What's the most basic level of organization ?
Chemical level
What's a covalent bond ?
The shared electrons in a mutually stabilizing relationship.
Reactant --> ?
Product
What's an inorganic compound
Bonus 15 points - what's an acid ?
Inorganic compound → a substance that does not contain both carbon and hydrogen.
Bonus - substance that release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution.
What's an organic compound ?
Bonus 25 points : what's a macromolecule ?
Organic compounds typically consist of groups of carbon atoms covalently bonded to hydrogen, usually oxygen and often other elements as well.
Bonus : large molecule
If they don't get that right they lose 100 points
What's an element ?
Bonus - 15 points if you can tell me what a compound is ?
A pure substance that is distinguished from all other matter by the fact that it cannot be created or broken down bu ordinary chemical means.
Bonus - Substance composed of two or more elements joined by chemical bonds.
What's a molecule ?
A moderately stable grouping of two or more atoms held together by chemical bond
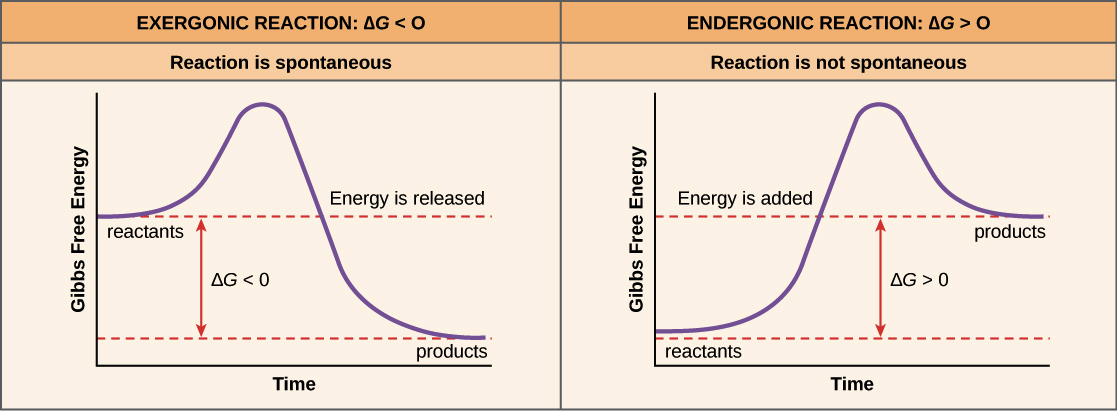
What's the difference between an exergonic and endergonic reaction?
Please Draw :)
What's an organic compound?
Bonus 30 points : what's the range for an acid, a base and what's neutral point ?
DOUBLE BONUS !! What's blood pH level ?
A substance that includes both carbon and hydrogen.
Bonus - A pH scale consists of a series of increments ranging from 0-14
A solution with a pH of 7 is considered neutral, the lower the number 1-6 is acidic and the higher the number 8-14 is basic.
BONUS BONUS : 7.4 pH (7.35-7.45)
What are the four most important organic compounds ?
Carbohydrates,
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids.
How many electrons fill the valence shell ?
8
If this isn't answered correctly they lose 200 points
What do the opposite bonds of anions and cations do ?
Bonus 20 points - what's a hydrogen bond ?
Mutual attracted to each other so they stay close together and form an ionic bond
Bonus - formed when a weakly positive hydrogen atom already bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom from another molecule.
Draw a synthesis, decomposition and exchange reaction
(A + B = AB)
(AB → A + B)
(A + BC → AB + C) OR
(AB + CD → AD + BC)
When do salt ions form ?
When ions form ionic bonds
How does carbon share electrons with other atoms?
Bonus 20 points : what is a long carbon chain referred to as ?
Carbon atoms share with other carbon atoms, often forming a long carbon chain
Bonus : (carbon skeleton)
What is matter ?
Bonus 25 - what is Mass ?
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
Bonus - amount of matter contained in an object
True or False ? hydrogen ions are hard to break ?
false :)
GET 10 POINTS
What is Work ?
Bonus 20 points for each
- What is radiant energy ?
- What is electrical energy ?
Mechanical energy directly powers the movement of matter
Bonus:
- Radiant energy is energy emitted and transmitted as waves rather than matter.
- Electrical energy contributes to the voltage changes that help transmit impulses in nerve and muscle cells.
Give an example as to why water is so important to human life
Bonus 30 points - what's a base ?
Water as a lubvricant and cushion
A heat sink → substance or object that absorbs and dissipates heat but does not experience a corresponding increase in temperature.
Water as a Component of Liquid Mixtures (as a solvent)
Bonus - substance that releases hydroxl ions (OH-) in solution or one that accepts H+ already present in solution.
What's a monomer ?
Several “copies” of single units, like beads in a long necklace, these monomers link covalent bonds to form long polymers
What are the most abundant elements in the body in order of concentration?
Bonus 50 points if you can tell me what isotopes =
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
Bonus : stable
What are the three types of bonds ?
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen
What's a factor that will influence rate of chemical reaction,
Shhh.. if they say temperature they lose 50 points :)
Properties of the reactants, temperature :), concentration and pressure + enzymes and other catalyst.
What's the difference between strong and weak acids/bases ?
Strong acids are compounds that release all of their H+ in solution, they ionize completely.
Weak acids do not inoize completely, some of their hydrogen ions remain bonded within a compound in solution.
Strong bases release most of their OH-
Weak bases release only some OH- to absorb only a few H+
What are the functioning groups ?
Bonus 50 : what's the structure of ATP
Hydroxl
Carboxyl
Amino
Methyl
Phosphate groups.
Bonus : ATP is composed of a ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three phosphate groups
What is a radioactive isotope (radioisotopes)?
A radioactive isotope (radioisotopes) → isotope whos nucleus readily decays giving off subatomic particles and electromagnetic energy.
A 2.5 question, even though you didn't want it..
double points - what are the three subunits nucleotides are composed of ?
Bonus 30 points - how do the bases connect ?
one or more phosphate groups
one pentose sugar: deoxyribose or ribose
a nitrogen containing base : adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine or uracil
Bonus : A-T(U) and C-G
TRIA :)
an exchange reaction is a reaction where both ?
synthesis reaction and decomposition reaction occur :)
BONUS 45 + GO AGAIN
What are the two types of chemical reactions involve the creation or the consumption of water ?
Please draw :)
What's the function of carbohydrates ?
Bonus 100 : what does cellular respiration look like?
In the the breakdown of glucose for energy, molecules of ATP are produced.
Bonus : cellular respiration = C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Electrons tend to stay in certain regions of space called ?
electron shell
What's a crystal ?
Ex. The attraction of many sodium and chloride ions results in the formation of large
groupings called crystals.
DOUBLE POINTS : what's the difference between DNA and RNA ?
DNA = contains deoxyribose plus one phosphate group and one nitrogen-containig base. (choices - Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine)
RNA = contains ribose, one phosphate group, and one nitrogen-containig base (choices - Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Uracil)
what property is critical to the function of ions in transmitting nerve impulses and prompting muscle contraction
Salts dissociate into ions = electrolytes → they are capable of conducting an electrical current in
solution
TRIVIA :)
Where does the body mostly get carbohydrates from ?
plant-based foods :)
GO AGAIN!
Trivia :)
what is the 6th element most abundant in the body?
calcium :)
GO AGAIN!
By giving an example, explain a polar covalent bond.
Polar molecules occur when atoms
share electrons unequally, in polar covalent bonds. The oxygen region has a slightly negative
charge and the regions of the hydrogen atoms have a slightly positive charge
Pick a reaction influencer and explain why it works?
Shhh.. if they talk about concentration & pressure they lose 60 points
surface area :
- If chemical reactions are to occur quickly, the atoms in the reactants have to have easy access to one another. The greater surface area of the reactants, the more readily they will interact.
- Gases tend to react faster than liquids or solids.
- The larger the molecule, the greater the number of total bonds, so reactions involving smaller molecules, with fewer total bonds, would be expected to proceed faster.
Temperature :Nearly all chemical reactions occur at a faster rate at higher temperatures. The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move, and the more likely they are to come in contact and react.
Concentration & pressure : The more particles present within a given space, the more likely those particles are to bump into one another. Chemists can speed up chemical reactions not only by increasing concentration of particles but also by decreasing the volume of the space which would correspondingly increase the pressure.
enzymes and other catalyst : Catalyst → substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing anu change.
What's a buffer ?
Solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base, vise versa, a buffer can neutralize small amounts of acids and bses in body fluids.
how many saccharides are in monosaccharides, disaccharide and polysaccharides ?
Because you answered this question...
ALL or NOTHING - what are the three types of polysaccharides important to the human body?
1, 2, and multiple.
ALL or NOTHING - starches, glycogen and cellulose