What is the Central Dogma of biology?
DNA --> (transcription) --> RNA --> (translation) --> Protein
Please list the three overall steps of translation.
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Which type of organism has promoters? Which type of organism has introns?
What is the genome of the Covid-19 virus?
linear mRNA genome - immediately infectious when injected into host cell
Which type of mutation is passed on to offspring?
Germline mutation
If a mutant grew on complete media but not on minimal media, what did Beadle and Tatum deduce?
Nutritional mutant - grow on single amino acid media to figure out nutritional pathway.
What are the three sites in a ribosome?
DAILY DOUBLE: What are their functions?
P - peptidyl - holds tRNA with growing peptide chain
A - aminoacyl - site for tRNA with next amino acid in sequence to enter ribosome
E - exit - not actually occupied by tRNA; exit site for exhausted tRNA's
DNA pol III has proofreading activity, RNA pol does not
RNA pol has helicase activity, DNA pol III does not
RNA pol can synthesize de novo, DNA pol III requires primer
How are myocytes (muscle cells) and osteocytes (bone cells) able to perform different functions?
Principle of differential expression - these cells contain the same the same genome but express different parts of it (different genes).
How many SNPs are you likely to share with your one of your grandparents?
1/4
 What will the anticodon of a tRNA carrying threonine be?
What will the anticodon of a tRNA carrying threonine be?
UG_
Account for the energy used in the three steps and explain why energy is being used.
Initiation: 1 GTP - recruitment of large subunit to small subunit with bound mRNA
Elongation: 1 GTP - recruit charged tRNA to ribosome; 1 GTP - translocation of ribosome to next codon
Termination: 2 GTP - dissociation of ribosomal subunits
DAILY DOUBLE: What is the function of each modification?
5' Cap - allows for recognition by ribosome
Splicing - removes introns from CDS and fuses exons together
3' Poly A tail - stabilizes mRNA and protects against degradation
How does a zygote result in a fully functional organism with multiple different cell types?
Zygote divides using mitosis millions of times to produce ample cells. The resulting cells contain exactly the same genome (principle of genetic equivalence). The resulting cells start to express different sets of genes allowing them to differentiate into the different cell types (principle of differential expression.)
Of all the mutations studied in class, two of them are most likely to be the most harmful. Pick one of these and explain why.
Nonsense mutation - premature stop codon results in truncated protein
Indel - possible frameshift mutation causes almost all amino acids from that point on to be wrong.

Consider the following gene sequence: AUGACACUAGAG
How is the protein product affected if the underlined C was deleted from the gene sequence?
Initial protein product: met-thr-leu-glu
New gene sequence: AUG AAC UAG AG
frameshift
New mutant protein product: met-asn
A scientist is observing a mutant cell line. She observes that initially translation proceeds normally but soon translation rates decline and quickly stops. She also observes that when she exogenously provides charged tRNA's translation resumes and then stops again. Where does the mutation lie?
mutant Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase - unable to charge tRNA's
When the cell is young it inherits some charged tRNA's from parent cell which allow for initial translation. When these tRNA's are depleted translation stops. Exogenous insertion of tRNAs allows for resumption of translation but stops again when these are exhausted as well.
During DNA replication, DNA Pol III made an error in the template strand and failed to correct it. During this error, the codon ATG was changed to ATT. What is the likely impact of this error on the protein product?
ATG WOULD NOT RESULT IN AUG IN THIS CASE. Remember, template strand so mRNA would be complimentary so ATG is actually UAC (tyrosine) on the mRNA strand.
ATT means UAA on mRNA which is a stop codon = premature termination leading to truncated (and most likely dysfunctional) protein
Explain how the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines confer immunity to humans.
Moderna and Pfizer vaccines contain the mRNA of the Spike protein particles of a Sars-CoV-2 virus.
These mRNAs are translated by host cells.
Host immune cells then recognize these protein particles as foreign and attack it. This immune response produces antibodies and immune memory.
The antibodies and immune memory are then used by the host immune system when it encounters an actual Sars-CoV-2 virus, by recognizing the Spike protein.
Which of the following inheritance patterns is not possible?
(Pull up associated image)
2, 3
While conducting their experiment, Beadle and Tatum come across the following results in a few nutritional mutants:
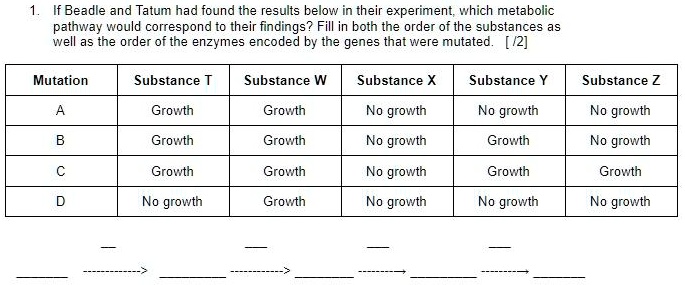
Please list the complete metabolic pathway.
X --(C)--> Z --(B)--> Y --(A)--> T --(D)--> W
Substance with least growth has to be at the start. Substance with most growth is the ultimate product.
Enzyme with most growth is the earliest. Enzyme with least growth is the latest.
A scientist is observing a mutant cell line. They observe that this cell is unable to produce protein. They notice that the cell is undergoing transcription, contains charged tRNAs and has an abundance of GTP. They also find that some of the mRNA is bound to some rRNA. Where does the mutation lie?
mutant large subunit
Cell has all the materials it needs to conduct translation: mRNA, charged tRNAs and energy. The mRNA bound to ribonucleoprotein is the mRNA bound the small ribosomal subunit. Therefore the only piece missing is the large subunit.
A scientist is observing a mutant cell line. They observe that regardless of glucose and lactose levels in the cell, lactose is never digested. They notice that RNA pol can successfully bind to the promoter but no functional lactase is produced. Where do the mutation(s) in the operon lie?
mutant repressor - unable to bind lactose so it never leaves the operator
mutant lactase gene - the operon works just fine but the protein product is dysfunctional so no lactose is digested.
Explain the "Dolly the Sheep" cloning experiment and what it allows us to conclude.
Despite three different sheep being involved in this process, the offspring was an exact clone of the nucleus donor. This means that somatic cells contain the entire genome necessary to create a full organism.
What mutation causes Sickle-Cell Anemia? Explain the prevalence of Sickle-Cell Anemia in Africa.
E6V --> hemoglobin crystallizes resulting in sickle shape of red blood cell.
Sickle cell allele confers some resistance to malaria. This results in selection for heterozygosity of the sickle-cell trait.