Which invention from the 17th century allowed for the development of modern cell theory?
What is:
The light microscope allowed scientists to view actual cells for the first time
The six main chemical elements (NCHOPS) that make up most living things are Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), and Sulfur (S).
These elements are combine to form large, complex organic molecules, or biomolecules.
Name them:
What is:
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids,.
What is Robert Hooke known for?
What is:
Robert Hooke is most known for discovering cells in 1665, and coining the term "cell" for the small structures he observed in cork under his microscope. i
Fats, oils and cholesterol are all types of what?
What is :
Lipids
What type of transport uses ATP
What is:
Active transport
Identify the microscope in which visible light passes through the specimen. Light and is bent through the lens system, allowing the user to see a magnified image. A benefit of this microscope is that it can often be performed on living cells, so it’s possible to watch cells carrying out their normal behaviors such as migrating or dividing.
What is a light microscope!

Identify the Macromolecule:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleic-acids-5a4e299d482c5200369e58c3.jpg)
What is nucleic acid.
They contain genetic/hereditary information.
Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow are the main contributors to what theory?
What is the cell theory.
The diagram below shows the general structure of an amino acid. Which type of molecule is formed from amino acids?

What is:
Protein
Proteins are long chains of amino acids folded into specific shapes, which determine their properties and reactivity.
Define osmosis
What is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from high to low.
Can you view live cells with an Electron Microscope?
Electron microscopes uses a beam of electrons rather than a beam of light to produce an image of a specimen.
Electron microscopes can be used to examine not just whole cells, but also the subcellular structures and compartments within them.
For example of electron microscope use is the detailed, three-dimensional surface imaging of samples, like the intricate details of a flea's face, using a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).
Another example is Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) used to see & Study internal structures of cells such as organelles.
One limitation, however, is that electron microscopy samples must be placed under vacuum in electron microscopy (and typically are prepared via an extensive fixation process).
What is:
Live cells cannot be imaged with an Electron Microscope. 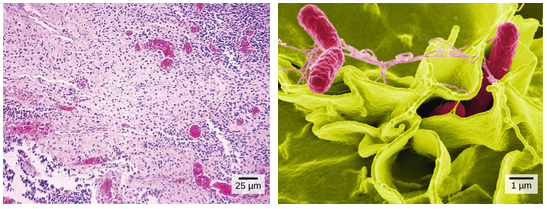
In the image above, you can compare how Salmonella bacteria look in a light micrograph (left) versus an image taken with an electron microscope (right). The bacteria show up as tiny purple dots in the light microscope image, whereas in the electron micrograph, you can clearly see their shape and surface texture, as well as details of the human cells they’re trying to invade.
Identify the macromolecule:
CHO in the ratio 1:2:1
Function: Energy
What is carbohydrate
- The cell theory describes the basic properties of all cells.
- Tell what it states.
What is:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- All new cells arise from existing cells.
What eukaryotic cell has a cell wall?
What is:
Eukaryotic cells that have a cell wall include plants, fungi, and some protists (like algae), while animal cells do not have a cell wall.
The composition of the cell wall varies between these groups; plant cell walls are primarily made of cellulose, fungal cell walls contain chitin, and algae have walls composed of various polysaccharides and glycoproteins.
Describe the cell membrane.
What is:
semi-permeable or selectively permeable
phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded within the membrane.
Can you use a Stereoscopic Dissecting microscope to observe living or dead organisms?
A dissecting microscope is also known as a stereo microscope or stereoscope. It is a low-power optical instrument used for observing three-dimensional objects and performing tasks like dissection or detailed inspection of larger specimens.
Yes, you can use a stereoscope (also known as a dissecting or stereo microscope) to observe live animals, particularly small ones. This tool is ideal for this purpose because, unlike a compound microscope, it provides a three-dimensional view and allows for the examination of entire, opaque specimens without the need for slides or special preparation.
Identify the macromolecule:
CHO
Function: Stored energy (Not primary source), 
What is:
Lipids.
Example: fats, oils, waxes, and steroids.
They are vital for life, functioning as energy storage, providing structural support for cell membranes, enabling the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, facilitating hormone production, and insulating the body.
What is the difference between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells.
What is:
Prokaryotic cells are simple. They lack membrane bound organelle and nucleus.
- Examples: Organisms from the domains Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic cells are more complex. They have membrane bound organelles & nucleus.
- Examples: Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes.
What is the difference between plant and animal vacuoles? 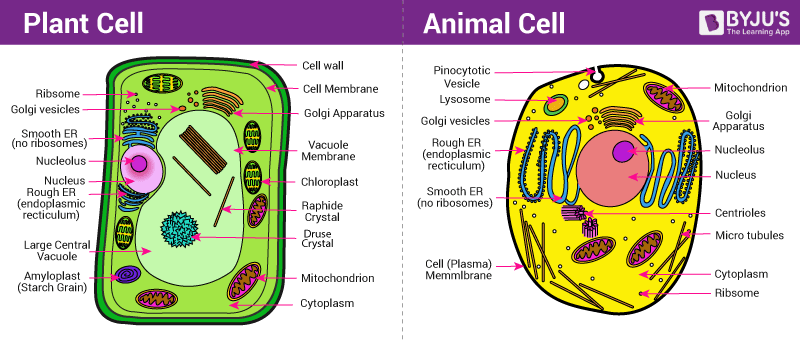
What is:
Vacuoles
Plants usually have one large/central vacuole where as animals are smaller and more numerous.
Plant vacuoles functions include: Storage tanks for water, nutrients, waste and help maintain turgor pressure. (Turgor pressure is the hydrostatic pressure exerted by water within a plant cell against its cell wall
Describe what would happen if you put an de-shelled egg in a hypertonic solution?
What is:
Is would shrink
Carmen conducted an experiment to determine if listening to different types of music would affect a person’s pulse. Her hypothesis was that pulse rate would change with different types of music. Each person listened to seven different selections of music for 30 seconds each. Each person’s pulse was taken before the music and then after each 30-second interval of music. The pulses were taken again after the music selections were completed. Based on her experiment, Carmen concluded that a person’s pulse rate changed when the person listened to different types of music. Which component is missing from Carmen’s experiment?
What is:
The experiment is lacking a control group.
Carmen should have also taken the pulse of people who were NOT listening to any music to make sure that a person’s pulse rate would not change randomly.
Identify the macromolecule:
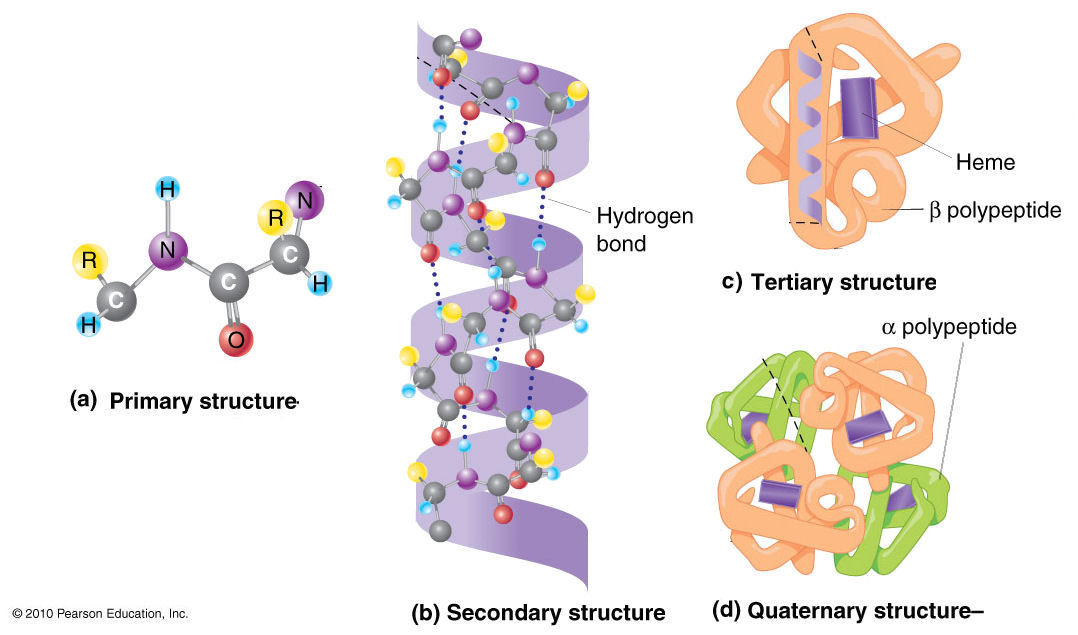
What is:
Protein
Example: Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells. It's role is to transport oxygen in the blood.
The primary structure of each subunit of hemoglobin has s specific shape and binds to oxygen.
Analogy:
Hemoglobin is the protein that carries oxygen and exists within each red blood cell. If your red blood cell was a vehicle, hemoglobin is in the driver's seat

Cell theory was first proposed in 1838. Evidence obtained through additional scientific investigations resulted in the current cell theory. Which statement describes a component of the original cell theory that was removed because of the new scientific knowledge?
What is:
Cells form through spontaneous generation. It was once believed that cells could form on their own. We now know that cells must form from preexisting cells.
Two part question:
1. What is the main job of a ribosome?
2. What kind of cell has ribosomes? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote).
What is:
The main job/function is to produce proteins.
Both Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells have ribosomes.
Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller (70S) and lack an enclosing membrane, whereas eukaryotic ribosomes are larger (80S) and are found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, in addition to within mitochondria and chloroplasts
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
What is:
Passive transport (osmosis and diffusion) do not require energy. They will occur if the substance is permeable to the membrane.
Active transport requires energy (ATP).