These biomolecules are the building blocks of life. They form muscles, enzymes, hormones, and structural components like skin and hair.
A. Carbohydrates B. Nucleic Acids C. Proteins D. Lipids
Proteins!
These simple cells include bacteria, and they have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
What is a Prokaryotic cell
This is the process in which plants and other autotrophs make their own food.
Chemical Reaction: Carbon dioxide + Water --> Oxygen + Glucose
What is Photosynthesis?
Another name for mitosis is the_______phase
A. G2 phase B. G1 phase C S phase D.M phase
M phase
Based on the image below, yellow is (dominant/recessive) and green is (dominant/recessive):

Based on the image below, yellow is (dominant/recessive) and green is (dominant/recessive):
Which of the following is not a primary role of DNA.
A. Codes for genetic information
B. Copies genes
C. Uses its code to make proteins
D. Primary source of energy in the cells.
D. Primary source of energy in the cells.
This type of cellular transport requires energy to move from a low concentration to a high concentration.
A. Active transport B. Passive transport C. Facilitated Diffusion
Hint:
What is ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Double or nothing: What is the name of the molecule, which supplies energy for this process?
This type of cell includes organelles like cell walls, and chloroplasts, which they use to capture energy from the sun (select 2 choices)
A. Plant cell B. Animal cell C. Bacteria Cell. D. Eukaryote E. Prokaryote
What is plant cells (eukaryotes)
This the process that is called the inverse of photosynthesis because it takes the products of it, and uses it to produce energy in the form of ATP.
A. Sexual reproduction
B. Meiosis
C. Mitosis
D. Cellular Respiration
What is cellular respiration?
What are the 6 phases of the cell cycle?
Hint: I pray more at the church.
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.
Triple the points: Which of the phases does DNA replication occur in?
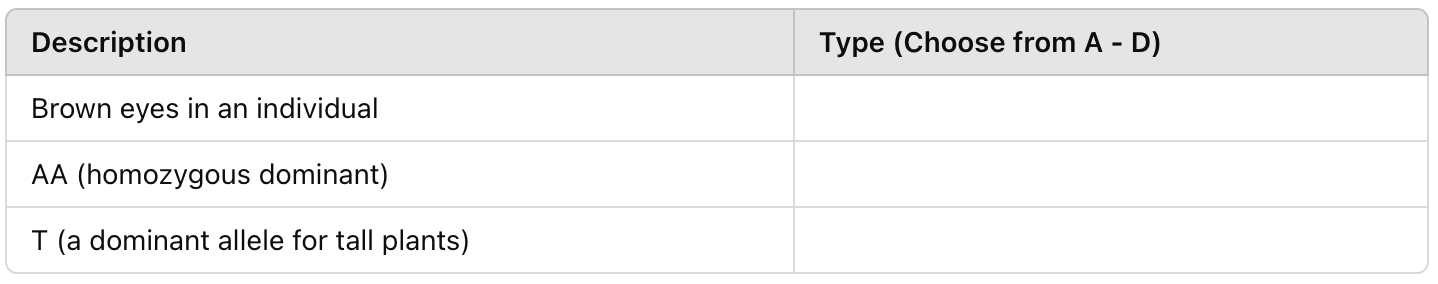
Fill in the blanks: Hint: alleles for "letters", genotype for "genes", phenotype for "physical appearance"
A. Phenotype, Genotype, Allele
B. Genotype, Allele, Phenotype
C. Allele, Phenotype, Genotype
D. Phenotype, Allele, Genotype
A. Phenotype, Genotype, Allele
Double no trouble: Give an example of a genotype, phenotype and allele.
What is the complementary strand of the DNA strand bleow?
CGCATG
Double the points: The 3' to 5' and 5' to 3' strands are called __________-parallel.
Which biomolecule belongs in each category? Choose: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
This pigment in plant cells captures and converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP for the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
A. Mitochondria
B. Cristae
C. Chlorophyll
D. green
C. Chlorophyll
This process above uses glucose and oxygen to make energy in the form of ATP.
A. photosynthesis B. Decomposition C. cellular respiration D. evolution
Cellular respiration
Suppose a medication stops cell growth by preventing replication of DNA chains. Which part of the cell cycle is disrupted by the medication?
A. G1 B. S phase C. G2 D. M phase
B. S (synthesis) phase
Bonus - 300 points: What disease can occur if cells grow uncontrollably?
According to this Punnett square ___% of the offspring will be homozygous dominant, ______ % of the offspring will be heterozygous, and the remaining 25% will homozygous (recessive/heterozygous)
As for the phenotypes, ______ % Of the flowers will be pink.
According to this Punnett square 25% of the offspring will be homozygous dominant, 50% of the offspring will be heterozygous, and the remaining 25% will homozygous recessive .
As for the phenotypes, 75% of the flowers will be pink.
Nucleic acids store _______. If a change occurs in RNA or DNA, _______ could be disrupted.
A. proteins; protein production
B. genetic information; protein production
C. chemical energy; cell division
D. carbon; energy production
B. genetic information; protein production
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks lactose -> glucose and galactose. Therefore, lactase is an ______. (select two choices)
A. protein. B. carbohydrate C. lipid D. enzyme E. nucleic acid
Protein and enzyme.
Double the points: What prefix tells you when a molecule is an enzyme??
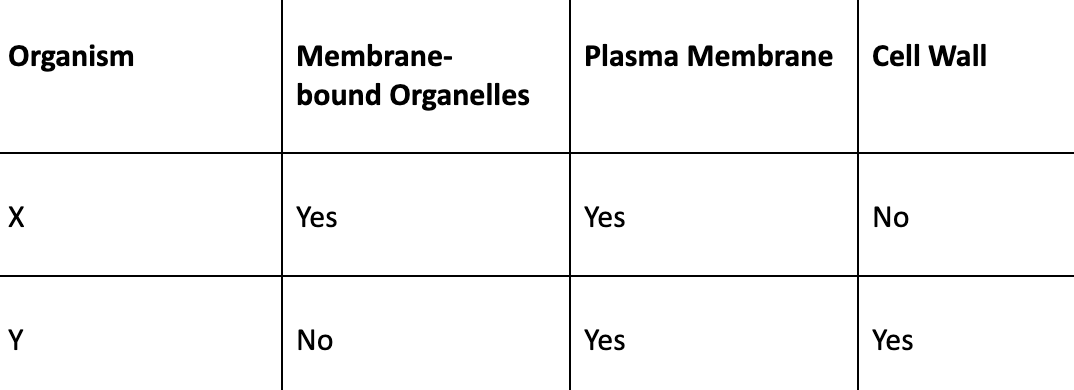
Organism X is a (eukaryote/prokaryote) and is (more/less/just as) complex as organism Y, which is a (eukaryote/prokaryote)
Organism X is a (eukaryote/prokaryote) and is (more/less/just as) complex as organism Y, which is a (eukaryote/prokaryote)
Double or nothing: Name one organelle that eukaryotes and prokaryotes share?
Which statement explains how the chemical equation for cellular respiration above demonstrates conservation of matter?
A.The number of glucose atoms is the same on both sides of the equation.
B.Hydrogen and oxygen atoms are rearranged in the reaction.
C. Glucose and oxygen change to carbon dioxide and water in the reaction
D. The number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms is the same in the reactants and the products.
D. The number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms is the same in the reactants and the products.
Which option identifies the description of each stage from 1–5 in the diagram, going in order from left to right?
A. DNA replication; cell growth; preparation for cell division; chromosome separation; cytoplasmic division
B. Cell growth; DNA replication; chromosome separation; preparation for cell division; cytoplasmic division
C. DNA replication; cell growth; preparation for cell division; cytoplasmic division; chromosome separation
D. Cell growth; DNA replication; preparation for cell division; chromosome separation; cytoplasmic division
D. Cell growth; DNA replication; preparation for cell division; chromosome separation; cytoplasmic division
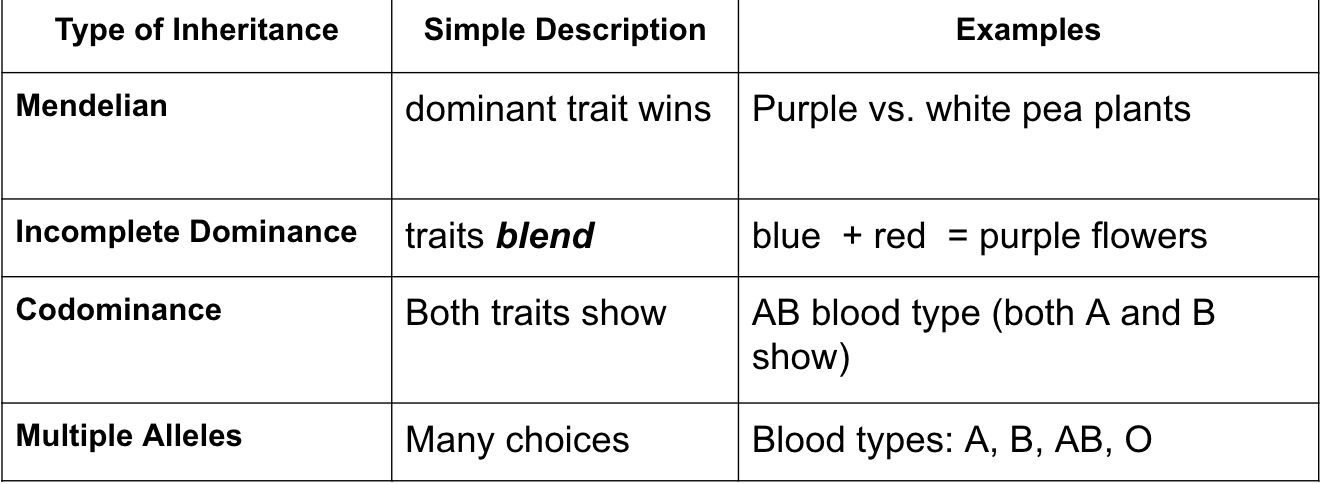
Use the table above to identify each example below as: mendelian, incomplete, codominant or multiple allele inheritance.
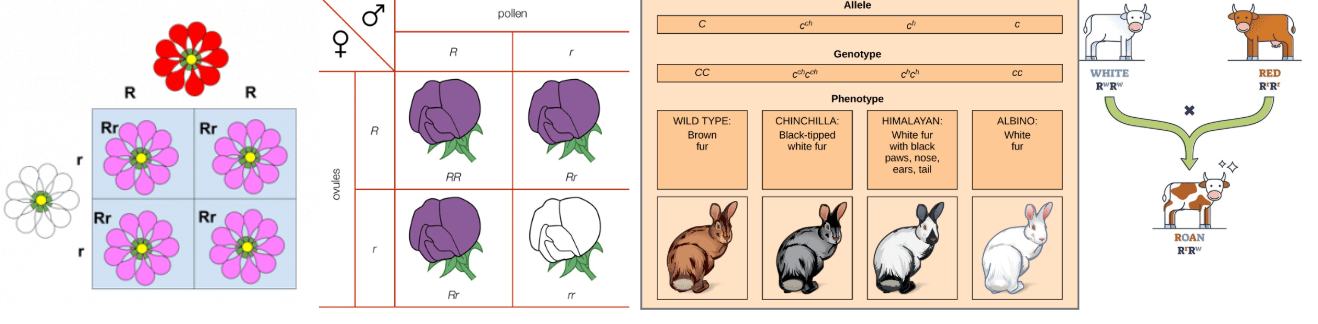
1. 2. 3. 4.
1. Incomplete - it blends
2. Mendelian - purple is dominant over white
3. multiple alleles - multiple varieties
4 codominant - Red and white share dominance
During DNA replication, DNA helicase enzyme (unzips/bonds/synthesizes) the DNA molecule and DNA polymerase (unzips/bonds/synthesizes) the nucleotide monomers together.
During DNA replication of of the cell cycle: DNA helicase enzyme unzips the DNA molecule and DNA polymerase bonds the nucleotide monomers together.
Double or nothing: what phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. prophase B. Metaphase C. Telaphase D. S phase
The graphs show the same reaction with and without an enzyme.
Which statement identifies the graph with the enzyme?
A. Graph B, because the enzyme binds to the reactant, lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur and speeding up the reaction.
B. Graph A, because the enzyme combines with the reactant molecule, producing a different end product
C. Graph B, because the enzyme absorbs the energy from the reactant, increasing the speed of the reaction
D. Graph A, because the enzyme releases energy from the reactant, changing the amount of product formed
A. Graph B, because the enzyme binds to the reactant, lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur and speeding up the reaction.
A researcher collects two specimens from a sample of pond water and takes them back to the lab, where they are prepared and placed under a microscope, as shown.
Which types of organisms are A and B? Select all that apply.
Organism A is a prokaryote because it has a chloroplast for converting energy.
Organism A is a eukaryote because its genetic material is enclosed in a nucleus.
Organism B is a eukaryote because it has a cell membrane and a cell wall.
Organism A is a eukaryotic because it has a chloroplasts which are only found in plants.
Organism B is a prokaryote because its DNA is not surrounded by a cell membrane in the nucleus.
Organism A is a eukaryote because its genetic material is enclosed in a nucleus.
Organism A is a eukaryotic because it has a chloroplasts which are only found in plants.
Organism B is a prokaryote because its DNA is not contained in the nucleus.
500 points: Where is prokaryotic DNA located?
The model shows the cycling of reactants and products in the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
To complete the model for the students, choose the option that identifies the correct labels, in order from 1-5 in the model.
A. Cellular respiration produces C6H12O6 + O2; ATP; Photosynthesis produces CO2 + H2O
B. Photosynthesis produces C6H12O6 + O2; ATP; Cellular respiration produces CO2 + H2O
C. Photosynthesis produces CO2 + H2O; ATP; Cellular respiration produces C6H12O6 + O2
D. Cellular respiration produces ATP; C6H12O6 + O2; Photosynthesis produces CO2 + H2O
B. Photosynthesis produces C6H12O6 + O2; ATP; Cellular respiration produces CO2 + H2O
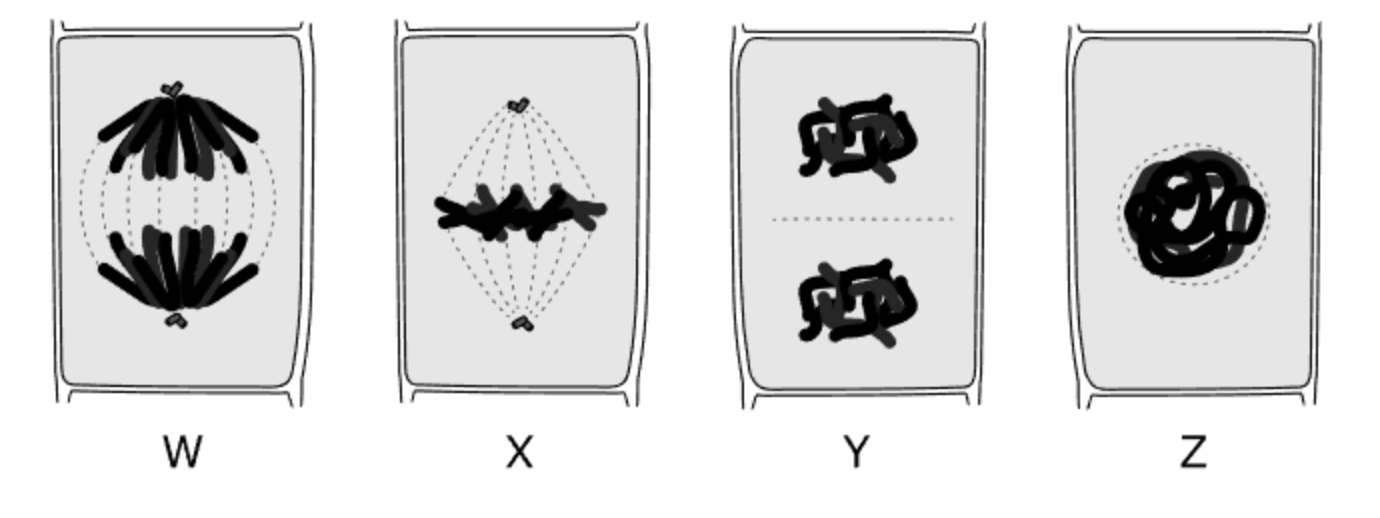 Arrange each phase in the correct order, then name:
Arrange each phase in the correct order, then name:
Prophase, Anaphase, Cytokinesis, Metaphase
W. Anaphase
X. Metaphase
Y. Cytokinesis
Z. Prophase
Prophase -> Metaphase -> Anaphase -> Cytokinesis
Carlos creates a diagram to demonstrate inheritance patterns in a monohybrid cross.
Which option identifies the genotypes labeled 1 and 2 in the diagram, in order from left to right? Hint: perform a monohybrid cross between the first two genotypes to get 1.
A. 1: AA; 2: aa
B. 1: Aa; 2: AA, Aa, aa
C. 1: Aa; 2: AA, Aa
D. Aa; 2: Aa, aa
C. 1: Aa; 2: AA, Aa
Label the DNA molecule below using the word bank: A. Antiparallel strands, B. double helix, C. nucleotide monomer, D. sugar + phosphate backbone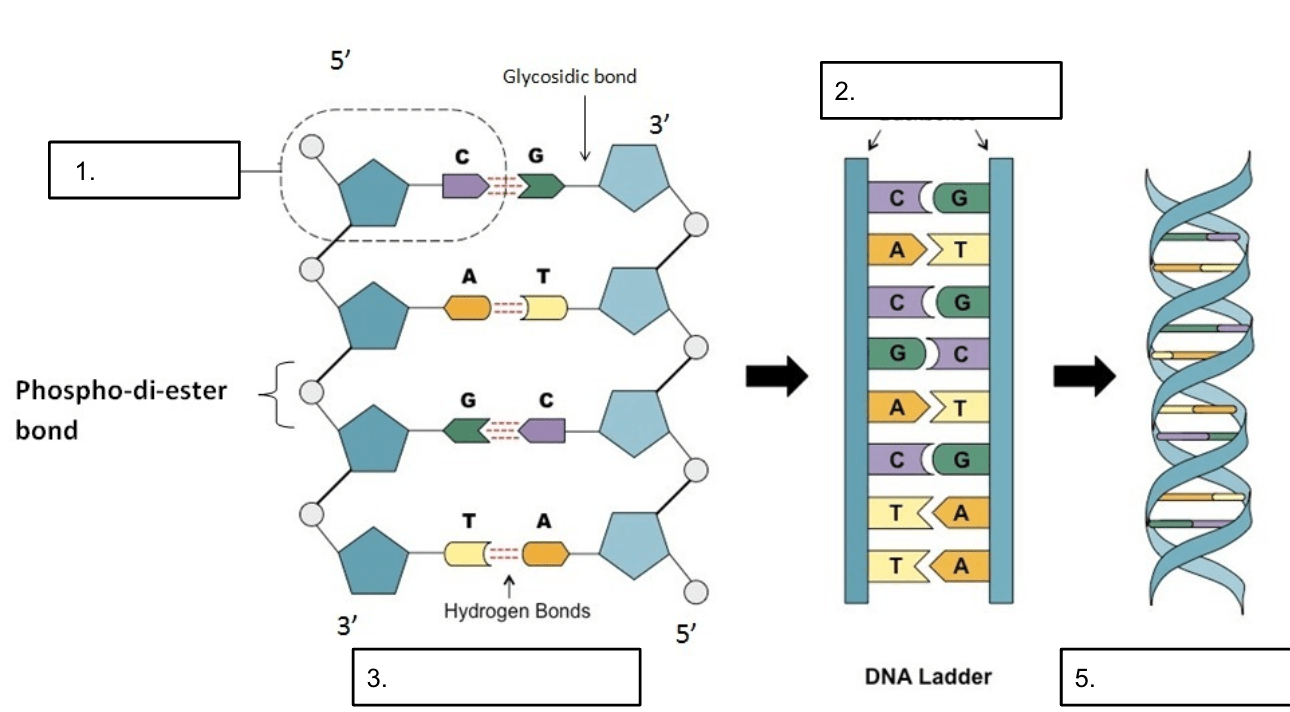
1. C. Nucleotide monomer
2. D. sugar phosphate backbone
3. A. Antiparallel strands
4. B. Double helix
