNA Polymerase I -At the end of DNA replication, this enzyme goes to the lagging strand and removes RNA primers (5' to 3' exonuclease activity) and adds back in actual DNA, or in other words it fills in the gaps between the okazaki fragments generated in the lagging strand.
Both: 5' to 3' polymerase activity and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
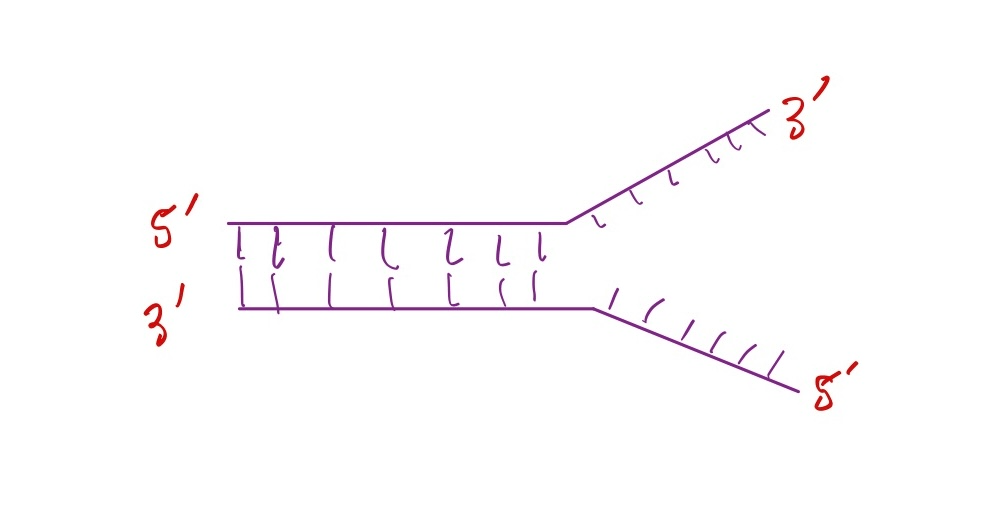
Which strand is the leading strand?
Top strand
Explanation: the direction of DNA synthesis of the top strand goes in the same direction the replication fork is opening, so it can be made continously.
What are the protective ends of eukaryotic chromosomes called, which are not found in prokaryotic DNA?
Telomeres
There is gap between the promoter sequence and the coding sequence, this gap gets ____ but not ____
transcribed, translated
Explain why DNA is more stable than RNA.
the presence of a 2'- OH group in ribose of RNA is more reactive towards chemical reactions, making RNA overall less stable.
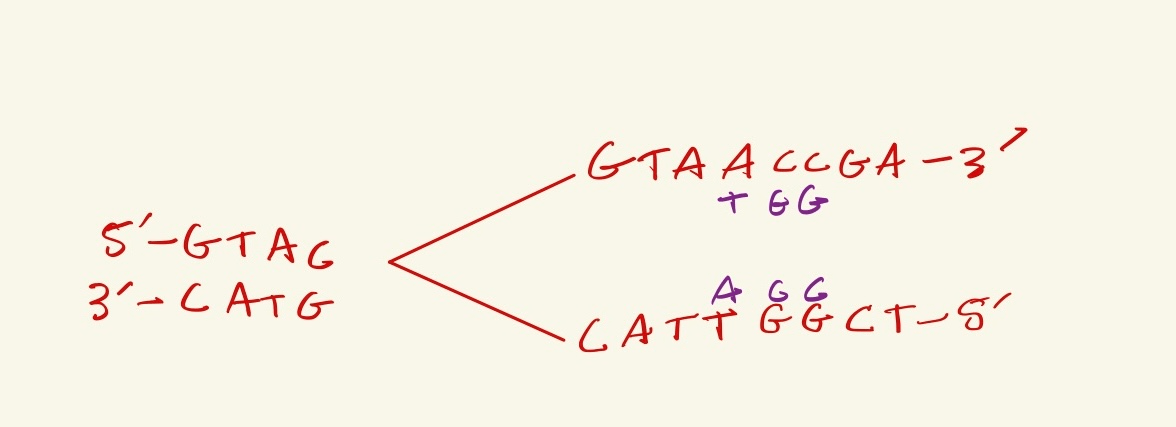
Above is DNA being actively replicated, the replication fork in moving towards the left. What are the next three nucleotides that will be synthesized in the LEADING strand?
TAC
1. Label the 5' and 3' ends of the new DNA strands being created
2. You find that the top strand is leading, because the new DNA strand created from the top template strand can only be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction, so it goes toward the replication fork, thus the new nucleotides would be TAC
Without single stranded DNA binding proteins, what would happen?
Single stranded binding proteins keep each individual strand of DNA straight and still apart after it has been unzipped by the helicase. Without these SSBs, the complementary bases would start reconnect with one another in the same strand, giving result to a hairpin like structure. Or the complementary bases from both separated strands could rejoin, forming a double helix again.
Which strand is the template strand for the RNA sequence 5’- UUGGAC -3’
5’- AACCTG -3’
5’- GTCCAA -3’
3’- TTCCTG -3’
3’- GCGAC -3’
None of the above
B
1. Write out the template strand
2. Reversing the sequence formed by step above results in the answer B
Key similarities in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication.
- both processes are semiconservative, one original strand and one new daughter strand
- Both processes involve DNA polymerase synthesizing in the 5' to 3' direction
What are the two differences and the 2 similarities between RNA and DNA polymerase
Differences
1. RNA polymerase does not require a primer, it requires a promoter instead
2. RNA polymerase unwinds DNA, so no helicase is needed in DNA transcription.
Similarities
1. Both add nucleotides in 5'-3' direction
2. Both form phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
What are some exceptions to Chargaff's Rule?
RNA - Chargaff's rule does not apply as RNA is single stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine
- Single Stranded DNA - Chargaff's Rule does not apply to single strands as there is no complimentary DNA strand to go with it, it is just one strand with bases in a random order, so amount of A would not necessarily equal to T, and G would not necessarily equal to C
- High Mutation Rates - Mutations can involve swapping a base out of a pair for another one, causing mismatching, overall this would result in base composition to deviate from expected ratios.
Below is a strand of RNA made from a template DNA strand, what is the sequence of the coding strand? Include polarity as well.
5' GCAUUU- 3'
5' -GCATTT -3'
Explanation: Define the DNA strands, the template strand is used to create the complementary strand, the coding strand is the other strand that was not used as the template, it would expect to have the same polarity and sequence as the RNA generated, except Uracil is replaced with Thymine
How does the topoisomerase work to relax supercoil?
The helicase unwinds the two strands of DNA, this causes the still wound DNA double helix to over twist because of the extra strain. Topoisomerase offers a solution by cutting one or two strands of DNA and then resealing the DNA to remove over twisting ahead of helicase coming and unwinding the double stranded DNA.
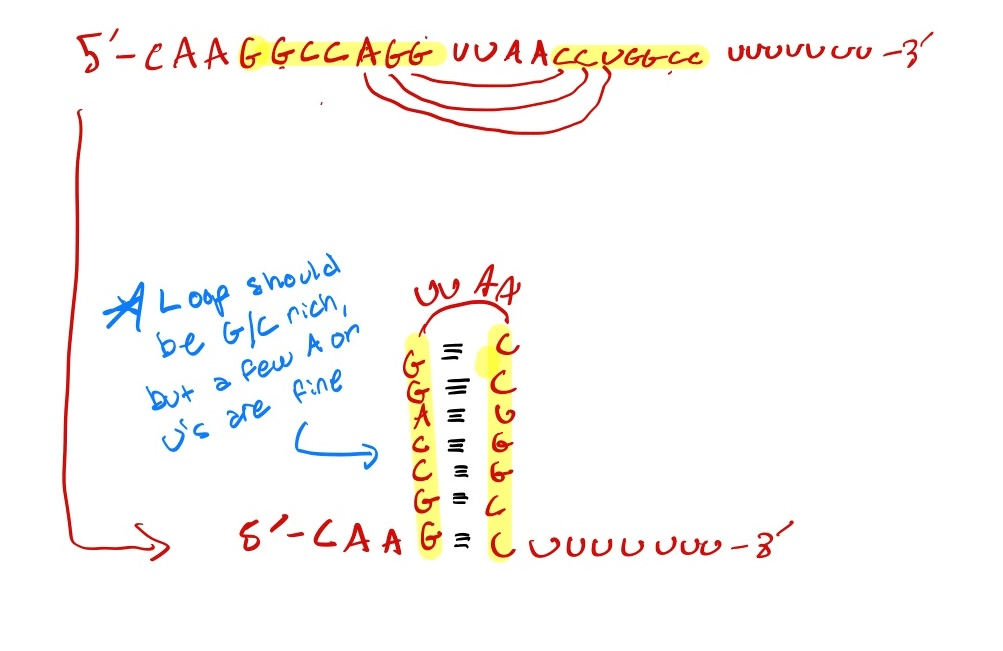
5’ -CAAGGCCAGGUUAACCUGGCCUUUUUUU -3’
Draw out the structure that would result from this RNA transcript.
What's a problem that occurs for eukaryotes as their DNA is linear, and not circular like prokaryotes?
Chromosome shortening
Explanation: Within eukaryotic DNA replication, enzymes can add nucleotides only to the 3' prime end of a growing linear DNA strand, doing so requires a primer to start with. That primer offered a pre existing 3' end for DNA polymerase to add nucleotides to. When the replication fork reaches the end of the linear strand, the RNA primers are removed. The problem arises at the very end of the lagging strand. When the last RNA primer is removed, there is no available DNA or primer upstream of it to provide the necessary 3' end. The DNA polymerase cannot initiate synthesis of the final segment to fill the gap. As a result, small sections of DNA at the ends — called telomeres — get shorter with each round of replication.This is not a problem in prokaryotes, as their genome is rather circular.
When performing RNA transcription, Give two examples of what the untranslated region between the promoter and coding sequence can become.
Transfer RNA and Ribosomal RNA
An untranslated region can still be active RNA molecules