Organisms like coyotes that hunt and kill other organisms for food.
What is a predator?

The "photo" part of photosynthesis. This is where plants get their energy.
What is sunlight? -or- What is light?
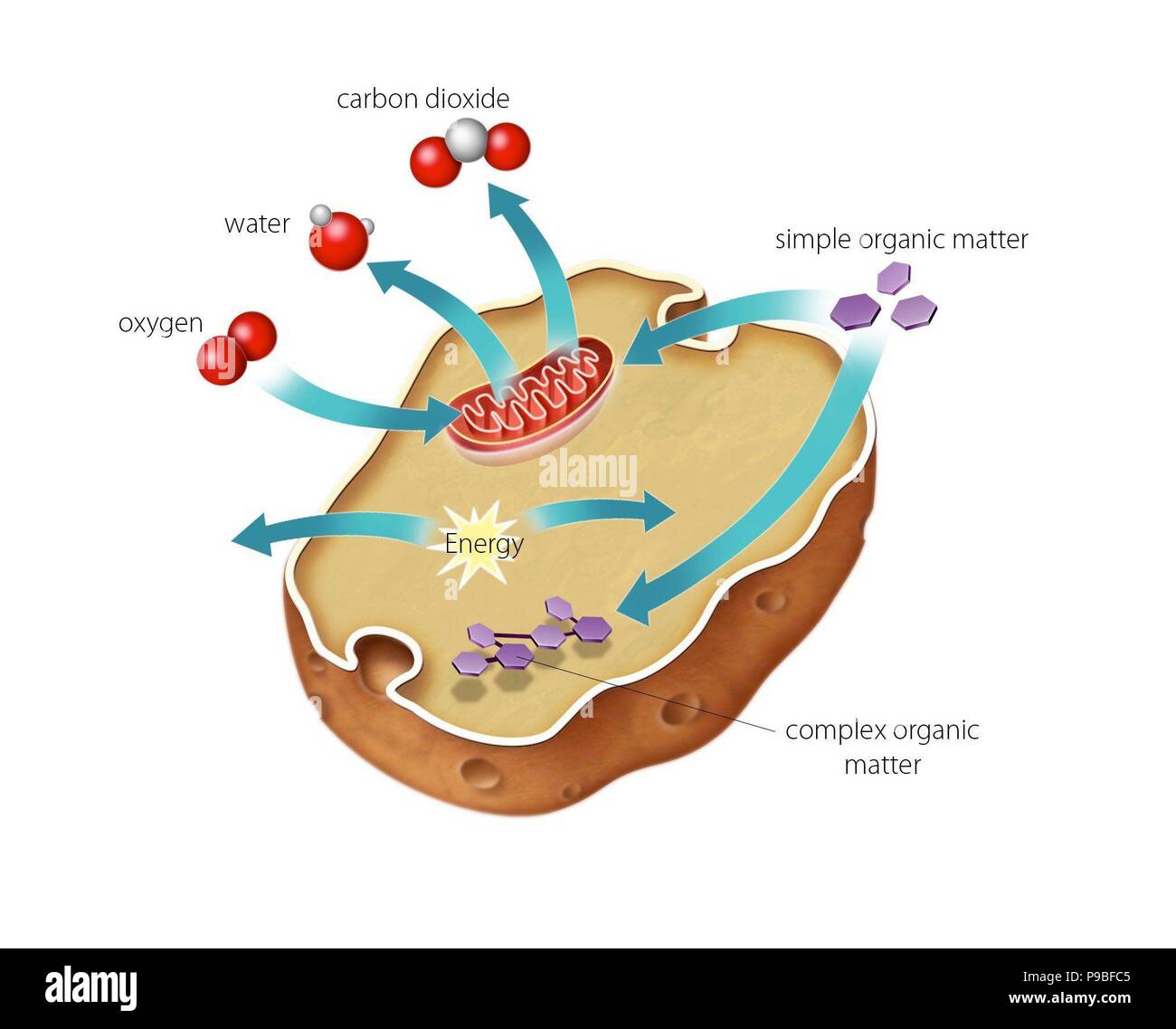
The process by which an organism releases energy from glucose.
What is cellular respiration? -or- What is breathing?
Traits are determined by genes where segments of DNA are found. The traits are also stored in this thread-like structure of nucleic acids and proteins found in the nucleus of all living cells.
What is a chromosome?
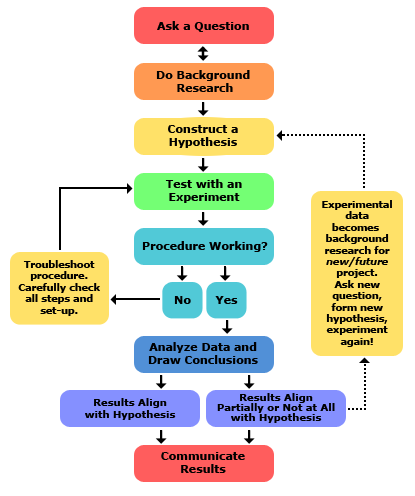
A series of steps designed to help you solve problems and answer questions.
What is the scientific method?
These are all non-living factors.
What are abiotic factors?
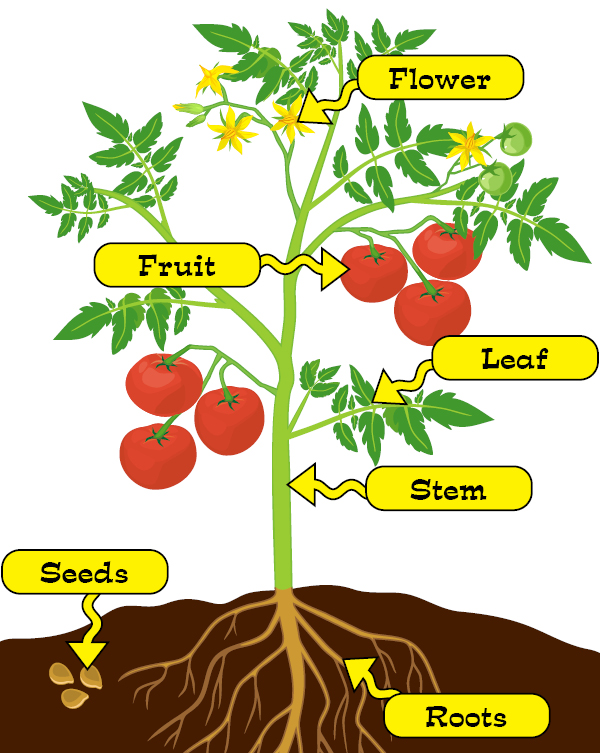
The part of the plant under the soil responsible for absorbing water from the ground.
What are the roots?

What this picture represents.
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
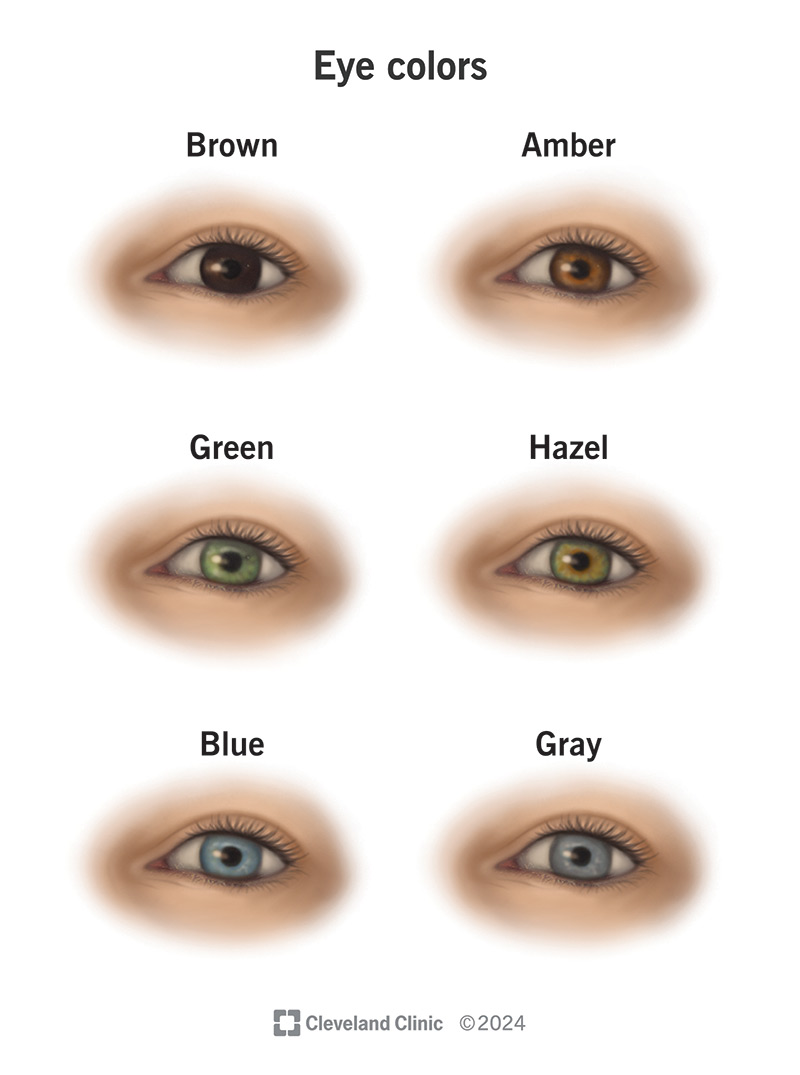
Physical traits, such as eye color, that result from gene makeup.
What is phenotype?

A tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in scientific method. It's the initial building block in the scientific method. Many describe it as an "educated guess" based on prior knowledge and observation. While this is true, this is more informed than a guess.
What is a hypothesis?
This is the primary producer in this food web.
What is grass?
This gas is produced alongside glucose during photosynthesis.
What is oxygen?

This gas is produced alongside ethyl alcohol during alcoholic fermentation.
What is carbon dioxide?
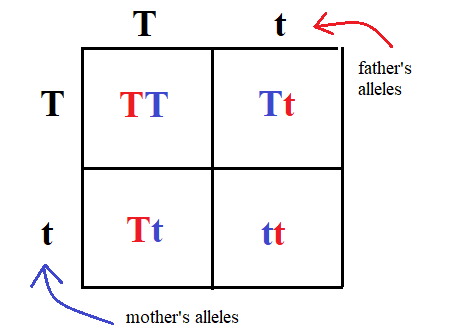
The letters that stand for the alleles for a trait. Example: TT, Tt, tt
What is genotype?
This is information gathered by the five senses that is recorded during the scientific method. For example, listening to the sound of whales.
What is an observation?
 This refers to how ecosystems maintain a biological equilibrium between the different components.
This refers to how ecosystems maintain a biological equilibrium between the different components.
What is homeostasis?

During photosynthesis plant cells capture energy from the sun and convert it into food in this molecule.
What is glucose? -or- What is carbohydrates?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_mitochondrion-5661ca005f9b583386c70c31.png)
The membrane-bound organelle where most energy is created during cellular respiration.
What is the mitochondria?
 This nucleotide pairs with cytosine in both DNA and RNA.
This nucleotide pairs with cytosine in both DNA and RNA.
What is Guanine?

This is a variable that is intentionally kept the same in all experimental groups. For example, in the balloon yeast lab we used the same size flask, the same amount of water, and the same amount of yeast.
What is a control variable?

Populations have limiting factors that keep them from growing too large. This is the maximum number of a species that can sustainably live in a given area
What is carrying capacity?

The green pigment inside the chloroplasts that absorbs and stores energy from the sun.
What is chlorophyll?
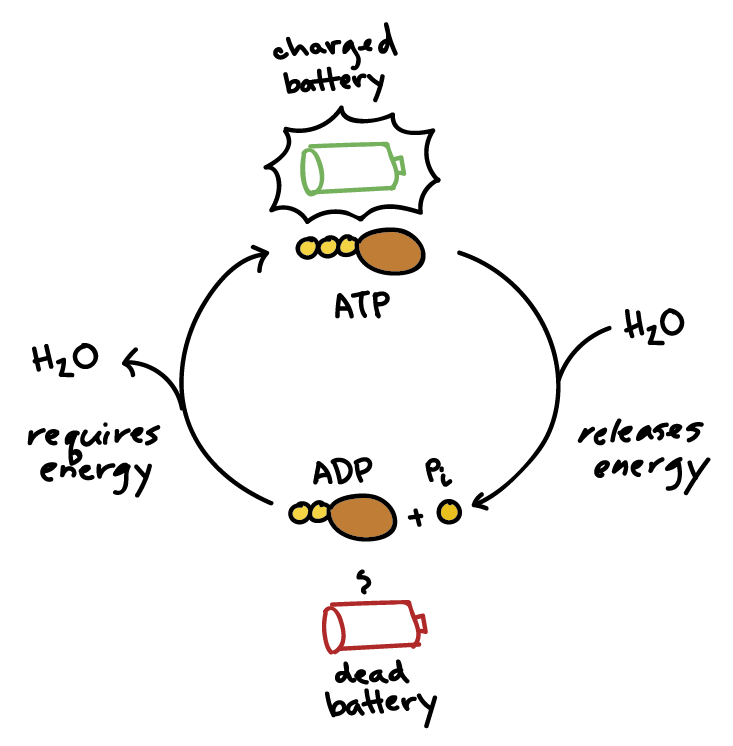
The energy molecules produced in the process of cellular respiration. This is like the "battery" or "energy currency" of the cell.
What is adenosine triphosphate?

In mRNA, this nucleotide pairs with Adenine instead of Thymine.
What is Uracil?
The variable that is deliberately changed/manipulated.
What is the independent variable?
