Plus likes...
What is Minus?
The two primary lipid types found in a cell membrane are...
What are phospholipids and cholesterol?
The functional monomers of a protein are...
What are amino acids?
The functional monomeric unit of a carbohydrate is the...
What is a monosaccharide?
The functional monomeric unit of a nucleic acid is the...
What is a nucleotide?
Polar and non-polar compounds don't like each other because of this kind of difference in the C-C bonds in the non-polar compounds and C-O covalent bonds in the polar ones...
What is the unequal sharing of electrons?
The primary monomeric unit of a lipid is the...
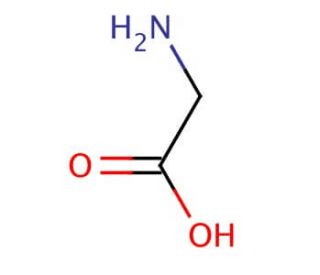
The name of the amino acid shown in the picture.
What is glycine?
Branched carbohydrate polymers made in the muscles of animals are called...
What is glycogen?
This atomic property makes the terminal phosphate of ATP unstable and good for transferring energy to chemical reactions that need it.
What is electronegativity?
Detergents can bring some hydrophobic proteins into a polar solution because of the existence of these two regions of the molecule.
What are polar and non-polar regions?
The primary transport and storage form of lipids are...
What are triglycerides?
The backbone of a protein is composed of repeats of these three atoms (in the correct order).
What is NCC?
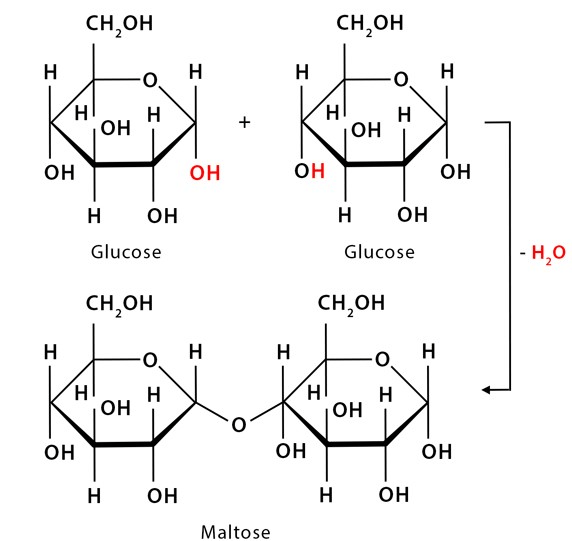
The process shown in the figure is called...
What is dehydration synthesis?
The connections/bonds between deoxynucleotide monomers in a DNA molecule are called...
What are phosphodiester bonds?
This is the difference between electrostatic interactions between a protein and another protein, and a protein with a nucleic acid.
What is, there is no difference?
Describe the polar and non-polar regions of a phospholipid (correctly assigned).
What are head-group/phosphate polar, and fatty acids tails non-polar?
These bonds connect neighboring amino acids in a polypeptide chain and are formed through dehydration synthesis.
What are peptide bonds?
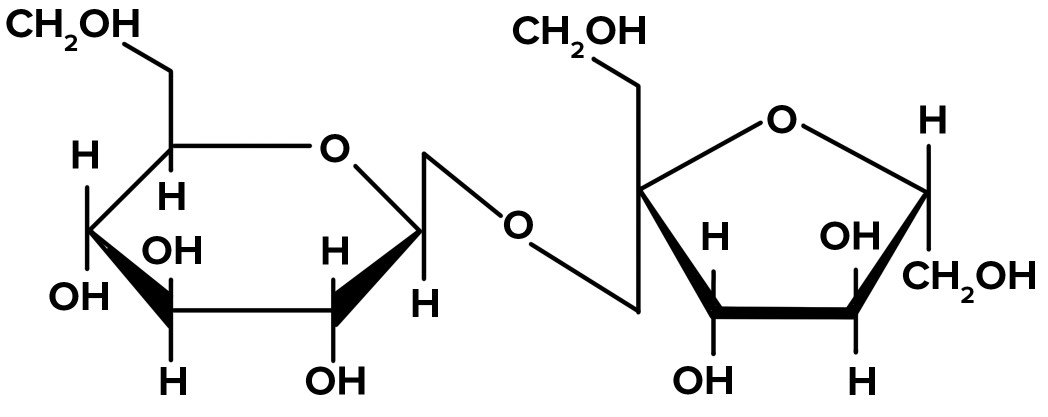
The two monosaccharides that compose sucrose are...
What are a-glucose and fructose?
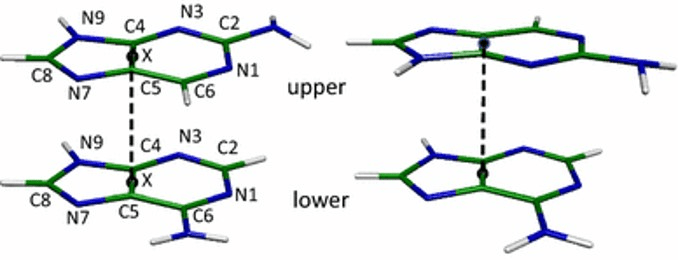
The interactions between bases "inside" the DNA double-helix structure, if they are on the same strand.
What are base-stacking, Pi interactions, or hydrophobic interactions?
The SARS-CoV2 virus has increased its ability to bind to and infect human cells by tightening its interactions with glycosylated proteins on the surface of cells. Name the unifying truth exhibited in this example.
What is, plus likes minus?
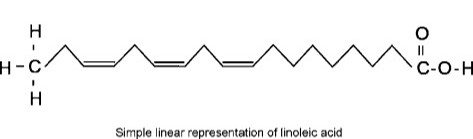
Linoleic acid shown above disrupts these non-covalent interactions by having multiple double bonds in its structure.
What are hydrophobic interactions?
If a soluble protein folds to obey the polar/non-polar rule, but still contains some hydrophobic amino acids, those amino acids will be located in this part of the spherical protein.
What is in the middle?
Polar carbohydrates that decorate the ends of lipids and proteins add specificity to cell-cell and cell-microbe interactions through these unifying truths of biochemistry.
What are plus likes minus, like charges repel each other, and polar and non-polar don't like each other?
Protein interactions with nucleic acids that DO NOT depend on the sequence of bases have this overall charge on the interacting surface.
What is positive?