
The lion in this food chain is an example of this.
What is a predator?

The waste product do you breathe out during cellular respiration.
What is carbon dioxide?

The process where a species becomes better suited to its environment over generations, through changes in specific traits that enhance survival and reproduction. For example, the long necks of giraffes let them grab leaves high up in trees.
What is an adaptation? -or- What is evolution? -or What is natural selection?
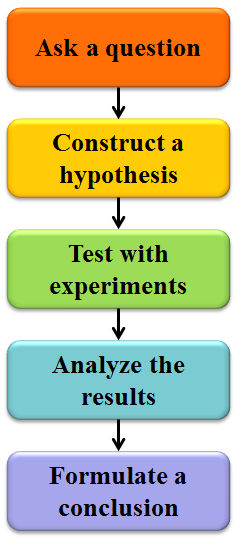
A series of steps designed to help you solve problems and answer questions.
What is the scientific method?

This letter pairs with G.
What is C?
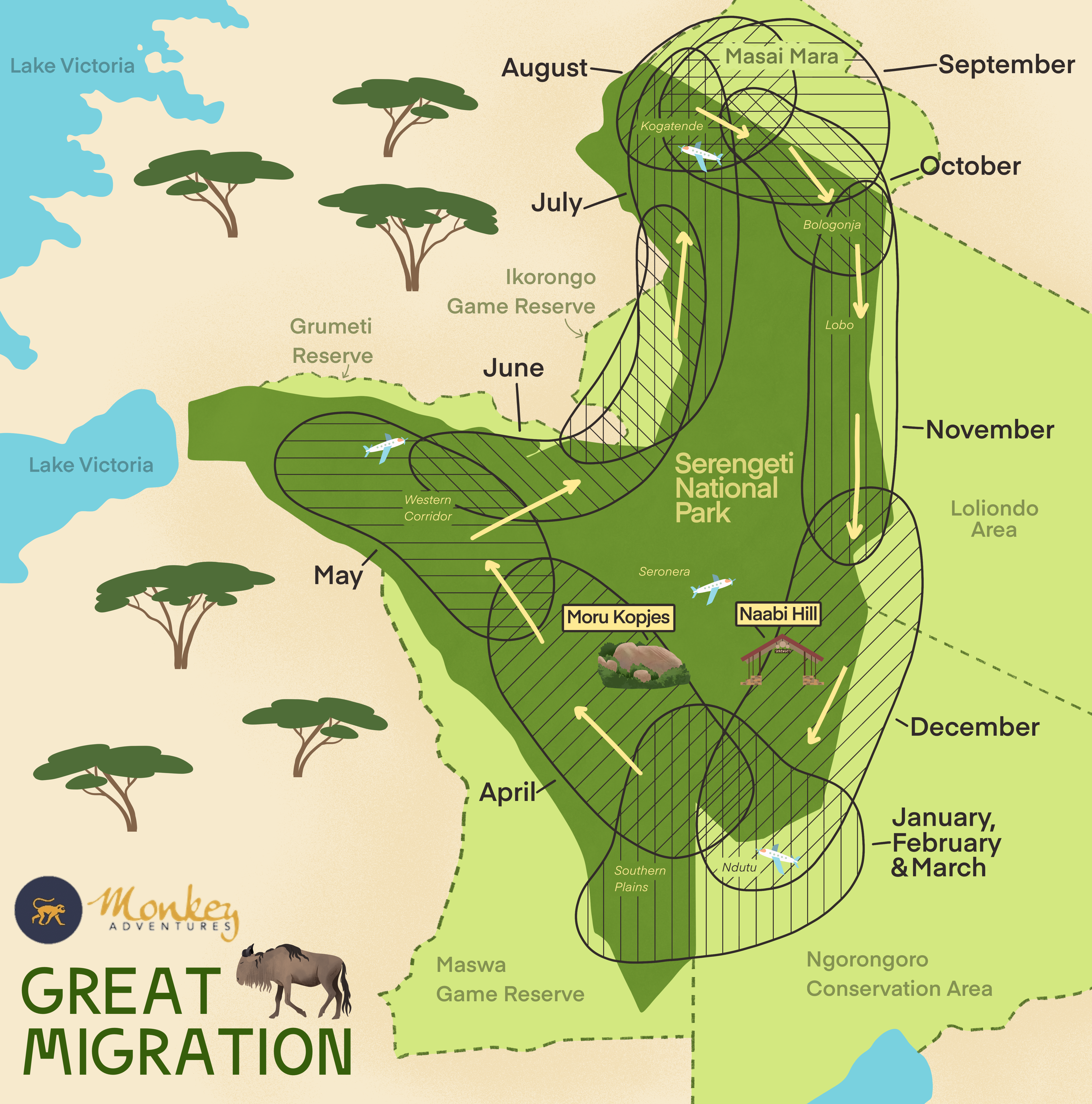
This is something that helps control how many animals an ecosystem can support. For example, wildebeest migrate because there is not enough grass for them to eat, so they must move to where there is more grass available.
What is a limiting factor?

These are the reactants or what goes into photosynthesis. Plants take these and combine them to create food.
What are carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight?

When humans select for certain traits and breed that trait into the next generation. For example, humans choose desirable traits in dogs and breed them so the trait becomes more frequent.
What is artificial selection?

A proposed explanation for a phenomenon or event, often used as a starting point for scientific investigation. This is sometimes considered an "educated guess" by someone doing an experiment.
What is a hypothesis?

This letter pairs with A.
What is T?
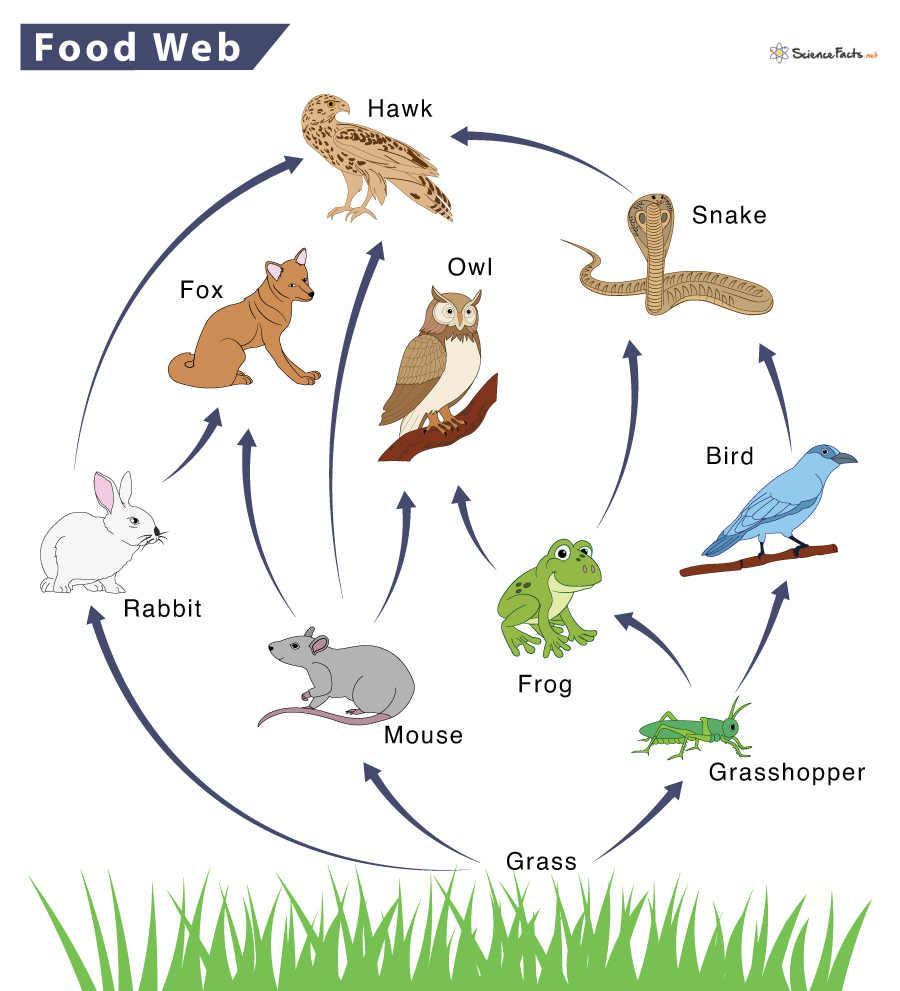
The primary producer of this food web. It starts and supports all other organisms in this food web.
What is grass?
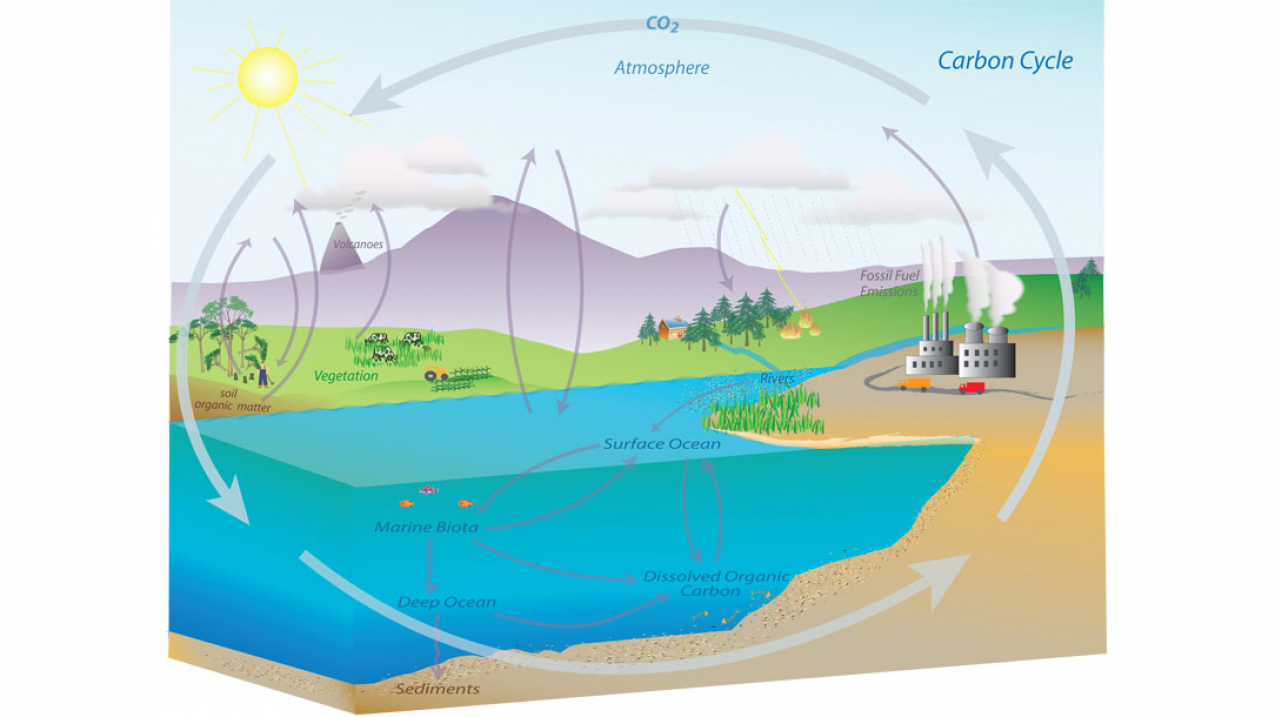
These processes are the reverse of each other. The products of one are the reactants of the other, and vice versa. They keep the atmosphere in an equilibrium.
What are photosynthesis and cellular respiration?

Darwin created this phrase to mean only some offspring survive in each generation. Those with the best traits are more likely to survive and pass their traits on.
This is information gathered by the five senses that is recorded during the scientific method. For example, recording the color of a flower.
What is an observation?

This percent of our offspring will have the recessive yellow trait.
What is 25%

When a population cannot grow any larger because it has reached its maximum size. This is usually due to limiting factors such as food, water, disease, and shelter.
What is carrying capacity?

When an organism creates energy without the presence of oxygen. For example, yeast did this process in our balloon yeast lab. Your muscles also do this when you're running low on oxygen.
What is fermentation?
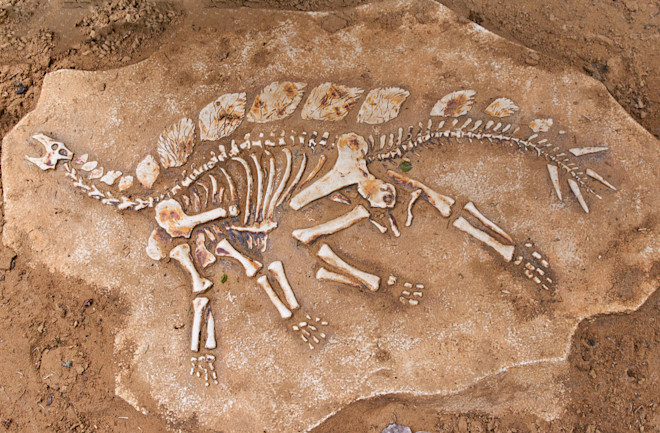

This evidence for evolution includes imprints and the hardened parts of organisms preserved in rock.
What are fossils?
This is a variable that is intentionally kept the same in all experimental groups. For example, in the balloon yeast lab we used the same size flask, the same amount of water, and the same amount of yeast.
What is a control variable?

The phenotype of all the offspring in this Punnett square.
What is Brown?

A large geographic area defined by its specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It's a major ecological community type, like a tropical rainforest or a desert.
What is a biome?

6CO2 + 6 H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the formula for photosynthesis?

This is evidence of evolution through similarities in the structure of an organism. For example, there are similar bones in organisms with a common ancestor.
What is anatomical evidence? -or- What are vestigial/homologous structures?

The variable that is deliberately changed/manipulated in this experiment.
What is fertilizer?

The genotype of all the offspring in this Punnett square.
What is Bb or heterozygous?